JDBC
1. JDBC 是什么
Java DataBase Connectivity(Java 语言连接数据库)
2. JDBC 的本质是什么?
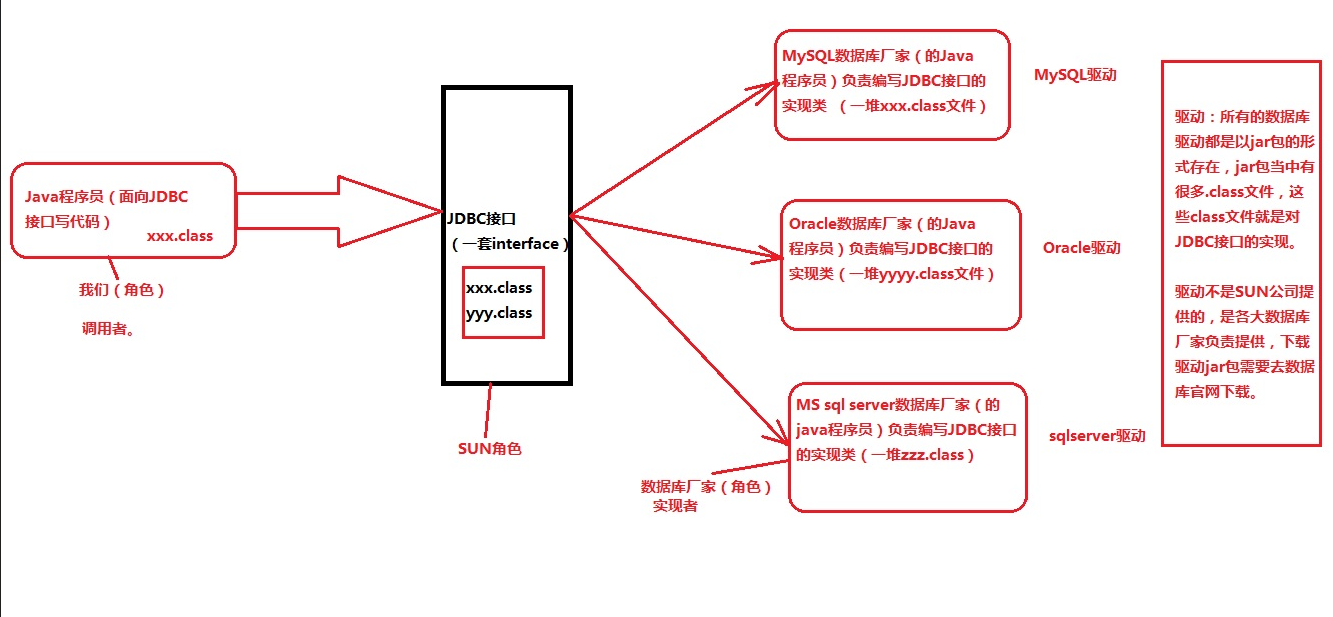
JDBC 是 SUN 公司制定的一套接口(interface)
java.sql.*; (这个软件包下有很多接口。)
接口都有调用者和实现者。
面向接口调用、面向接口写实现类,这都属于面向接口编程。
2.1 为什么要面向接口编程?
解耦合:降低程序的耦合度,提高程序的扩展力。
多态机制就是非常典型的:面向抽象编程。(不要面向具体编程)
建议:
Animal a = new Cat();
Animal a = new Dog();
// 喂养的方法
public void feed(Animal a){ // 面向父类型编程。
}
不建议:
Dog d = new Dog();
Cat c = new Cat();
2.2 思考:为什么 SUN 制定一套 JDBC 接口呢?
因为每一个数据库的底层实现原理都不一样。
Oracle 数据库有自己的原理。
MySQL 数据库也有自己的原理。
MS SqlServer 数据库也有自己的原理。
....
每一个数据库产品都有自己独特的实现原理。
2.3 JDBC 的本质到底是什么?
一套接口
3. JDBC 开发前的准备工作
先从官网下载对应的驱动 jar 包,然后将其配置到环境变量 classpath 当中。
classpath=.;D:\course\06-JDBC\resources\MySql Connector Java 5.1.23\mysql-connector-java-5.1.23-bin.jar
以上的配置是针对于文本编辑器的方式开发,使用 IDEA 工具的时候,不需要配置以上的环境变量。IDEA 有自己的配置方式。
4. JDBC 编程六步
第一步:注册驱动(作用:告诉 Java 程序,即将要连接的是哪个品牌的数据库)
第二步:获取连接(表示 JVM 的进程和数据库进程之间的通道打开了,这属于进程之间的通信,重量级的,使用完之后一定要关闭通道。)
第三步:获取数据库操作对象(专门执行 sql 语句的对象)
第四步:执行 SQL 语句(DQL DML....)
第五步:处理查询结果集(只有当第四步执行的是 select 语句的时候,才有这第五步处理查询结果集。)
第六步:释放资源(使用完资源之后一定要关闭资源。Java 和数据库属于进程间的通信,开启之后一定要关闭。)
插入数据的实现
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
// 1. 注册驱动
// 多态
Driver driver = null;
try {
driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctest?serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//System.out.println("数据库连接对象:" + connection );
// 3. 获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql
String sql = "INSERT INTO emp (id, workno, name, gender, age, idcard, workaddress, entrydate)\n" + "VALUES (1, '00001', '柳岩666', '女', 20, '123456789', '北京', '2000-01-01');";
// 专门执行DML语句的(insert delete update)
// 返回值是 "影响数据库中的记录条数"
int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "保存成功" : "保存失败");
// 5. 处理查询结果集
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 6. 释放资源
// 为了保证资源一定释放 , 在finally语句块中关闭资源
// 并且要遵循从小到大依次关闭
// 分别对其try catch
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
删除的实现
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实现数据的添加
Statement statement = null;
Connection connection = null;
// 1. 注册驱动
Driver driver = null;
try {
driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// 2. 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctest?serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url , user , password);
// 测试一下
//System.out.println("connection 的对象地址为:" + connection);
// connection 的对象地址为:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@4d5d943d
// 3. 获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql
String sql = "delete from emp where id = 2";
// 返回值是 "影响数据库中的记录条数"
int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "删除成功" : "删除失败");
// 5. 处理查询结果集
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源 ——> 分别进行释放
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
修改的实现
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数据的修改
// 1. 注册驱动
Driver driver = null;
Statement statement = null;
Connection connection = null;
try {
driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// 2. 获取驱动
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctest?serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url , user , password);
// 测试
//System.out.println("connection 的对象地址为:" + connection);
// 3. 获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql
String sql = "update emp set name = '陈平安' where id = 1;";
int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
// 返回值是 "影响数据库中的记录条数"
System.out.println(count == 1 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
// 5. 处理查询结果集
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源 , 分别进行释放
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
查询的实现
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
// 处理查询结果集
public class JDBCTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用资源绑定器绑定属性配置文件
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet res = null;
// 1. 注册驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
// 2. 获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql
String sql = "select * from emp";
res = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 5. 处理查询结果集
boolean flag = res.next();
System.out.println(flag);
if (flag) {
// 光标指向的行有数据
// 取数据
// getString()方法的特点是:不管数据库中的数据类型是什么,都以String的形式取出。
String id = res.getString(1);
String workno = res.getString(2);
String name = res.getString(3);
String gender = res.getString(4);
String age = res.getString(5);
String idcard = res.getString(6);
String workaddress = res.getString(7);
String entrydate = res.getString(8);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(workno);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(gender);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(idcard);
System.out.println(workaddress);
System.out.println(entrydate);
}
while (res.next()) {
String id = res.getString(1);
String workno = res.getString(2);
String name = res.getString(3);
String gender = res.getString(4);
String age = res.getString(5);
String idcard = res.getString(6);
String workaddress = res.getString(7);
String entrydate = res.getString(8);
System.out.println(id + ", " + workno + ", " + name + ", " + gender + ", " + age + ", " + idcard + ", " + workaddress + ", " + entrydate);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (res != null) {
res.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. SQL 注入
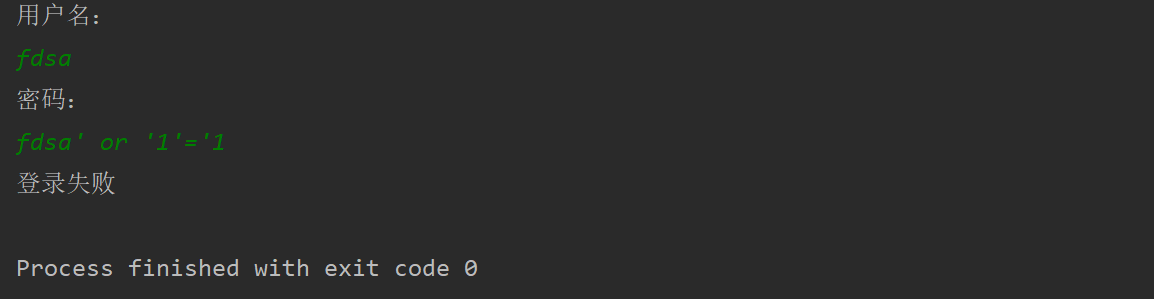
导致 SQL 注入的根本原因是什么?
用户输入的信息中含有 sql 语句的关键字,并且这些关键字参与 sql 语句的编译过程,导致 sql 语句的原意被扭曲,进而达到 sql 注入。
用户名:fdsa
密码:fdsa' or '1'='1
登录成功
这种现象被称为SQL注入(安全隐患)。(黑客经常使用)
解决 SQL 注入问题?
只要用户提供的信息不参与 SQL 语句的编译过程,问题就解决了。
即使用户提供的信息中含有 SQL 语句的关键字,但是没有参与编译,不起作用。
要想用户信息不参与 SQL 语句的编译,那么必须使用java.sql.PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement 接口继承了 java.sql.Statement
PreparedStatement 是属于预编译的数据库操作对象。
PreparedStatement 的原理是:预先对 SQL 语句的框架进行编译,然后再给 SQL 语句传“值”。
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.Scanner;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
/**
* 需求功能:
* 1. 需求:
* 模拟用户登录的实现
* 2. 业务描述:
* 程序运行的时候 ,提供一个输入的入口 ,可以让用户输入用户名和密码 ,用户输入用户名和密码之后提交信息
* java程序连接数据库验证用户名和密码是否合法
* 合法 :显示登录成功
* 不合法 :显示登录失败
* 3. 数据的准备
* 在实际开发中,表的设计会使用专业的建模工具,我们这里安装一个建模工具:PowerDesigner
* 使用PD工具来进行数据库表的设计。(参见user-login.sql脚本)
*/
public class JDBCTest08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化一个界面
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = initUI();
// 验证用户和密码
boolean loginSuccess = login(userLoginInfo);
// 最后输出结果
System.out.println(loginSuccess ? "登录成功" : "登录失败");
}
/**
* 用户登录
* @param userLoginInfo 用户登录信息
* @return false表示失败 , true表示成功
*/
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
// 打标记的意识
boolean loginSuccess = false;
// 单独定义变量
String loginName = userLoginInfo.get("loginName");
String loginPwd = userLoginInfo.get("loginPwd");
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
Connection connection = null;
ResultSet res = null;
// 使用资源绑定器绑定属性配置文件
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
// JDBC代码
// 1. 注册驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
// 2. 获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// SQL语句的框子。其中一个?,表示一个占位符,一个?将来接收一个“值”,注意:占位符不能使用单引号括起来。
String sql = "select * from t_user where loginName = ? and loginPwd = ?";
// 3. 获取预编译数据库操作对象
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给占位符?传值(第1个问号下标是1,第2个问号下标是2,JDBC中所有下标从1开始。)
preparedStatement.setString(1 , loginName);
preparedStatement.setString(2 , loginPwd);
// 4. 执行sql
res = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 5. 处理结果集
if (res.next()) {
// 登录成功
loginSuccess = true;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 6. 释放资源
try {
if (res != null) {
res.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return loginSuccess;
}
/**
* 初始化用户界面
* @return 用户输入的用户名和密码等登录信息
*/
private static Map<String, String> initUI() {
// 键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("用户名:");
String loginName = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("密码:");
String loginPwd = scanner.nextLine();
Map<String, String> userLoginInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLoginInfo.put("loginName", loginName);
userLoginInfo.put("loginPwd", loginPwd);
// 返回操作对象
return userLoginInfo;
}
}
结果显示:
解决 SQL 注入的关键是什么?
用户提供的信息中即使含有 sql 语句的关键字,但是这些关键字并没有参与编译。不起作用。
6. 对比一下 Statement 和 PreparedStatement?
Statement 存在 sql 注入问题,PreparedStatement 解决了 SQL 注入问题。
Statement 是编译一次执行一次。PreparedStatement 是编译一次,可执行 N 次。PreparedStatement 效率较高一些。
PreparedStatement 会在编译阶段做类型的安全检查。
综上所述:PreparedStatement 使用较多。只有极少数的情况下需要使用 Statement
什么情况下必须使用 Statement 呢?
业务方面要求必须支持 SQL 注入的时候。
Statement 支持 SQL 注入,凡是业务方面要求是需要进行 sql 语句拼接的,必须使用 Statement。
7. JDBC 事务机制
JDBC 中的事务是自动提交的,什么是自动提交?
只要执行任意一条 DML 语句,则自动提交一次。这是 JDBC 默认的事务行为。
但是在实际的业务当中,通常都是 N 条 DML 语句共同联合才能完成的,必须
保证他们这些 DML 语句在同一个事务中同时成功或者同时失败。
8. JDBC 工具类的封装
package com.north.util;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* JDBC工具类 :简化JDBC编程
*/
public class DBUtil {
/**
* 工具类中的构造方法都是私有的。
* 因为工具类当中的方法都是静态的,不需要new对象,直接采用类名调用。
*/
private DBUtil(){
}
// 静态代码块在类加载时执行,并且只执行一次。
static {
// 注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 获取数据库连接对象
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctest?serverTimezone=UTC" , "root" , "123456");
}
/**
* 关闭资源
* @param connection 连接对象
* @param statement 数据库操作对象
* @param resultSet 结果集
*/
public static void close(Connection connection , Statement statement , ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
JDBC 实现模糊查询
package com.north.jdbcdemo;
import com.north.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCTest10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
Connection connection = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 获取连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 获取预编译的数据库操作对象
String sql = "select name from emp where name like ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1 , "_平%");
// 处理结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("name"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
DBUtil.close(connection , preparedStatement , resultSet);
}
}
}
9. 悲观锁和乐观锁的概念
