Python Magic Methods & Operator Overloading All In One
Python Magic Methods & Operator Overloading All In One
__init__&__add__
Magic Methods
__sub__ for -
__mul__ for *
__truediv__ for /
__floordiv__ for //
__mod__ for %
__pow__ for **
__and__ for &
__xor__ for ^
__or__ for |

The expression x + y is translated into x.__add__(y).
However, if x hasn't implemented add, and x and y are of different types, then y.__radd__(x) is called.
There are equivalent r methods for all magic methods just mentioned.
__rsub__ for -
__rmul__ for *
__rtruediv__ for /
__rfloordiv__ for //
__rmod__ for %
__rpow__ for **
__rand__ for &
__rxor__ for ^
__ror__ for |
https://www.sololearn.com/learn/courses/python-intermediate/lesson/912154723?p=3
demos
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
__author__ = 'xgqfrms'
__editor__ = 'vscode'
__version__ = '1.0.1'
__github__ = 'https://github.com/xgqfrms/Raspberry-Pi'
__git__ = 'https://github.com/xgqfrms/Raspberry-Pi.git'
__copyright__ = """
Copyright (c) 2012-2050, xgqfrms; mailto:xgqfrms@xgqfrms.xyz
"""
"""
/**
*
* @author xgqfrms
* @license MIT
* @copyright xgqfrms
* @created 2020-01-01
* @updated 2023-07-01
*
* @description
* @augments
* @example
* @link
*
*/
"""
# print("Hello, Python 3 🐍")
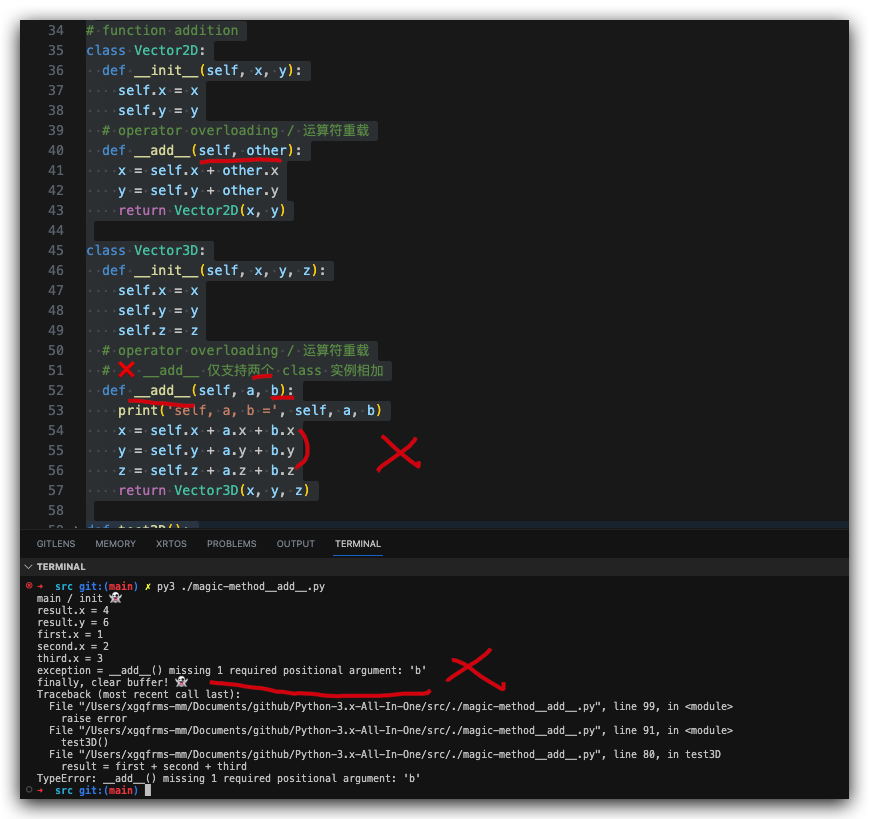
# function addition
class Vector2D:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# operator overloading / 运算符重载
def __add__(self, other):
x = self.x + other.x
y = self.y + other.y
return Vector2D(x, y)
class Vector3D:
def __init__(self, x, y, z):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.z = z
# operator overloading / 运算符重载
# ❌ __add__ 仅支持两个 class 实例相加
def __add__(self, a, b):
print('self, a, b =', self, a, b)
x = self.x + a.x + b.x
y = self.y + a.y + b.y
z = self.z + a.z + b.z
return Vector3D(x, y, z)
def test2D():
first = Vector2D(1, 2)
second = Vector2D(3, 4)
# print('first =', first)
# print('first.x =', first.x)
# print('second =', second)
# print('second.x =', second.x)
# ✅ 自动调用 __add__
result = first + second
# print('result =', result)
print('result.x =', result.x)
print('result.y =', result.y)
def test3D():
first = Vector3D(1, 1, 1)
second = Vector3D(2, 2, 2)
third = Vector3D(3, 3, 3)
print('first.x =', first.x)
print('second.x =', second.x)
print('third.x =', third.x)
# ❌ exception = __add__() missing 1 required positional argument: 'b'
result = first + second + third
print('result =', result)
# print('result.x =', result.x)
# print('result.y =', result.y)
# print('result.z =', result.z)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('main / init 👻')
try:
test2D()
test3D()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('Ctrl + C exit ✅')
except RuntimeError as error:
print('error =', error, error.args[0])
pass
except Exception as error:
print('exception =', error)
raise error
finally:
# cleanup
print('finally, clear buffer! 👻')
# print('exit Python REPL')
exit()
'''
# $ python3 ./magic-method__add__.py
$ py3 ./magic-method__add__.py
main / init 👻
result.x = 4
result.y = 6
first.x = 1
second.x = 2
third.x = 3
exception = __add__() missing 1 required positional argument: 'b'
finally, clear buffer! 👻
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/xgqfrms-mm/Documents/github/Python-3.x-All-In-One/src/./magic-method__add__.py", line 99, in <module>
raise error
File "/Users/xgqfrms-mm/Documents/github/Python-3.x-All-In-One/src/./magic-method__add__.py", line 91, in <module>
test3D()
File "/Users/xgqfrms-mm/Documents/github/Python-3.x-All-In-One/src/./magic-method__add__.py", line 80, in test3D
result = first + second + third
'''
class SpecialString:
def __init__(self, strs):
self.strs = strs
def __truediv__(self, other):
# text = "".join([self.strs, ' ', other.strs])
text = self.strs + ' ' + other.strs
line = "=" * len(text)
return "\n".join([line, text])
spam = SpecialString("Hello")
hello = SpecialString("world!")
test = spam / hello
print(test)
"""
$ py3 ./magic-method__truediv__.py
============
Hello world!
"""
运算符函数
operator 模块提供了一套与 Python 的内置运算符对应的高效率函数。例如,operator.add(x, y) 与表达式 x+y 相同。
函数包含的种类有:对象的比较运算、逻辑运算、数学运算以及序列运算。
对象比较函数适用于所有的对象,函数名根据它们对应的比较运算符命名。
许多函数名与特殊方法名相同,只是没有双下划线。
为了向后兼容性,也保留了许多包含双下划线的函数,为了表述清楚,建议使用没有双下划线的函数。
# Python 实例
# add(), sub(), mul()
# 导入 operator 模块
import operator
# 初始化变量
a = 4
b = 3
# 使用 add() 让两个值相加
print ("add() 运算结果 :",end="");
print (operator.add(a, b))
# 使用 sub() 让两个值相减
print ("sub() 运算结果 :",end="");
print (operator.sub(a, b))
# 使用 mul() 让两个值相乘
print ("mul() 运算结果 :",end="");
print (operator.mul(a, b))
https://www.runoob.com/python3/python-operator.html
refs
https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-function.html
REPL
https://www.runoob.com/try/runcode.php?filename=HelloWorld&type=python3
©xgqfrms 2012-2021
原创文章,版权所有©️xgqfrms, 禁止转载 🈲️,侵权必究⚠️!
未经授权禁止转载,违者必究!