Python学习——Day 8
字典
· 字典
· Python内置的数据结构之一,与列表一样是一个可变序列
· 以键值对的方式存储数据,字典是一个无序的序列
· 字典的实现原理
· 字典的实现原理与查字典类似,查字典是先根据部首或拼音查找对应的页码,Python中的字典是根据key查找value所在的位置
· 字典的创建
· 最常用的方式:使用花括号

· 使用内置函数

#使用{}创建字典
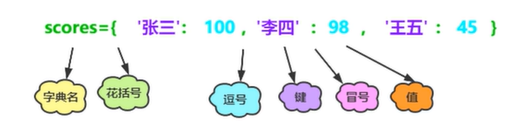
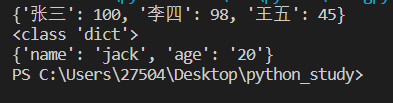
scores={'张三':100,'李四':98,'王五':45}
print(scores)
print(type(scores))
#第二种创建dict()
student=dict(name='jack',age='20')
print(student)
· 字典中元素的获取
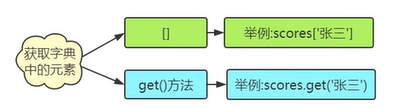
· []取值与使用get()取值的区别
· []如果字典中不存在指定的key,抛出keyError异常
· get()方法取值,如果字典中不存在指定的key,并不会抛出KeyError而是返回None,可以通过参数设置默认的value,以便指定的key不存在时返回
scores={'张三':100,'李四':98,'王五':45}
#第一种方式,使用[]
print(scores['张三'])
#print(scores['陈六']) #KeyError:'陈六'
#第二种方式,使用get()方法
print(scores.get('张三'))
print(scores.get('陈六')) #None
print(score.get('麻七',99)) #99是在查找'麻七'所对的value不存在时提供的一个默认值

· key的判断

· 字典元素的删除

· 字典元素的新增

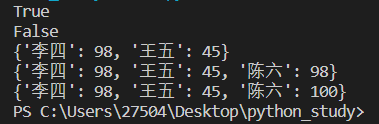
scores={'张三':100,'李四':98,'王五':45}
print('张三' in scores)
print('张三' not in scores)
del scores['张三'] #删除指定的key-value对
#scores.clear() #清空字典的元素
print(scores)
scores['陈六']=98 #新增元素
print(scores)
scores['陈六']=100 #修改元素
print(scores)
· 获取字典视图的三个方法
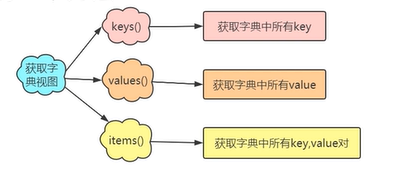
scores={'张三':100,'李四':98,'王五':45}
#获取所有的key
keys=scores.keys()
print(keys)
print(type(keys))
print(list(keys)) #将所有的key组成的视图转成列表
#获取所有的value
values=scores.values()
print(values)
print(type(values))
print(list(values))
#获取所有的key-value对
items=scores.items()
print(items)
print(list(items))

· 字典的遍历
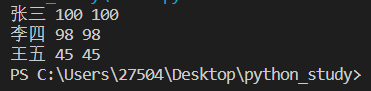
scores={'张三':100,'李四':98,'王五':45}
for item in scores:
print(item,scores[item],scores.get(item))
· 字典的特点

字典生成式

· 内置函数zip()
· 用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表
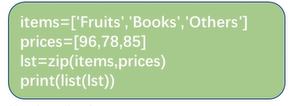
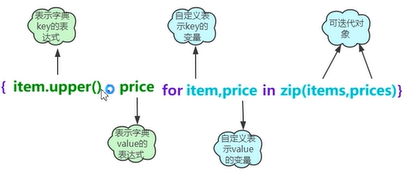
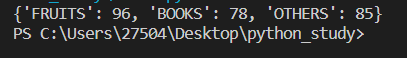
items=['Fruits','Books','Others']
prices=[96,78,85]
d={item.upper():price for item,price in zip(items,prices)}
print(d)