oop PTA 4~6题目集总结
一. 前言
第4次题目集主要考察了我们java的封装性,要求我们根据题目要求对类中的属性以及方法进行设计,在考察封装的基础之上,有一些题目还需要使用一些特殊的数据结构来帮助我们去实现这道题目,比如说7-2 有重复的数据和7-3 去掉重复的数据都是用了LinkedHashSet,来对数据进行去重等操作。7-4 单词统计与排序使用了ArryList和LinkedHashSet来进行排序。7-7 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数中使用了题目要求的LocalDate和time.temporal.ChronoUnit来对日期进行操作。3-4与第6次题集7-1为同一类题,这里不做分析,会与7-1一起分析。我认为初学这些数据结构对我来说有一些难度,因为需要学习基本语法以及使用方法。下文会对7-3和7-7进行分析。
第5次题目集主要考察了正则表达式的使用,字符串的基本使用方法,以及类与类之间的聚合关系。其中7-1和7-3以及7-4考察正则表达式的应用,最后两题考察类与类之间的聚合关系。其中正则表达式是新学的一种判断字符串的方法,使用起来较为方便,因题型都较为相似,下文就取7-3作为代表来进行分析。后面两道聚合题也是前几次作业一直在做的日期类的题目,只不过在前几次作业的基础之上修改了day,month,year的关系,下文会以7-5为例子进行分析。
第6次题目集只有一道题,7-1 菜单计价程序-4,是第四次题集的3-4的升级版,这道题难度较大,我认为是对前段时间所学的Java知识的一个总结,涵盖内容较多,细节较多,涉及到类的封装,类与类之间的关系,细节很多,难度较大,我只写出了最基础的部分(基本满足3-4的要求),没有写题目要求中的各种订单错误部分,下文会重点分析。
二. 设计与分析
主要对我认为比较有价值以及需要改进的题目进行分析,对于重要步骤的理解我会写在注释当中,改进写在最后。
题目集4 7-3 去掉重复的数据
题意:输入一个正整数n,然后输入n个整数,将这n个整数按照输入顺序输出去除重大概就是保持原有的顺序,并且去重。
完整代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int a;
LinkedHashSet<Integer> s = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();//使用linkedhashset
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a=input.nextInt();
s.add(a);//将输入的输逐一加入到容器当中去
}
Iterator<Integer> it = s.iterator();
int i=0;
while(it.hasNext()){
i++;
System.out.print(it.next());//因为linkedhashset是有序的,所以可以直接从0开始输出
if(i!=s.size()) System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
总结分析:题目要求按顺序并且去重,这时就需要用到LinkHashSet这个容器,原因有以下几点:LinkedHashSet中的元素没有重复,LinkedHashSet中的元素有顺序,符合题意。将n个数按照顺序加入LinkedHashSet即可,自动排序,并且有序,最后从0开始输出到结束。
心得:了解LinkedHashSet的基本用法,并且学会如何使用。
题目集4 7-7 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
题意:输入两个日期,包括年月日,然后判断第一个日期是比第二个日期早还是比第二个日期晚,并且判断两个日期之间相隔多少日以及多少星期。并且题目要求使用String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法,LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String str1=input.nextLine();//输入日期1
String str2=input.nextLine();//输入日期2
String [] arr1=str1.split("-");//将年月日分隔开
String [] arr2=str2.split("-");
int year1=Integer.parseInt(arr1[0]);//将字符串的年月日转化为int类型
int year2=Integer.parseInt(arr2[0]);
int month1=Integer.parseInt(arr1[1]);
int month2=Integer.parseInt(arr2[1]);
int day1=Integer.parseInt(arr1[2]);
int day2=Integer.parseInt(arr2[2]);
LocalDate date1=LocalDate.of(year1,month1,day1);//初始化日期
LocalDate date2=LocalDate.of(year2,month2,day2);
if(date1.isBefore(date2)){//利用localdate中的方法判断时间前后
System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更早");
}else{
System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更晚");
}
long num1=date1.until(date2, ChronoUnit.DAYS);//判断间隔多少日,注意返回值为long
if (num1<-0) num1*=-1;
long num2=date1.until(date2, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);//判断间隔多少星期
if(num2<0) num2*=-1;
System.out.println("两个日期间隔"+num1+"天");
System.out.println("两个日期间隔"+num2+"周");
}
}
总结分析:题目中要求的使用的类以及其中的方法大多数需要自己去寻找资料去学习,但都是非常实用方便的方法。本题基本思路:先将两个日期信息以字符串形式输入,再使用split使得年月日分开,再使用parselnt方法使得字符串变为数字,再分别将两个日期的年月日初始化给LocalDate类,再使用LocalDate类中的isAfter方法判断谁先谁后,最后再利用ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS来计算出俩日期中间间隔多少天以及多少星期。
心得:学会了String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法,LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
题目集4 7-3 正则表达式训练-验证码校验
题意:输入一段字符串,利用正则表达式去判断该字符串是否是由四位数字或者字母(包含大小写)组成的字符串。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
if(str.matches("[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}")){//利用正则表达式
System.out.println(str+"属于验证码");
}else{
System.out.println(str+"不属于验证码");
}
}
}
总结分析:本题主要就是要求我们使用正则表达式来判断字符串是否满足要求,只需学会基础的正则表达式的使用方法即可。
心得:学会了正则表达式的基本使用方法。
题目集5 7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
题意:基于前几次题目集的日期类的题目,设计日期类,来完成三个功能: 求下n天 求前n天 求两个日期相差的天数。并且需要用到类与类之间的聚合关系。
部分代码(因整体代码与之前日期类基本一致,这部分代码会突出聚合的部分):
class Year{//最基本的Year类
private int value ;
public Year(){
}
public Year(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue(){
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(){
if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) return true;
return false;
}
public boolean validate(){
if(value>=1900&&value<=2050){
return true;
}
//System.out.println(value);
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement(){
value++;
}
public void yearReduction(){
value--;
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
private Year year;//包含了Year
public Month(){
}
public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){
value=monthValue;
year=new Year(yearValue);
}
public int getValue(){
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public Year getYear(){//获取month中的year,便于后续操作
return this.year;
}
public void setYear(Year year){
this.year=year;
}
public void reseMin(){//使得month的value变为1,用于跨年(计算后n天)
value=1;
}
public void reseMax(){//使得month的value变为12,用于年份减1时(计算前n天)
value=12;
}
public boolean validate(){
if(value>=1&&value<=12) return true;
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement(){
value++;
}
public void monthReduction(){
value--;
}
}
class Day{
private int value;
private Month month;//含有month类,而month类中可以调用year类,就可以一连串调用
public int [] mon_maxnum={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Day(){
}
public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){
this.value=dayValue;
month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
}
public int getValue(){
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public Month getMonth(){//提供获取month的方法,以便调用的时候使用
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month value){
month=value;
}
public void reseMin(){//跨月或跨年时,使得day的value变为1(用于计算往后算n天操作)
value=1;
}
public void reseMax(){//往前倒退的时候,月份减小一月或者年份减小一年的时候,使得day的value变为当月最大值( 用于计算前n天操作)
if(month.getValue()==2){
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()){
this.value=29;
}else{
this.value=28;
}
}else{
this.value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
}
public boolean validate(){
if(value>0){
if(month.getValue()==2){
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()){
if(value<=29) return true;
}else{
if(value<=28) return true;
}
}else{
if(value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void dayIncrement(){
value++;
}
public void dayReduction(){
value--;
}
}
class DateUtil{//这个类中包含了所有题目要求的测试点的方法
private Day day;//包含day类,但day中包含month,month中包含year,所以只要有day就能够使用他们三个,我认为这也是该题目主要的考察目的
public DateUtil(){
}
public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
day=new Day(d,m,y);
}
public Day getDay(){
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day d){
day=d;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){//判断日期是否合法
if(day.getMonth().validate()&&day.validate()&&day.getMonth().getYear().validate()){//我认为这一步是题目考察重点的一个小小体现
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较第一个日期是否在第二个日期之前
int year1= day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int year2= date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int month1=day.getMonth().getValue();
int month2=date.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
int day1=day.getValue();
int day2=date.getDay().getValue();
if(year1<year2){
return true;
}else{
if(year1>year2){
return false;
}else{
if(month1<month2){
return true;
}else{
if(month1>month2){
return false;
}else{
if(day1<day2){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
}
//看两个日期是否相同
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil dat
int year1= day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int year2= date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int month1=day.getMonth().getValue();
int month2=date.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
int day1=day.getValue();
int day2=date.getDay().getValue();
if(year1==year2&&month1==month2&&day1==day2) return true;
return false;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//算下n天的方法
Month month =day.getMonth();//先用getmonth来获取month方便操作
Year year =month.getYear();//获取完month再用getyear来获取year,也是方便操作
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(month.getValue()==12){
day.dayIncrement();
if(day.getValue()>day.mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]){
month.reseMin();
year.yearIncrement();
day.reseMin();
}
}else{
if(year.isLeapYear()){
day.mon_maxnum[1]=29;
}else day.mon_maxnum[1]=28;
day.dayIncrement();
if(day.getValue()>day.mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]){
month.monthIncrement();
day.reseMin();
}
}
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDayes(int n){//获取前n天
Month month =day.getMonth();
Year year =month.getYear();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(month.getValue()==1){
day.dayReduction();
if(day.getValue()==0){
month.reseMax();
year.yearReduction();
day.reseMax();
}
}else{
if(year.isLeapYear()){
day.mon_maxnum[1]=29;
}else day.mon_maxnum[1]=28;
day.dayReduction();
if(day.getValue()==0){
month.monthReduction();
day.reseMax();
}
}
}
return this;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){//计算两天之间差了多少天
Month month1 =day.getMonth();
Year year1 =month1.getYear();
Month month2=date.getDay().getMonth();
Year year2=month2.getYear();
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return 0;
int r=0;
//下面是相差的算法(不重要)
for(int i=Math.min(year2.getValue(),year1.getValue());i<Math.max(year2.getValue(),year1.getValue());i++){
if((i%4==0&&i%100!=0)||i%400==0) r+=366;
else r+=365;
}
int r1=0,r2=0;
if(year1.isLeapYear()){
day.mon_maxnum[1]=29;
}else day.mon_maxnum[1]=28;
for(int i=1;i<month1.getValue();i++){
r1+=day.mon_maxnum[i-1];
}
r1+=day.getValue();
if(year2.isLeapYear()){
date.getDay().mon_maxnum[1]=29;
}else date.getDay().mon_maxnum[1]=28;
for(int i=1;i<month2.getValue();i++){
r2+=date.getDay().mon_maxnum[i-1];
}
r2+=date.getDay().getValue();
if(year2.getValue()>year1.getValue()) r+=r2-r1;
if(year2.getValue()<year1.getValue()) r+=r1-r2;
if(year2.getValue()==year1.getValue()) r+=Math.abs(r1-r2);
return r;
}
}
本题类图:
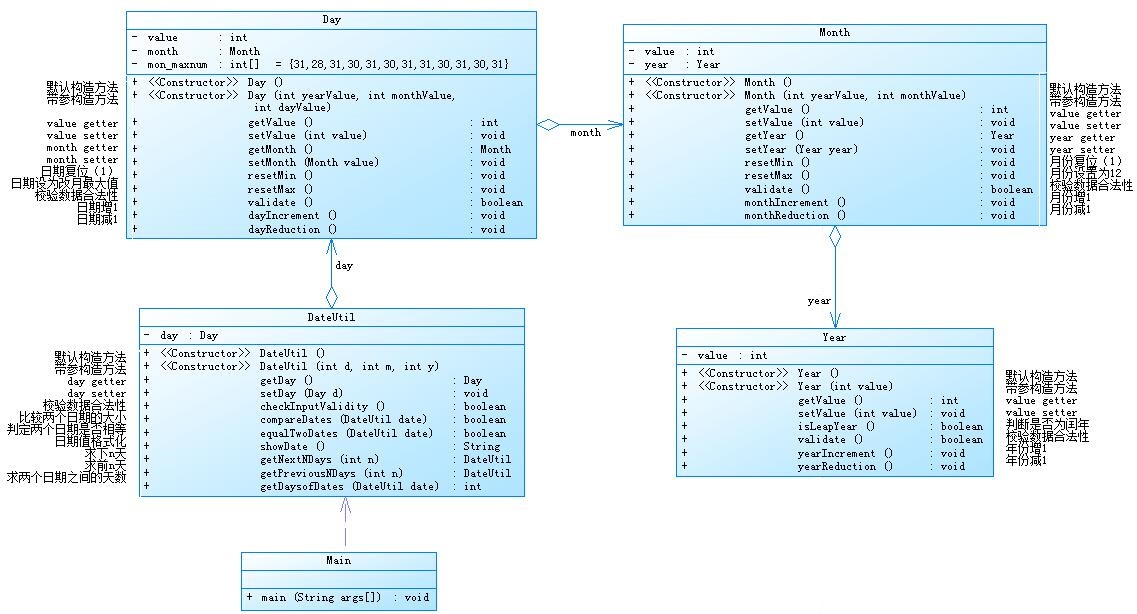
总结分析:本题主要就是在前几次题目的日期类的题目的基础之上增加了类与类的聚合,根据类图,先创建year类,再创建month类,将year类加入month类中,再创建day类,将month类加入day类中,最后创建dateutil类,因为聚合的作用,里面只需要写一个day类就可以满足题目要求,然后再利用前面几题的算法,求出前,后n天,以及俩个日期之间相差的天数。
心得:掌握了类与类之间聚合的基本写法,并且能够应用。
题目集6 7-1 菜单计价程序-4
题意:本题是在第四次题集的3-4的基础之上,添加了多种纠错的要求。
这道题我没有得分,我只能将自己写了的部分拿出来分析,我写了的部分是没有任何纠错的,只有3-4的基础部分(能够完成基本的点单功能)
package Pta;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {//主方法
Menu menu =new Menu();//在主方法中创建菜单类,方便操作
Table []tables=new Table[20];//创建table数组,因为不止一桌,所以使用数组
Order[]orders=new Order[20];//每桌一个订单
int cnt=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
while(!str.equals("end")){//输入end表示菜单输入结束
String str1[]=str.split(" ");//将菜单信息分隔开,以便正确的部分加入order当中
if(str1[0].equals("table")){//如果第一部分是table的话,说明此时输入的是table信息
int number=Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);//table的编号
String str2[]=str1[2].split("/");//再分一次,将年月日分割开来
int year=Integer.parseInt(str2[0]);//将年月日填入
int month=Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int day=Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
String str3[]=str1[3].split("/");//将小时,分钟,秒填入
int hour=Integer.parseInt(str3[0]);
int min=Integer.parseInt(str3[1]);
int s=Integer.parseInt(str3[2]);
tables[cnt]=new Table(number,year,month,day,hour,min,s);
orders[cnt]=new Order(menu);
tables[cnt].setOrder(orders[cnt]);
//System.out.println(cnt+"here!!!");
cnt++;
}else{
if(str1.length==4){//此时输入的是table下的菜单信息
int orderNumber=Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
String dishName=str1[1];
int portion=Integer.parseInt(str1[2]);
int num=Integer.parseInt(str1[3]);
//orders[cnt]=new Order(menu);
// System.out.println(cnt);
orders[cnt-1].addARecord(orderNumber,dishName,portion,num);
}else{
if(str1[1].equals("delete")){//删除订单
int number=Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
for(int i=0;i<tables[cnt-1].order.records.length;i++){
if(tables[cnt-1].order.records[i]==null||tables[cnt-1].order.records[i].flag==0){
tables[cnt-1].deleteNum++;
break;
}
if(tables[cnt-1].order.records[i].orderNum==number){
tables[cnt-1].order.records[i].flag=0;
break;
}
}
}else{//这一部分是在table之上的输入原始菜品,将菜品加入菜单
int unit_price=Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
Dish dish=new Dish(str1[0],unit_price);
menu.addDish(dish.name, dish.unit_price);
}
}
}
str=sc.nextLine();
}
for(int i=0;i<tables.length;i++){//输入每一个table点的菜的单价
if(tables[i]==null) break;
System.out.println("table "+tables[i].number+":");
for(int j=0;j<tables[i].order.records.length;j++){
if(tables[i].order.records[j]==null) {
//System.out.println(j);
break;
}
if(tables[i].order.records[j].d.unit_price==0){
System.out.println(tables[i].order.records[j].d.name+" does not exit");
}else{
System.out.println(tables[i].order.records[j].orderNum+" "+tables[i].order.records[j].d.name+" "+tables[i].order.records[j].getPrice());
}
}
for(int j=0;j<tables[i].deleteNum;j++){//其实写到这一步就明显感觉到这题被我写复杂了(这一步是输入删除错误的部分)
System.out.println("delete error;");
}
}
for(int i=0;i<tables.length;i++) {//输出每个table打折后的总价
if(tables[i]==null) break;
if(tables[i].isOpen())
System.out.println("table "+tables[i].number+": "+tables[i].sumMoney());
else {
System.out.println("table "+tables[i].number+" out of opening hours");
}
}
}
static class Dish {//dish类,最基本的菜品类
String name;
int unit_price;
// private String special;
Dish(){
}
Dish(String name,int unit_price){
this.name=name;
this.unit_price=unit_price;
//this.special=special;
}
public int getPrice(int portion){
double rate=0;
if(portion==1) rate=1;
if(portion==2) rate=1.5;
if(portion==3) rate=2;
//System.out.println(unit_price+" "+rate+" "+portion);
// System.out.println((int)((10*unit_price*rate+5)/10));
return (int)((10*unit_price*rate+5)/10);
}
/*public boolean isSpecial(){
if(special.equals("T")) return true;
return false;
}*/
}
static class Menu {//菜单类
Dish[] dishs=new Dish[20] ;//菜单包括所有的菜品
Menu(){
}
Dish searthDish(String dishName) {//在菜单里寻找一个菜品,并且返回dish
for(int i=0;i<dishs.length;i++){
if(dishs[i]==null) break;
if(dishs[i].name.equals(dishName)){
return dishs[i];
}
}
return null;
}
void addDish(String dishName,int unit_price) {//添加一种菜品
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<dishs.length;i++){
if(dishs[i]==null){
break;
}
cnt++;
}
Dish dish=new Dish(dishName,unit_price);
dishs[cnt]=dish;
//return dish;
}
}
static class Record {//菜品记录类,一个table点了一个菜就会有一个菜品记录
int orderNum;
Dish d;
int portion;//菜的大中小分量
int num=1;
int flag=1;
Record(){
}
Record(int orderNum,Dish d,int portion,int num){
this.orderNum=orderNum;
this.d=d;
this.portion=portion;
this.num=num;
}
int getPrice(){
return d.getPrice(portion)*num;
}
}
static class Order {//订单类,记录了一个table中所有点的record
Menu menu;
Record[] records=new Record[20];//记录所有的record
Order(Menu menu){
this.menu=menu;
}
public int getTotalPrice(){//计算orde的总价格人,在乘以折扣后,就会是总价格
int r=0;
for(int i=0;i<records.length;i++){
if(records[i]!=null){
if(records[i].flag==1)
r+=records[i].getPrice();
//System.out.println(records[i].orderNum+" "+records[i].d.name+" "+records[i].getPrice());
}else{
break;
}
}
return r;
}
void addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){//添加一个record
Dish dish=menu.searthDish(dishName);
if(dish==null){
dish=new Dish(dishName,0);
}
Record record=new Record(orderNum,dish,portion,num);
for(int i=0;i< records.length;i++){
if(records[i]==null){
records[i]=record;
break;
}
}
//return record;
}
void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){//根据订单序号,删除订单
for(int i=0;i<records.length;i++){
if(records[i].orderNum==orderNum){
records[i]=null;
for(int j=i;j<records.length-1;j++){
records[j]=records[j+1];
}
}
}
}
Record findRecordByNum(int orderNum){
for(int i=0;i<records.length;i++){
if(records[i].orderNum==orderNum){
return records[i];
}
}
return null;
}
}
static class Table{//桌子类,里面包含一个order
int number;
Order order;
int year,month,day,hour,min,s;
int deleteNum;
Table(){
}
Table(int number,int year,int month,int day,int hour,int min,int s){//初始化table
this.number=number;
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
this.hour=hour;
this.min=min;
this.s=s;
}
public boolean isOpen(){//判断是否为开门时间
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(year,month-1,day);
int weekDay=calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
if(weekDay>=2&&weekDay<=6){
if((hour>=17&&(hour<=19))||(hour==20&&min<=30)){
return true;
}else {
if((hour==10&&min>=30)||(hour>=11&&hour<=13)||(hour==14&&min<=30)){
return true;
}
}
}else{
if((hour==9&&min>=30)||(hour>9&&hour<21)||(hour==21&&min<=30)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void setOrder(Order order){
this.order=order;
}
public int sumMoney() {//先根据order的价格算出原本订单价格,再根据时间进行打折
int sum = 0;
sum=order.getTotalPrice();
/*for (int i = 0; i < order.records.length; i++) {
if (order.records[i] == null) {
return sum;
} else {
sum += order.records[i].getPrice();
System.out.println(order.records[i].getPrice());
}
}*/
double rate=1;
Calendar calendar=Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(year,month-1,day);
int weekDay=calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
if(weekDay>=2&&weekDay<=6){
if((hour>=17&&(hour<=19))||(hour==20&&min<=30)){
rate=0.8;
}else {
if((hour==10&&min>=30)||(hour>=11&&hour<=13)||(hour==14&&min<=30)){
rate=0.6;
}
}
}else{
if((hour==9&&min>=30)||(hour>9&&hour<21)||(hour==21&&min<=30)){
rate=1;
}
}
return (int)((10*sum*rate+5)/10);
}
}
}
类图如下:
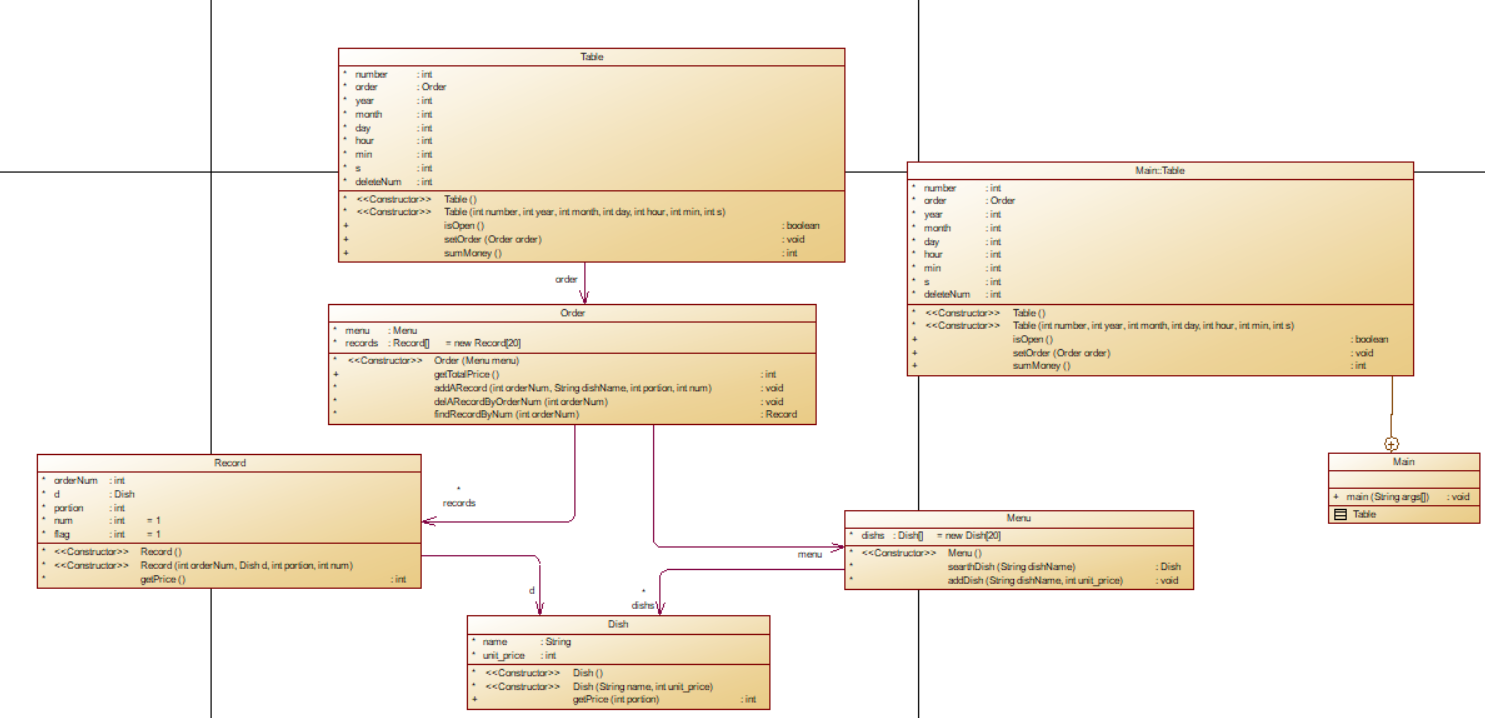
总结分析:本题的结构较为复杂,没有想好就开始写,导致整体结构非常混乱,最后越写越复杂。本意是想写得层次分明一点,最基本的dish,将所有dish加入menu,一个table一个order,一个order里若干个record,record中记录了菜品的客户点的菜品的详细信息。我认为导致最后出写不出的原因在于一开始使用了数组。
心得:写这种题目没有明确说明到底总数有多少的,就别用数组,用的很难受,一不小心就会指向null,就应该用arrylist。这种较为复杂的结构,用数组只会越用越复杂。
三.踩坑心得
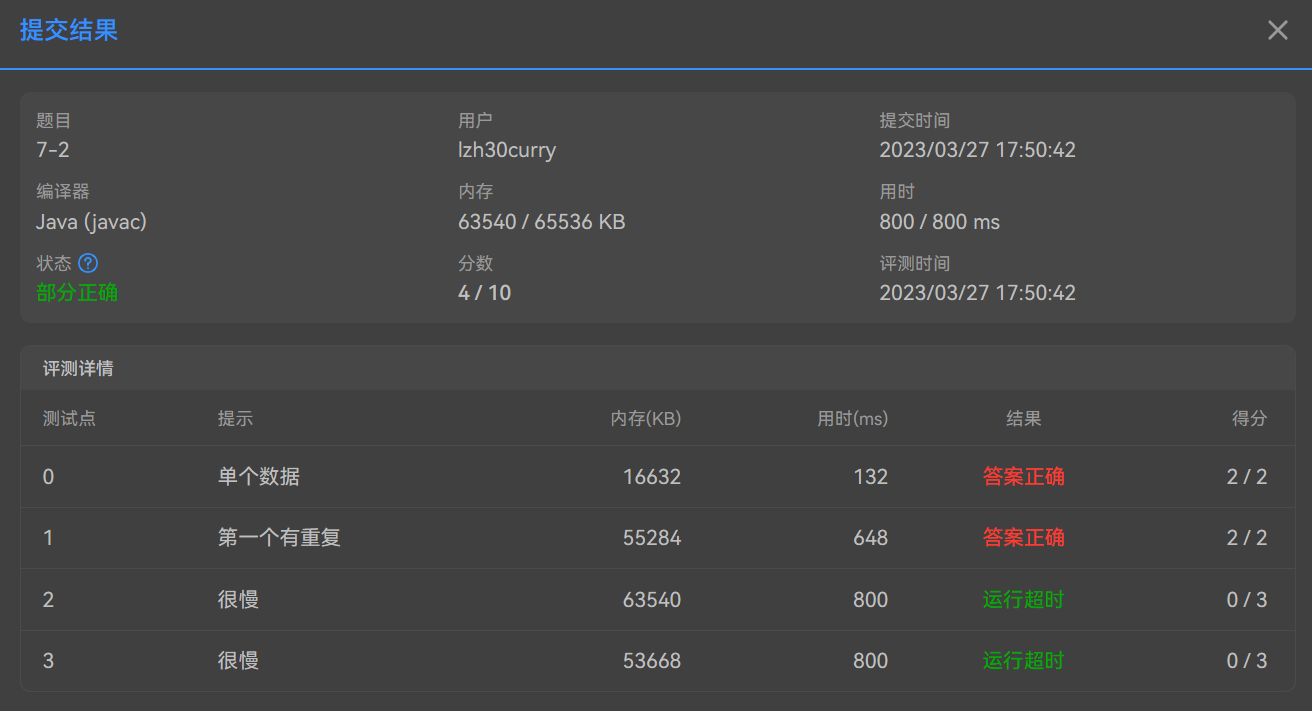
1.在做7-2去掉重复数据的时候,第一眼看见这个题目,就很明显感觉做过,并且感觉也不难,马上开始上去就是直接开个数组,然后两重循环。结果就是运行超时。
运行结果:
核心算法:
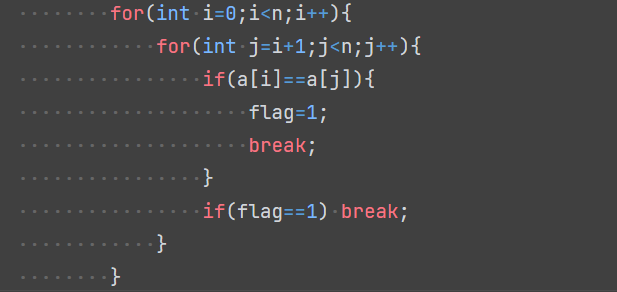
心得:以后看到这一类的题目,不要上去就嘎嘎写,要先瞄一眼限制时间,然后再根据限制时间设计合适的算法时间复杂度
2.在做7-1 菜单计价程序-4的时候,一开始没有考虑那么多,上去就直接用数组去存储各种数据,因为数据结构相对比较复杂,后面就会越写越乱。首先不好的一点就是数组你得限制大小,但是题目没给的数据范围的话,你就一点办法没有,你设置数组长度小了的话,测试点可能就会越界,数组长度设置长了的话,浪费空间。其次最烦的就是,你的题目如果代码很长的话,你利用的是数组,其实数组名就是指向你new出来的那一块空间,你在后面的操作过程中,肯定得要有各种查找,删除其中的元素。在查找的过程当中就很容易会报错,说数组指向了null,因为你步骤太多,每一步都得new一块空间来存储数据,实在是麻烦,所以为了以防万一,你就得用下图的操作:
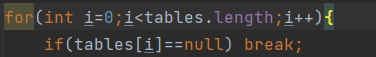
查找很多,每次都加就显得很蠢,而且麻烦容易出错。
还有就是删除,你用数组搞删除的话,确实艰难,我用的方法是将删除的那一个结点先指向null,然后从这个结点开始往后,每一个结点的数据用后面一个结点的数据进行覆盖。。。既麻烦又容易出错。
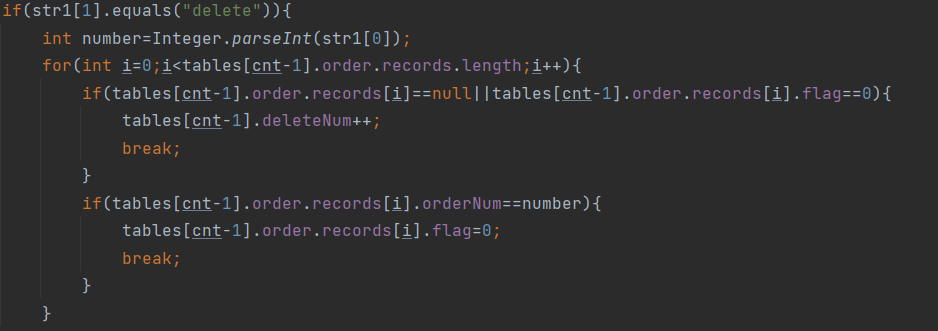
心得:所以我认为我这道题没写出来的原因就是一开始选择用了数组,不管是一开始数据的输入存储,还是后面的查找删除,只会越写越烦,超级容易出错。下次面对这种代码量比较大的题目时,一定不要一上来就数组,要选择合适的容器。
四.改进建议
以后写题,要三思而后行,尤其时要看下题目的时间复杂度,并且先分析一下代码整体大概该是个什么结构,就是先设计一下类,然后根据这些数据结构选择合适的容器去进行存储,不要上来就先写,不然很容易需要推翻前面写的,然后重头开始写,这就不好了,就想最后一题菜单一样。
所以大概就是碰到那种短小精悍的题目,只是需要你去写一段算法的题目,要先注意时间复杂度。遇到这种代码量大的题目,一定要先大概设计一下类该怎么写,之间的关系是怎么样的。
五.总结
总之这几次的题目让我比较难受,但是也认我去学习一些新的容器,并且学以致用。对代码量较大,题目结构比较复杂的题目有了基本的分析问题能力。在此后的学习当中还是得多写,多学以致用。