2) Chernoff bound, Hoeffding's Lemma, Hoeffding's inequality
Given a random variable (r.v.) \(X\) and \(\epsilon>0\), for any \(t>0\) the following inequality holds: where \(M(t)=\mathbb{E}[e^{tX}]\) called moment-generating function (矩生成函数). 证明: 将 Markov's inequality 中的 \(\epsilon\) 用 \(e^{t\epsilon}\) 代替, \(\mathbb{E}[X]\) 用 \(\mathbb{E}[e^{tX}]\) 代替, 所以上界应为 \(\mathbb{E}[e^{tX}]/e^{t\epsilon}=e^{-t\epsilon}M(t)\). Let \(X\) be a r.v. with \(\mathbb{E}[X]=0\) and \(X\in[a,b], (b>a)\). Then for any \(t>0\): 证明: 所以 (用到了期望的特性和给定条件 \(\mathbb{E}[X]=0\)) 其中 \(\phi(t)=ta+\log(\frac{b}{b-a}+\frac{-a}{b-a}e^{t(b-a)})\). 接下来的证明是根据 \(\phi(t)\) 的一阶导和二阶导求 \(\phi(t)\) 的上界, 省去大量的计算公式直接给出结论: \(\phi(t)\leq \frac{t^2(b-a)^2}{8}\). Let \(X_1,...,X_m\) be \(n\) independent r.v.s with \(X_i\in[a_i,b_i], (b_i>a_i)\), and \(S_m\) be the sum of them (\(S_m = \sum_{i=1}^{m}X_i\)). Then for any \(\epsilon>0\): or 证明: 第一行用到了 Chernoff bound, 第二行将 \(S_m\) 替换成累加, 移出指数函数外就是累乘, 如果蓝线部分为 \(Y_i\), 可以算出它的期望和区间 (右侧蓝色部分), 随机变量 \(Y_i\) 满足 Hoeffding's lemma 的条件, 所以可以使用这个定理得出第三行, 公式整理后得到第四行. 这里的 \(t\) 只要满足大于 0 取任何值不等式都成立, 所以令 \(t\) 等于右下角黑色字体的公式, 整理后即为Hoeffding's inequality 的形式. Hoeffding's inequality 用处十分广泛, 比较重要.防盗
1. Chernoff bound (切尔诺夫限)
2. Hoeffding's Lemma (the upper bound of moment-generating funtion)
由于 \(t>0\), \(e^{tx}\) 为 convex 函数, 所以有以下性质:3. Hoeffding's inequality
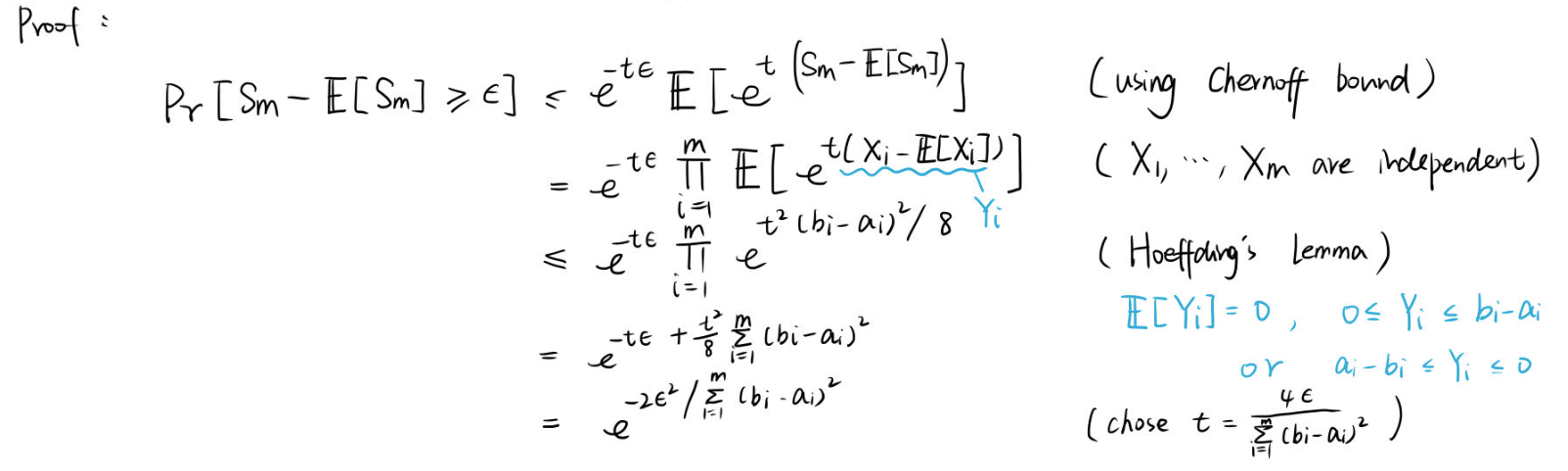
防盗