
class StepByStep():
def __init__(self, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.model = model.to(self.device)
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
self.optimizer = optimizer
def to(self, device):
# This method allows the user to specify a different device
# It sets the corresponding attribute (to be used later in
# the mini-batches) and sends the model to the device
try:
self.device = device
self.model.to(self.device)
except RuntimeError:
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Couldn't send it to {device}, sending it to {self.device} instead.")
self.model.to(self.device)


class StepByStep():
def __init__(self, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.model = model.to(self.device)
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
self.optimizer = optimizer
# These attributes are defined here, but since they are
# not available at the moment of creation, we keep them None
self.train_loader = None
self.val_loader = None
self.writer = None
def to(self, device):
# This method allows the user to specify a different device
# It sets the corresponding attribute (to be used later in
# the mini-batches) and sends the model to the device
try:
self.device = device
self.model.to(self.device)
except RuntimeError:
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Couldn't send it to {device}, sending it to {self.device} instead.")
self.model.to(self.device)
def set_loaders(self, train_loader, val_loader=None):
self.train_loader = train_loader
self.val_loader = val_loader
def set_tensorboard(self, name, folder='runs'):
# This method allows the user to create a SummaryWriter to interface with TensorBoard
suffix = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.writer = SummaryWriter(f'{folder}/{name}_{suffix}')


class StepByStep():
def __init__(self, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.model = model.to(self.device)
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
self.optimizer = optimizer
# These attributes are defined here, but since they are
# not available at the moment of creation, we keep them None
self.train_loader = None
self.val_loader = None
self.writer = None
# These attributes are going to be computed internally
self.losses = []
self.val_losses = []
self.total_epochs = 0
def to(self, device):
# This method allows the user to specify a different device
# It sets the corresponding attribute (to be used later in
# the mini-batches) and sends the model to the device
try:
self.device = device
self.model.to(self.device)
except RuntimeError:
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Couldn't send it to {device}, sending it to {self.device} instead.")
self.model.to(self.device)
def set_loaders(self, train_loader, val_loader=None):
self.train_loader = train_loader
self.val_loader = val_loader
def set_tensorboard(self, name, folder='runs'):
# This method allows the user to create a SummaryWriter to interface with TensorBoard
suffix = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.writer = SummaryWriter(f'{folder}/{name}_{suffix}')

class StepByStep():
def __init__(self, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.model = model.to(self.device)
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
self.optimizer = optimizer
# These attributes are defined here, but since they are
# not available at the moment of creation, we keep them None
self.train_loader = None
self.val_loader = None
self.writer = None
# These attributes are going to be computed internally
self.losses = []
self.val_losses = []
self.total_epochs = 0
# Create the train_step function for model, loss function and optimizer
# Note: there are NO ARGS there! It makes use of the class attributes directly
self.train_step_fn = self._make_train_step_fn()
# Create the val_step function for model and loss function
self.val_step_fn = self._make_val_step_fn()
def to(self, device):
# This method allows the user to specify a different device
# It sets the corresponding attribute (to be used later in
# the mini-batches) and sends the model to the device
try:
self.device = device
self.model.to(self.device)
except RuntimeError:
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Couldn't send it to {device}, sending it to {self.device} instead.")
self.model.to(self.device)
def set_loaders(self, train_loader, val_loader=None):
self.train_loader = train_loader
self.val_loader = val_loader
def set_tensorboard(self, name, folder='runs'):
# This method allows the user to create a SummaryWriter to interface with TensorBoard
suffix = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.writer = SummaryWriter(f'{folder}/{name}_{suffix}')
def _make_train_step_fn(self):
# Build function that performs a step in the train loop
def perform_train_step_fn(x, y):
self.model.train()
yhat = self.model(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(yhat, y)
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
return loss.item()
return perform_train_step_fn
def _make_val_step_fn(self):
# Build function that performs a step in the validation loop
def perform_val_step_fn(x, y):
self.model.eval()
yhat = self.model(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(yhat, y)
return loss.item()
return perform_val_step_fn




class StepByStep():
def __init__(self, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.model = model.to(self.device)
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
self.optimizer = optimizer
# These attributes are defined here, but since they are
# not available at the moment of creation, we keep them None
self.train_loader = None
self.val_loader = None
self.writer = None
# These attributes are going to be computed internally
self.losses = []
self.val_losses = []
self.total_epochs = 0
# Create the train_step function for model, loss function and optimizer
# Note: there are NO ARGS there! It makes use of the class attributes directly
self.train_step_fn = self._make_train_step_fn()
# Create the val_step function for model and loss function
self.val_step_fn = self._make_val_step_fn()
def to(self, device):
# This method allows the user to specify a different device
# It sets the corresponding attribute (to be used later in
# the mini-batches) and sends the model to the device
try:
self.device = device
self.model.to(self.device)
except RuntimeError:
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Couldn't send it to {device}, sending it to {self.device} instead.")
self.model.to(self.device)
def set_seed(self, seed=42):
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
torch.manual_seed(seed)
def set_loaders(self, train_loader, val_loader=None):
self.train_loader = train_loader
self.val_loader = val_loader
def set_tensorboard(self, name, folder='runs'):
# This method allows the user to create a SummaryWriter to interface with TensorBoard
suffix = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')
self.writer = SummaryWriter(f'{folder}/{name}_{suffix}')
def train(self, n_epochs, seed=42):
self.set_seed(seed)
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# Keep track of the numbers of epochs by updating the corresponding attribute
self.total_epochs += 1
loss = self._mini_batch(validation=False)
self.losses.append(loss)
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss = self._mini_batch(validation=True)
self.val_losses.append(val_loss)
# If a SummaryWriter has been set...
if self.writer:
scalars = {'training': loss}
if val_loss is not None:
scalars.update({'validation': val_loss})
self.writer.add_scalars(main_tag='loss',
tag_scalar_dict=scalars,
global_step=epoch)
if self.writer:
# Flush the writer
self.writer.flush()
def save_checkpoint(self, filename):
checkpoint = {'epoch': self.total_epochs,
'model_state_dict': self.model.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state_dict': self.optimizer.state_dict(),
'losses': self.losses,
'val_losses': self.val_losses}
torch.save(checkpoint, filename)
def load_checkpoint(self, filename):
checkpoint = torch.load(filename)
self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
self.optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_state_dict'])
self.total_epochs = checkpoint['epoch']
self.losses = checkpoint['losses']
self.val_losses = checkpoint['val_losses']
self.model.train() # always use TRAIN for resuming training
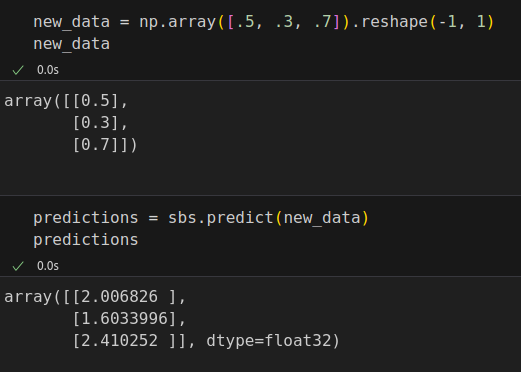
def predict(self, x):
# Set it to evaluation mode for predictions
self.model.eval()
x_tensor = torch.as_tensor(x).float().to(self.device)
y_hat_tensor = self.model(x_tensor)
# Set it back to train mode
self.model.train()
return y_hat_tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
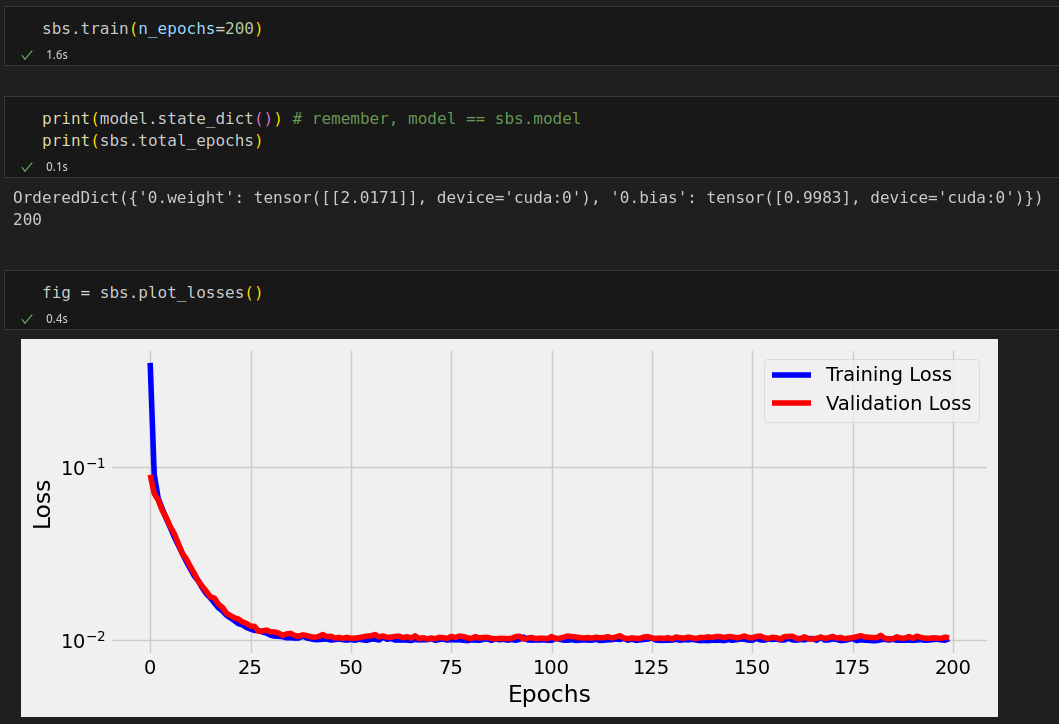
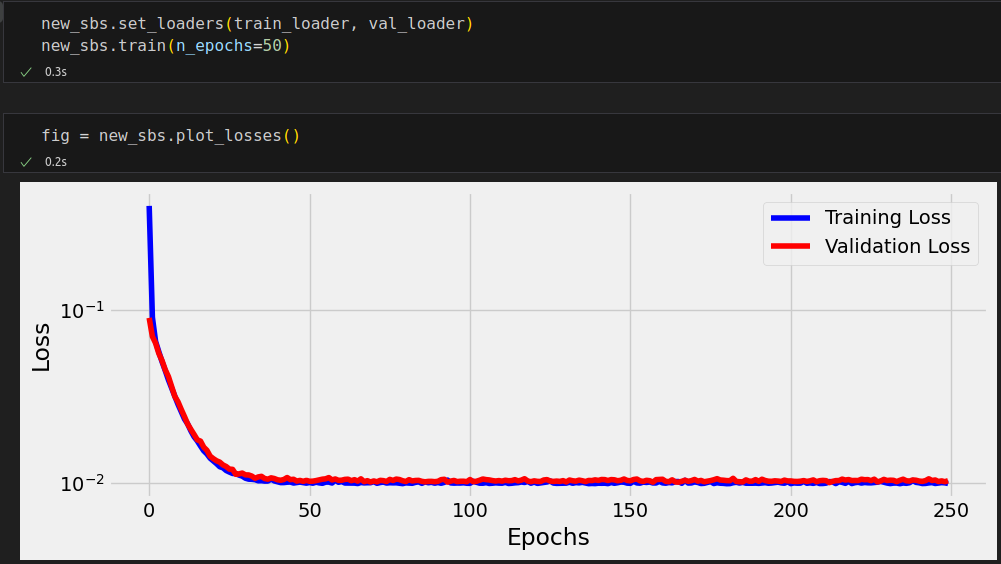
def plot_losses(self):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.plot(self.losses, label='Training Loss', c='b')
if self.val_losses:
plt.plot(self.val_losses, label='Validation Loss', c='r')
plt.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
return fig
def add_graph(self):
if self.train_loader and self.writer:
# Fetche a single mini-batch so we can use add_graph
x_sample, y_sample = next(iter(self.train_loader))
self.writer.add_graph(self.model, x_sample.to(self.device))
def _make_train_step_fn(self):
# Build function that performs a step in the train loop
def perform_train_step_fn(x, y):
self.model.train()
yhat = self.model(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(yhat, y)
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
return loss.item()
return perform_train_step_fn
def _make_val_step_fn(self):
# Build function that performs a step in the validation loop
def perform_val_step_fn(x, y):
self.model.eval()
yhat = self.model(x)
loss = self.loss_fn(yhat, y)
return loss.item()
return perform_val_step_fn
def _mini_batch(self, validation=False):
# The mini-batch can be used with both loaders
# The argument `validation` defines which loader and
# corresponding step function is going to be used
if validation:
data_loader = self.val_loader
step_fn = self.val_step_fn
else:
data_loader = self.train_loader
step_fn = self.train_step_fn
mini_batch_losses = []
for x_batch, y_batch in data_loader:
x_batch = x_batch.to(self.device)
y_batch = y_batch.to(self.device)
mini_batch_loss = step_fn(x_batch, y_batch)
mini_batch_losses.append(mini_batch_loss)
loss = np.mean(mini_batch_losses)
return loss


%%writefile model_configuration/v4.py
lr = .1
torch.manual_seed(42)
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(1, 1))
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')


sbs = StepByStep(model, loss_fn, optimizer)
sbs.set_loaders(train_loader, val_loader)
sbs.set_tensorboard('classy')





sbs.save_checkpoint('model_checkpoint.pth')



new_sbs = StepByStep(model, loss_fn, optimizer)







# %load data_preparation/v2.py
torch.manual_seed(13)
# Build tensors from numpy arrays BEFORE split
x_tensor = torch.from_numpy(x).float().reshape(-1, 1)
y_tensor = torch.from_numpy(y).float().reshape(-1, 1)
# Build dataset containing ALL data points
dataset = TensorDataset(x_tensor, y_tensor)
# Perform split
ratio = .8
n_total = len(dataset)
n_train = int(n_total * ratio)
n_val = n_total - n_train
train_data, val_data = random_split(dataset, [n_train, n_val])
# Build a loader for each set
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(dataset=val_data, batch_size=16)
# %load model_configuration/v4.py
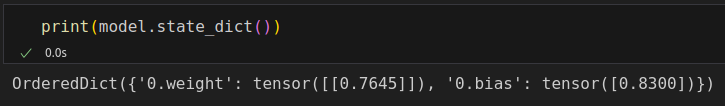
lr = .1
torch.manual_seed(42)
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(1, 1))
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
n_epochs = 200
sbs = StepByStep(model, loss_fn, optimizer)
sbs.set_loaders(train_loader, val_loader)
sbs.set_tensorboard('classy')
sbs.train(n_epochs=n_epochs)


































