JAVA第4-6次作业总结
前言:
在经过了前三次JAVA作业的洗礼后,我们迎来了4-6次的OOP训练,难度比前三次都提升颇多,我感触也颇多。学习JAVA一定要有方法,经过将近两个月的学习之后,(作为一个菜鸡)我也想谈谈自己对于JAVA学习的看法(虽然这样的看法并不够准确),因为大部分是自学,少部分是老师教,虽然也有课后作业辅以练习,但也不像在企业中学了就能够实践,印象特别深刻。所以在自学的时候,因为没有实践的及时反馈,所以记笔记就显得特别重要。因为记笔记就像写作一样,是整理思路的绝佳方法。在学习编程方面,人跟人是不一样的,别人觉得难理解的东西,我可能并不觉得,而我觉得难理解的东西,别人可能又会觉得特简单。学习笔记就是自己专有的“难点手册”,与高考时的“错题本”类似,以后无论是学习,考试,考研,随时都可以翻出来看看,自是获益匪浅。对我而言,我更喜欢电子笔记,因为对于程序来说,手写的未免有点太过于苍白,我喜欢用文档记录知识点,再配上代码实例和运行的结果来方便自己加强对于这些的理解。
对于笔记,我也很喜欢分类,比如我会把《JAVA基础知识》作为一个单独的文档,去记录一些基础且离散的知识点,比如正则表达式,比如stringbuilder、stringbuffer等等,同样的,《封装》、《继承与多态》、《集合》等都会成为一个单独的文档,所有相关知识我都会分别在里面记录。
除了笔记之外,练习显然也是一个必不可少的部分,甚至我想说,你可以光有练习而没有笔记,但你绝不可以光有笔记而不练习,对于一个学习编码的人来说,没有代码的练习就好像没有桨的船,寸“水”难行。而且练完以后,总结与代码的改进也是必不可少的,目前我的目标是在能把代码写出来的基础上,尽量减少shit山的堆叠。这是一个漫长而艰巨的过程,我还任重而道远。
以上是我对JAVA学习的一些浅浅的总结与看法,接下来我会同上次一样,从三次作业遇到的BUG(踩坑警告),代码思路与解决方案,作业总结与代码改进,以及自己的一些感想来分析JAVA第4~6次作业,如有不足,欢迎讨论!
目录:
一:三次作业遇到的BUG(踩坑警告)
二:代码思路与解决方法
三:作业总结与代码改进
四:一些感想
一:三次作业遇到的BUG(踩坑警告)
1:OOP训练集04
7-1:菜单计价3
需求分析多,内容多,难点杂,需要大量代码以实现,同时有必要去自学
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.LocalTime;
等头文件,这样可方便解题速度大大提升。
7-4:单词统计与排序
可以用传统方法,但如果用List<String>和Set<String>以及Collections.sort等集合写起来更快、更方便,这部分可以放到代码改进里说。
2:OOP训练集05
7-2 :日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
应该说这一题是关于日期类设计中最难的题目了,思路都在,写法都会,但是关于方法的不断调用非常值得我们去巩固与探讨
OOP5 7-5
此题可以说是日期类的题目中最难的一题了,但难的其实不是思路,代码的实现有了之前的相关的题目的铺垫,也并不困难,重点在于方法的调用,由于方法使用的限制,需要用大量方法的调用,所以如何实现各种方法的衔接就是本题的重点与难点。
OOP5 7-6
相较于上一题,此题的难度有明显的降低,原因就是方法使用的限制减少了,我们不需要写诸如day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),而是只需要写year.getValue()>date.year.getValue(),这种只调用传进参数的方法,远远比方法间的不断调用来的更快捷。
3:OOP训练集06
OOP6 7-4
ATM机类结构设计又是一个全新的挑战,从未接触过该类的设计很是让我头疼。思路的设计和方法的运用是该题的重点。
OOP6 7-5
在上一题的基础上,ATM机类结构设计二包含了借记卡和信用卡两类,且允许跨行办理相关业务(例如在中国建设银行的ATM机上使用中国工商银行的银行卡进行业务操作),需求扩大,题目变难的基础上,如何合理的解决,同样的,思路的设计和方法的运用依然是该题的重点,而如何利用上一题的代码,在上一题得到基础上对代码进行改进,则又是该题的一个重点。
二:代码思路与解决方法
OOP4 7-1
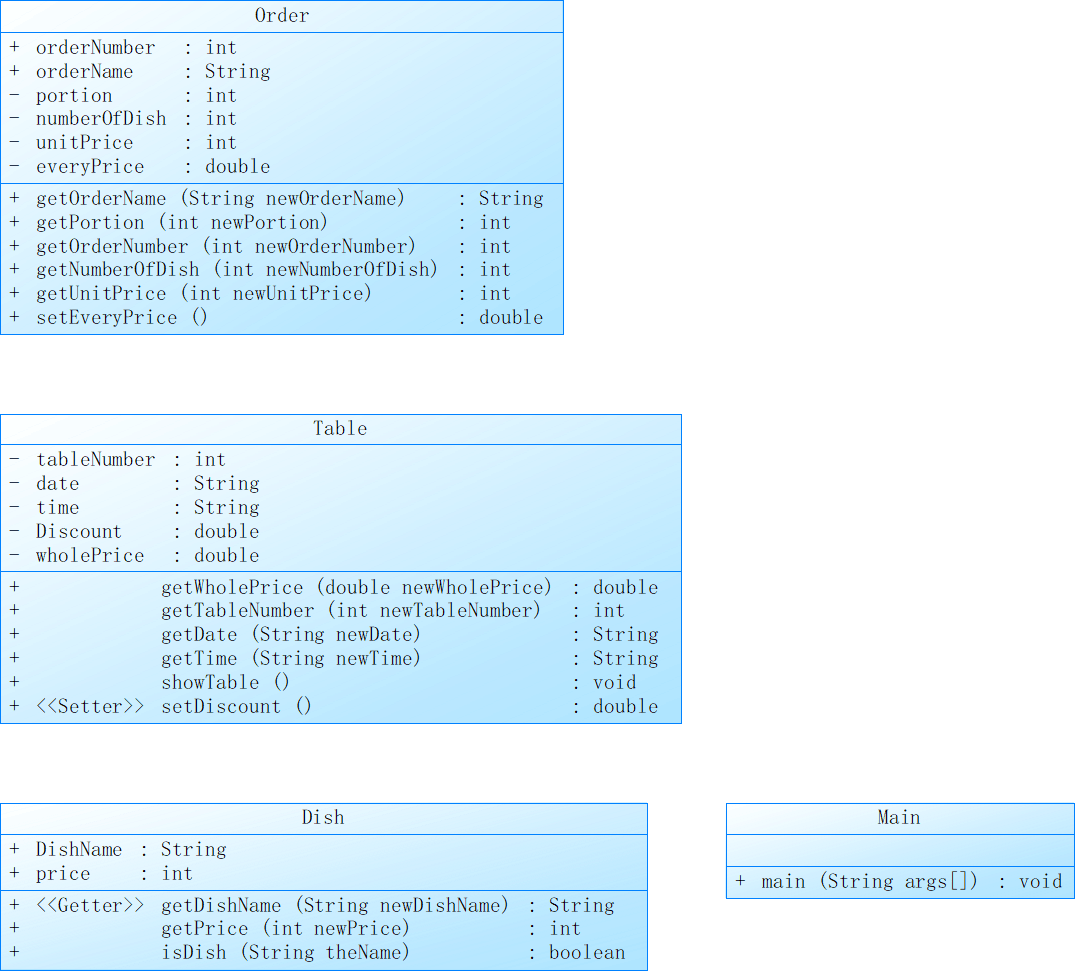
类图实现
代码实现
import java.time.DayOfWeek; import java.util.Scanner; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import java.time.LocalTime; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int count = 1; //计算循环进行了多少次 String wholeJudge = ""; //判断何时进入下一个循环 Dish[] dishes = new Dish[100]; int menuCount = 0; //计算菜单数量 while(input.hasNext()){ //记录菜单信息 wholeJudge = input.next(); if(wholeJudge.equals("table")) break; //输入table后进入下一个模块 if(wholeJudge.equals("end")) break; //空菜单 if(count%2 != 0){ dishes[menuCount] = new Dish(); //创建一个新的对象 dishes[menuCount].getDishName(wholeJudge); //获取菜名 }else{ dishes[menuCount].getPrice(Integer.parseInt(wholeJudge));//获取单价 menuCount++; //菜单数量加一 } count++; } /*菜单模块结束*/ System.out.println("table 1: "); //输出 "table 1" Table[] tables = new Table[100]; //创建餐桌对象数组 int tableCount = input.nextInt(); //记录餐桌数量且餐桌数量从1开始 tables[tableCount] = new Table(); //创建一个餐桌对象 tables[tableCount].getTableNumber(tableCount);//获取桌号 wholeJudge = input.next(); tables[tableCount].getDate(wholeJudge); //获取日期 wholeJudge = input.next(); tables[tableCount].getTime(wholeJudge); //获取时间 /*第一张餐桌的时间信息记录完毕 */ count = 1; //记录循环进行了几次 boolean existDish = true; Order[] order = new Order[100]; //创建订单对象数组 int orderCount = 0; //记录订单数量 order[orderCount] = new Order(); //创建一个订单对象 double everyPriceMain = 0; //每份菜的价格 double evertTablePrice = 0; //每桌菜的总价 int deleteNumber = 0; //删除订单编号 while(input.hasNext()){ wholeJudge = input.next(); if(wholeJudge.equals("end")){ for(int i=1;i<=tableCount;i++){ for(int j=0;j<orderCount;j++){ //System.out.println(order[j].setEveryPrice()); tables[i].getWholePrice(order[j].setEveryPrice()); } tables[i].showTable(); //输出每桌的总价 } break; } if(wholeJudge.equals("table")){ tableCount++; //餐桌数量加一 tables[tableCount] = new Table(); wholeJudge = input.next(); tables[tableCount].getDate(wholeJudge); //获取日期 wholeJudge = input.next(); tables[tableCount].getTime(wholeJudge); //获取时间 } if( count%4 == 1) { order[orderCount].getOrderNumber(Integer.parseInt(wholeJudge));//获取订单编号 deleteNumber = Integer.parseInt(wholeJudge); count++; } else if( count%4 == 2) { /*输入delete*/ if(wholeJudge.equals("delete")){ count = 1; if(deleteNumber>orderCount-1){ System.out.println("delete error"); }else { order[deleteNumber-1].getPortion(0); } } /*未输入delete*/ else { order[orderCount].getOrderName(wholeJudge); count++; int i = 0; //判断是否循环到底 for (i = menuCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (dishes[i].isDish(order[orderCount].orderName)) { order[orderCount].getUnitPrice(dishes[i].price); //获取相对应的菜品的单价 existDish = true; break; } } if(i==-1) { System.out.println(wholeJudge+" does not exist"); existDish = false; } } } else if( count%4 == 3){ order[orderCount].getPortion(Integer.parseInt(wholeJudge)); count++; }else if( count%4 == 0){ order[orderCount].getNumberOfDish(Integer.parseInt(wholeJudge));//获取份数 everyPriceMain = order[orderCount].setEveryPrice(); //输出每份菜的价格 if(existDish) { System.out.print(order[orderCount].orderNumber + " " + order[orderCount].orderName + " "); System.out.printf("%.0f\n", everyPriceMain); } count++; orderCount++; order[orderCount] = new Order(); //创建一个订单对象 } } } } class Dish{ public String DishName; public int price; public String getDishName(String newDishName){ DishName = newDishName; return DishName; } public int getPrice(int newPrice){ price = newPrice; return price; } public boolean isDish(String theName){ return theName.equals(DishName); } } class Order{ public int orderNumber; public String orderName; private int portion; private int numberOfDish; private int unitPrice; private double everyPrice; public String getOrderName(String newOrderName){ orderName = newOrderName; return orderName; } public int getPortion(int newPortion){ portion = newPortion; return portion; } public int getOrderNumber(int newOrderNumber){ orderNumber = newOrderNumber; return orderNumber; } public int getNumberOfDish(int newNumberOfDish){ numberOfDish = newNumberOfDish; return numberOfDish; } public int getUnitPrice(int newUnitPrice){ unitPrice = newUnitPrice; return unitPrice; } /*public double deletePrice(){ everyPrice = 0; return everyPrice; }*/ public double setEveryPrice(){ if(portion==1) everyPrice = unitPrice * numberOfDish; if(portion==2) everyPrice = Math.round( unitPrice * 1.5 *numberOfDish); if(portion==3) everyPrice = unitPrice * 2 *numberOfDish; if(portion==0) everyPrice = 0; return everyPrice; } } class Table{ private int tableNumber; private String date; private String time; private double Discount; private double wholePrice; public double getWholePrice(double newWholePrice){ wholePrice += newWholePrice; return wholePrice; } public int getTableNumber(int newTableNumber) { tableNumber = newTableNumber; return tableNumber; } public String getDate(String newDate){ date = newDate; return date; } public String getTime(String newTime){ time = newTime; return time; } public void showTable(){ double nowDiscount = setDiscount(); System.out.print("table "+tableNumber); if(nowDiscount==0) System.out.println(" out of opening hours"); else {System.out.print(": ");System.out.println(Math.round(wholePrice*Discount));} } public double setDiscount(){ String inputDate = date; String[] dateParts = inputDate.split("/"); // 使用正则表达式分割字符串 String formattedDate = dateParts[0] + "/" + String.format("%02d", Integer.parseInt(dateParts[1])) + "/" + String.format("%02d", Integer.parseInt(dateParts[2])); String inputTime = time; String[] timeParts = inputTime.split("/"); // 使用正则表达式分割字符串 String formattedTime = timeParts[0] + ":" + String.format("%02d", Integer.parseInt(timeParts[1])) + ":" + String.format("%02d", Integer.parseInt(timeParts[2])); DateTimeFormatter dateFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd"); LocalDate judgeDate = LocalDate.parse(formattedDate,dateFormatter); DateTimeFormatter timeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss"); LocalTime judgeTime = LocalTime.parse(formattedTime,timeFormatter); LocalTime startEvenTime = LocalTime.parse("16:59:59", timeFormatter); LocalTime endEvenTime = LocalTime.parse("20:30:01", timeFormatter); LocalTime startNoonTime = LocalTime.parse("10:29:59", timeFormatter); LocalTime endTNoonTime = LocalTime.parse("14:30:01", timeFormatter); LocalTime weekendStartTime = LocalTime.parse("09:29:59", timeFormatter); LocalTime weekendEndTime = LocalTime.parse("21:00:01", timeFormatter); DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = judgeDate.getDayOfWeek(); int dayOfWeekValue = dayOfWeek.getValue(); if (dayOfWeekValue >= 1 && dayOfWeekValue <= 5) { if(judgeTime.isAfter(startNoonTime)&& judgeTime.isBefore(endTNoonTime)){ Discount = 0.6; }else if(judgeTime.isBefore(endEvenTime)&& judgeTime.isAfter(startEvenTime)){ Discount = 0.8; }else{ Discount = 0; //不在营业时间 } } else { if(judgeTime.isAfter(weekendStartTime)&& judgeTime.isBefore(weekendEndTime)){ Discount = 1; }else{ Discount = 0; //不在营业时间 } } return Discount; } }
代码分析
该点菜系统涉及到菜品(Dish),订单(Order)和餐桌(Table)这三个类。
主函数方面,通过循环和条件判断获取菜单信息、记录餐桌信息、订单信息和价格计算等操作。
Dish 类表示菜品,包含菜名(DishName)和单价(price)属性,提供了获取菜名、获取单价、判断菜品名是否匹配的方法。
Order 类表示订单,包含订单编号、菜名、菜品数量、单价等属性,以及计算每份菜的价格的方法。
Table 类表示餐桌,包含桌号、日期、时间等属性,以及计算折扣、展示每桌的总价等方法。
代码分为以下几个部分:
菜单信息的记录:通过 Scanner 对象接收用户输入的菜名和单价,将其存储在 Dish 类的对象数组中。
餐桌信息的记录:通过 Scanner 对象接收用户输入的餐桌数量、日期和时间,将其存储在 Table 类的对象数组中。
订单信息的记录:通过 Scanner 对象接收用户输入的订单编号、菜名、菜品数量等,将其存储在 Order 类的对象数组中。
计算每桌总价:遍历订单数组,将每份菜的价格累加到相应的餐桌对象中,计算每桌的总价。
根据不同时间段提供折扣:根据餐桌上的日期和时间判断折扣比例,将折扣应用于每桌的总价。
OOP5 7-5
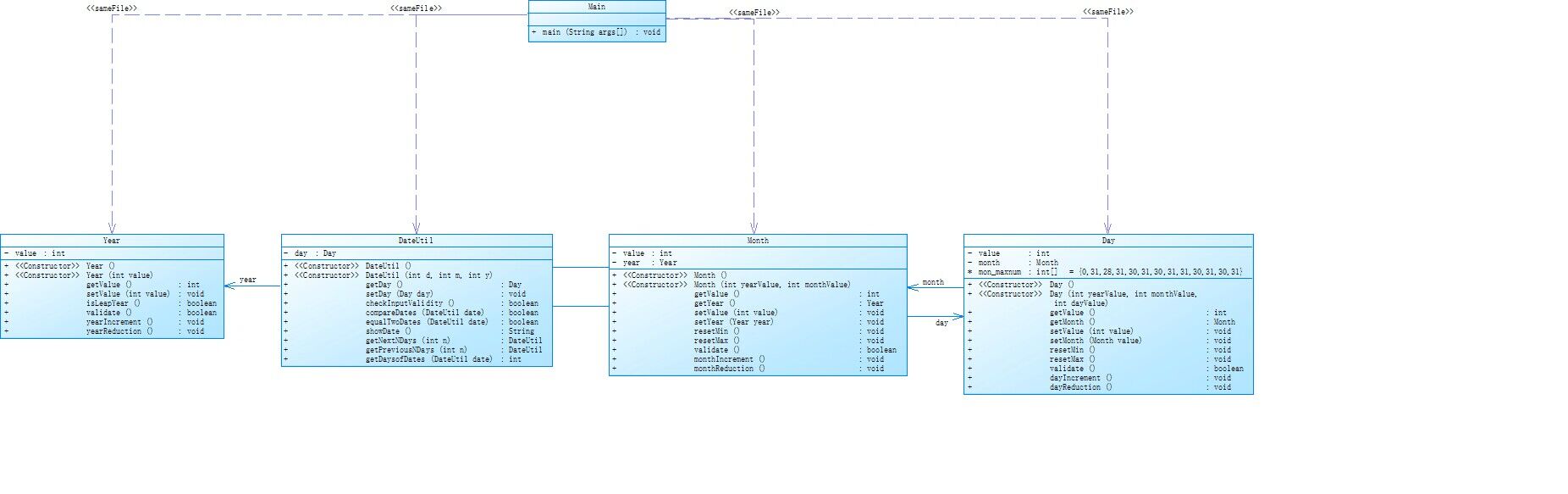
类图实现
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner; class Year{ private int value; public Year(){} public Year(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断是否为闰年 if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean validate(){//校验数据合法性 if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement(){ value=value+1; } public void yearReduction(){ value=value-1; } } class Month{ private int value; private Year year;//无参构造 public Month(){}//空参构造 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ this.year=new Year(yearValue); this.value=monthValue; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public Year getYear(){ return year; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public void setYear(Year year){//year作为Year大类中的对象,与其一起构成参数传进去 this.year=year; } public void resetMin(){//月份复位为1 value=1; } public void resetMax(){//月份复位为12 value=12; } public boolean validate(){ if(value>=1&&value<=12) return true; else return false; } public void monthIncrement(){//不需要传参 value=value+1; } public void monthReduction(){ value=value-1; } } class Day{ private int value; private Month month; int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public Day(){} public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value=dayValue; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public Month getMonth(){ return month; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public void setMonth(Month value){//参数 this.month=value; } public void resetMin(){//日期复位 value=1; } public void resetMax(){//日期设为该月最大值 value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]; } public boolean validate(){//校验数据合法性 if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//如果是闰年 mon_maxnum[2]=29; if(value>=1&&value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return true; else return false; } public void dayIncrement(){ value=value+1; } public void dayReduction(){ value=value-1; } } class DateUtil{ private Day day; //无参构造 public DateUtil() { } //有参构造 public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) { this.day = new Day(d , m , y); } public Day getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } //检查数据合法性 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ return day.getMonth().validate() && day.validate() && day.getMonth().getYear().validate(); } //比较两日期大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//date即为输入的年月日 if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()){//年 return true; }else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getValue()){//月 return true; }else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()){//日 return true; } return false; } //判断两日期是否相等 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && day.getValue() == date.day.getValue(); } //日期格式化 public String showDate(){ return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); } //求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else day.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]+1){// day.resetMin(); day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); } if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 13){//月份为13 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.getMonth().resetMin(); } } return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() , day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); } //求前n天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else day.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayReduction(); if(day.getValue() == 0){//日期减为0 day.getMonth().monthReduction();//月份开始自减 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 0){//月份减为0 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();//年份开始自减 day.getMonth().setValue(12);//月份变为12 } day.resetMax(); } } return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() , day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); } //求两日期间的天数 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int res = 0;//将两日期之间的天数设出来 if(this.compareDates(date)){ while(true){ if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) date.day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else date.day.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; date.day.dayIncrement();//相当于day++ if(date.day.getValue() == date.day.mon_maxnum[date.day.getMonth().getValue()] + 1){ date.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); date.day.resetMin(); } if(date.day.getMonth().getValue() == 13){ date.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); date.day.getMonth().resetMin(); } if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.day.getMonth().getValue() == day.getMonth().getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } }else{ while(true){ if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else day.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()] + 1){ day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); } if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 13){ day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.getMonth().resetMin(); } if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.day.getMonth().getValue() == day.getMonth().getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } } return res + 1; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int a,b; a = input.nextInt();//输入判断类型 year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt();//输入年月日 DateUtil c = new DateUtil(year,month,day); if(a==1){//求下n天 b = input.nextInt();//输入n if(!c.checkInputValidity()||b<0){//数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getNextNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==2) { b = input.nextInt();//输入n if (!c.checkInputValidity() || b < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getPreviousNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==3){ int y1,m1,d1; y1 = input.nextInt(); m1 = input.nextInt(); d1 = input.nextInt();//输入第二个年月日 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y1,m1,d1); if(!c.checkInputValidity()||!date.checkInputValidity()){//如果数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getDaysofDates(date)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }
代码分析
在前文已经说到这题难度是相关题目中难度最大的一题,且跟同类型的题目区别很不一样。首先是再方法上,在之前的题目中,对于比如天数的增加,我们都是直接写的,月份、年份的增加也是同样的道理,而当天数到了30/31天后,当需要变为1时,同样需要我们自己去书写,但是在该题的类图中,已经提前给我们写好了方法,如resetMin()(日期复位), resetMax()(月份设为该月最大值),同样的,还有dayIncrement()(日期增加一天),dayReduction()(日期减少一天),事实上,在当时对于value我还理解的不是很清楚,我一直把value当做天数来看待,但是发现到后面就很难进行分析了,因为value在每个类的设计中都出现了,所以我猜测value应该是作为一个参数贯穿始终,而这样想后整道题也就相对清晰了。接下来的重头戏就是在前文说的方法的调用,我们试举一例进行分析,如day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),首先我们看day出现在哪,出现在前文中的 private Day day;我们发现这个day是Day的一个对象,那么我们再去找Day出现在哪,发现Day作为一个大类,出现在class Day中所以,day.getMonth()就是调用了day中的getMonth方法,那么我们再找Month出现在哪,发现出现Month也作为一个大类出现在class Month中,所以我们再往Month中去找,发现了getYear,所以day.getMonth().getYear()就是调用了Month和Year中的方法,再在Year中查看,发现了getValue方法,而在前文已经说了value是作为参数传进来的,所以day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()本质上的意思就是传进来的日期参数,但是要注意方法的调用在Year中停止了,所以day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()就是比较年的大小,确定年份大小相同后再对月份、日期进行逐一的比较。
对每个类的分析:
Year 类:
定义了一个私有整型变量 value,表示年份;
提供了 getter 和 setter 方法;
isLeapYear() 方法判断年份是否为闰年;
validate() 方法检查年份是否在有效范围内(1900年至2050年);
yearIncrement() 和 yearReduction() 方法分别实现年份的自增和自减。
Month 类:
定义了一个私有整型变量 value,表示月份;
定义了一个 Year 类型的变量 year;
提供了 getter 和 setter 方法;
resetMin() 和 resetMax() 方法分别将月份设置为 1 和 12;
validate() 方法检查月份是否在有效范围内(1至12);
monthIncrement() 和 monthReduction() 方法分别实现月份的自增和自减。
Day 类:
定义了一个私有整型变量 value,表示日期;
定义了一个 Month 类型的变量 month;
提供了 getter 和 setter 方法;
resetMin() 和 resetMax() 方法分别将日期设置为 1 和该月最大值;
validate() 方法检查日期是否在有效范围内(1至该月最大值);
dayIncrement() 和 dayReduction() 方法分别实现日期的自增和自减。
DateUtil 类:
定义了一个 Day 类型的变量 day;
提供了 getter 和 setter 方法;
checkInputValidity() 方法检查输入的日期是否合法;
compareDates() 方法比较两个日期的大小;
equalTwoDates() 方法判断两个日期是否相等;
showDate() 方法以字符串形式展示日期;
getNextNDays() 方法计算指定日期的 n 天后的日期;
getPreviousNDays() 方法计算指定日期的 n 天前的日期;
getDaysofDates() 方法计算两个日期之间的天数。
Main 类:
从输入中读取年、月、日以及操作类型(1:求下 n 天,2:求前 n 天,3:计算两个日期之间的天数);
根据操作类型调用 DateUtil 类的相关方法进行计算。
OOP5 7-6
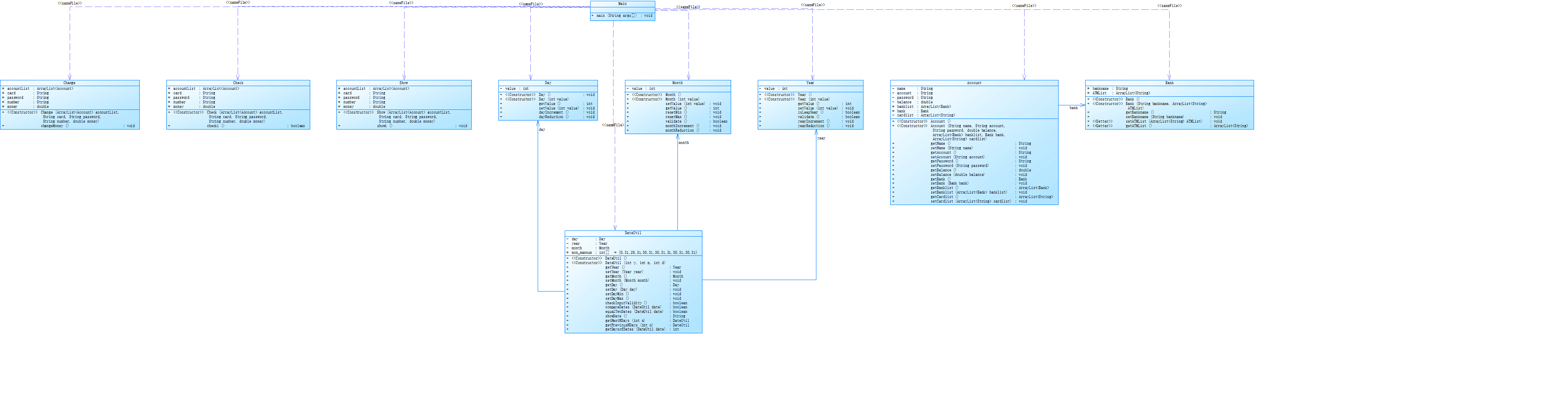
类图实现
代码实现
mport java.util.Scanner; class Day{ private int value; public void Day(){} public Day(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public void dayIncrement(){ value=value+1; } public void dayReduction(){ value=value-1; } } class Month{ private int value;//无参构造 public Month(){}//含参构造 public Month(int value){ this.value=value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void resetMin(){ value=1; } public void resetMax(){ value=12; } public boolean validate(){ if(value<=12&&value>=1) return true; else return false; } public void monthIncrement(){ value=value+1; } public void monthReduction(){ value=value-1; } } class Year{ private int value; public Year(){} public Year(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断闰年 if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||(value % 400==0)) return true; else return false; } public boolean validate(){//校验数据合法性 if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement(){ value=value+1;//年份加一 } public void yearReduction(){ value=value-1;//年份减一 } }class DateUtil{ private Day day; private Year year; private Month month; int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public DateUtil(){} public DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ this.day=new Day(d); this.year=new Year(y); this.month=new Month(m); } public Year getYear(){ return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public Month getMonth(){ return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public Day getDay(){ return day; } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } public void setDayMin(){//最小天 day.setValue(1); } public void setDayMax(){//最大天 if(year.isLeapYear()){ mon_maxnum[2]=29; }else{ mon_maxnum[2]=28; } day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]); } public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检验日期合法性 if(year.getValue()<=2020 && year.getValue() >= 1820 && month.getValue()<=12 && month.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() >=1 && day.getValue() <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return true; else return false; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较两日期大小 if(year.getValue()>date.year.getValue()){ return true; }else if(year.getValue()==date.year.getValue() && month.getValue()>date.month.getValue()){ return true; }else if(year.getValue()==date.year.getValue() && month.getValue()==date.month.getValue()&&day.getValue()>date.day.getValue()){ return true; } return false; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){//判断两日期是否相等 if(year.getValue() == date.year.getValue() && month.getValue() == date.month.getValue() && day.getValue() == date.day.getValue()){ return true; } return false; } public String showDate(){//格式化日期 return year.getValue() + "-" + month.getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//求下n天 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]+1){ day.setValue(1); month.monthIncrement(); } if(month.getValue() == 13){ year.yearIncrement(); month.setValue(1); } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue()); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; day.dayReduction(); if(day.getValue() == 0){ month.monthReduction(); if(month.getValue() == 0){ year.yearReduction(); month.setValue(12); } day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]); } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(), month.getValue(), day.getValue()); } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int res = 0; if(this.compareDates(date)){ while(true){ if(date.year.isLeapYear()) date.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else date.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; date.day.dayIncrement(); if(date.day.getValue() == date.mon_maxnum[date.month.getValue()] + 1){ date.month.monthIncrement(); date.day.setValue(1); } if(date.month.getValue() == 13){ date.year.yearIncrement(); date.month.resetMin(); } if(date.year.getValue() == year.getValue() && date.month.getValue() == month.getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } }else{ while(true){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == mon_maxnum[month.getValue()] + 1){ month.monthIncrement(); day.setValue(1); } if(month.getValue() == 13){ year.yearIncrement(); month.resetMin(); } if(date.year.getValue() == year.getValue() && date.month.getValue() == month.getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } } return res + 1; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int a = sc.nextInt();//输入字符 int year = sc.nextInt();//年 int month = sc.nextInt();//月 int day = sc.nextInt();//日 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year , month , day); if(a == 1){ //求下n天 int n = sc.nextInt(); if(!date.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; }else{ System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + "next " + n + " " + "days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(n).showDate()); } }else if(a == 2){ int n = sc.nextInt(); if(!date.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; }else{ System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + "previous " + n + " " + "days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } }else if(a == 3){ //求相差天数 int year2 = sc.nextInt(); int month2 = sc.nextInt(); int day2 = sc.nextInt(); DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(year2 , month2 , day2); if(!date.checkInputValidity() || !date2.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); }else{ System.out.print("The days between " + year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + "and" + " " + year2 + "-" + month2 + "-" + day2 + " are:"); System.out.println(date.getDaysofDates(date2)); } }else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
代码分析:同7-5差不多,只不过不用再不断地调用方法,只需要调用方法中的参数即可。
OOP6 7-4
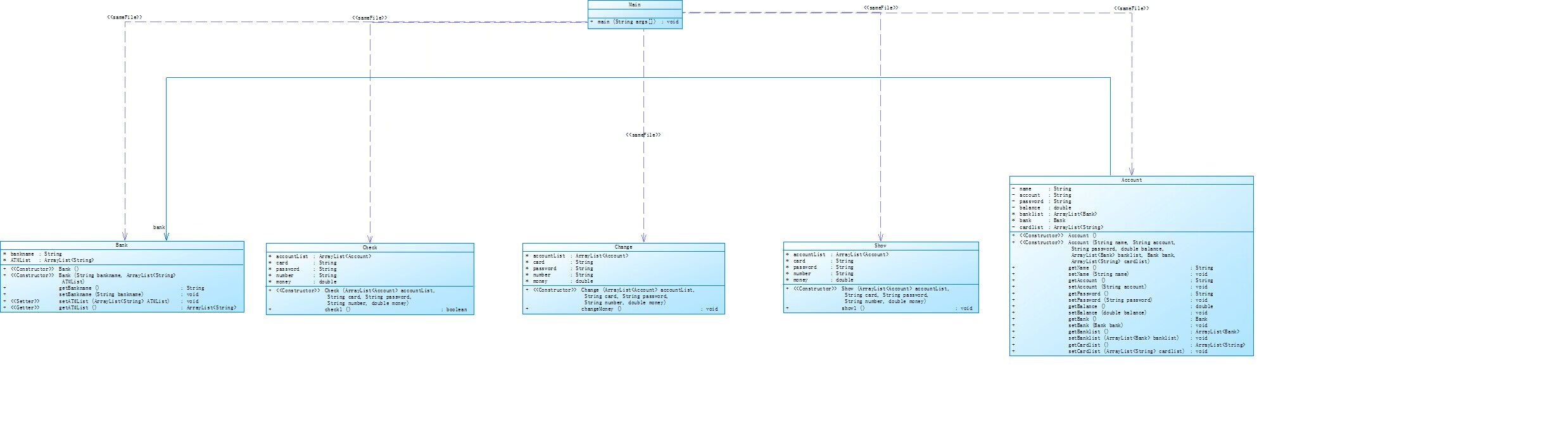
类图实现
代码实现
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; //Bank类 class Bank{ String bankname; ArrayList<String> ATMList; public Bank(){} public Bank(String bankname,ArrayList<String> ATMList) { this.bankname = bankname; this.ATMList = ATMList; } public String getBankname(){ return bankname; } public void setBankname(String bankname){ this.bankname=bankname; } public void setATMList(ArrayList<String> ATMList){ this.ATMList=ATMList; } public ArrayList<String> getATMList(){ return ATMList; } } //Account类 class Account{ private String name;//姓名 private String account;//账户 private String password;//密码 private double balance;//余额 ArrayList<Bank> banklist; Bank bank; private ArrayList<String> cardlist; public Account(){} public Account(String name,String account,String password,double balance,ArrayList<Bank> banklist,Bank bank,ArrayList<String> cardlist){ this.name = name; this.account = account; this.password = password; this.balance = balance; this.bank = bank; this.banklist = banklist; this.cardlist = cardlist; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getAccount(){ return account; } public void setAccount(String account){ this.account = account; } public String getPassword(){ return password; } public void setPassword(String password){ this.password = password; } public double getBalance(){ return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance){ this.balance = balance; } public Bank getBank(){ return bank; } public void setBank(Bank bank){ this.bank = bank; } public ArrayList<Bank> getBanklist(){ return banklist; } public void setBanklist(ArrayList<Bank> banklist){ this.banklist = banklist; } public ArrayList<String> getCardlist(){ return cardlist; } public void setCardlist(ArrayList<String> cardlist){ this.cardlist = cardlist; } } //存取款的检查 class Check{ ArrayList<Account> accountList; String card; String password; String number; double money; public Check(ArrayList<Account> accountList,String card,String password,String number,double money){ this.accountList = accountList;//账户数组 this.card = card; this.password = password; this.number = number; this.money = money; } public boolean check1(){ int flag = 0; int i,j; int k = 0; for(i = 0;i<accountList.size();i++){//遍历账户数组 for(j = 0;j<accountList.get(i).getCardlist().size();j++) {//遍历卡号数组 if (card.equals((accountList.get(i).getCardlist().get(j)))) {//传进来的卡号等于卡号数组 flag = 1; k = i; break; } } if(flag == 1){ break; } } //检查密码是否正确 if(flag == 1){ if(password.equals(accountList.get(k).getPassword())){ flag = 2; } else{ System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong.");//密码错误 return false; } } else{ System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist.");//卡号不存在 return false; } //ATM编号是否正确 if(flag == 2){ for(i=0;i<accountList.get(k).banklist.size();i++){ for(j=0;j<accountList.get(k).banklist.get(i).ATMList.size();j++){ if(number.equals(accountList.get(k).banklist.get(i).ATMList.get(j))){ flag = 3; break; } } } } //金额是否正确 if (flag == 3) { if (money <= accountList.get(k).getBalance()) { flag = 4; } else { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient.");//取款金额大于账户余额 return false; } } else { System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong.");//ATM机编号不存在 return false; } //是否跨行 if (flag == 4) { for (i = 0; i < accountList.get(k).bank.ATMList.size(); i++) { if (number.equals(accountList.get(k).bank.ATMList.get(i))) { flag = 5; break; } } } if (flag != 5) { System.out.println("Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported.");//跨行存取款 return false; } else return true; } } //改变余额 class Change { ArrayList<Account> accountList; String card; String password; String number; double money; public Change(ArrayList<Account> accountList, String card, String password, String number, double money) { this.accountList = accountList; this.card = card; this.password = password; this.number = number; this.money = money; } public void changeMoney() { int t = 0; for (int i = 0; i < accountList.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < accountList.get(i).getCardlist().size(); j++) { if (card.equals(accountList.get(i).getCardlist().get(j))) { t = i; break; } } } accountList.get(t).setBalance(accountList.get(t).getBalance() - money); } } class Show { ArrayList<Account> accountList; String card; String password; String number; double money; public Show(ArrayList<Account> accountList, String card, String password, String number, double money) { this.password = password; this.number = number; this.card = card; this.accountList = accountList; this.money = money; } public void show1() { int i, j; int t = 0; for (i = 0; i < accountList.size(); i++) { for (j = 0; j < accountList.get(i).getCardlist().size(); j++) { if (card.equals(accountList.get(i).getCardlist().get(j))) { t = i; break; } } } if (money >= 0) {//取款 System.out.printf(accountList.get(t).getName() + "在" + accountList.get(t).bank.bankname + "的" + number + "号ATM机上取款¥%.2f\n", money); } else { money = -money; System.out.printf(accountList.get(t).getName() + "在" + accountList.get(t).bank.bankname + "的" + number + "号ATM机上存款¥%.2f\n", money); } System.out.printf("当前余额为¥%.2f\n", accountList.get(t).getBalance()); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //对账户和ATM机进行初始化 //ATM机 ArrayList<String> ATMList1 = new ArrayList<>(); ATMList1.add("01"); ATMList1.add("02"); ATMList1.add("03"); ATMList1.add("04"); Bank jsyh = new Bank("中国建设银行", ATMList1); ArrayList<String> ATMList2 = new ArrayList<>(); ATMList2.add("05"); ATMList2.add("06"); Bank gsyh = new Bank("中国工商银行", ATMList2); //银行 ArrayList<Bank> bankList = new ArrayList<>(); bankList.add(jsyh); bankList.add(gsyh); //用户账户 ArrayList<String> cardList1 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList1.add("6217000010041315709"); cardList1.add("6217000010041315715"); Account account1 = new Account("杨过", "3217000010041315709", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, jsyh, cardList1); ArrayList<String> cardList2 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList2.add("6217000010041315718"); Account account2 = new Account("杨过", "3217000010041315715", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, jsyh, cardList2); ArrayList<String> cardList3 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList3.add("6217000010051320007"); Account account3 = new Account("郭靖", "3217000010051320007", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, jsyh, cardList3); ArrayList<String> cardList4 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList4.add("6222081502001312389"); Account account4 = new Account("张无忌", "3222081502001312389", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, gsyh, cardList4); ArrayList<String> cardList5 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList5.add("6222081502001312390"); Account account5 = new Account("张无忌", "3222081502001312390", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, gsyh, cardList5); ArrayList<String> cardList6 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList6.add("6222081502001312399"); cardList6.add("6222081502001312400"); Account account6 = new Account("张无忌", "3222081502001312399", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, gsyh, cardList6); ArrayList<String> cardList7 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList7.add("6222081502051320785"); Account account7 = new Account("韦小宝", "3222081502051320785", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, gsyh, cardList7); ArrayList<String> cardList8 = new ArrayList<>(); cardList8.add("6222081502051320786"); Account account8 = new Account("韦小宝", "3222081502051320786", "88888888", 10000.00, bankList, gsyh, cardList8); //用户总数组 ArrayList<Account> accountList = new ArrayList<>(); accountList.add(account1); accountList.add(account2); accountList.add(account3); accountList.add(account4); accountList.add(account5); accountList.add(account6); accountList.add(account7); accountList.add(account8); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String s = sc.nextLine(); while (!s.equals("#")) { String[] str = s.split("\\s+"); if (str.length == 1) { String card = str[0]; boolean flag = false; int tmp = 0; for (int i = 0; i < accountList.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < accountList.get(i).getCardlist().size(); j++) { if (card.equals(accountList.get(i).getCardlist().get(j))) { flag = true; System.out.printf("¥%.2f\n", accountList.get(i).getBalance()); break; } } if (flag) break; } if (flag == false) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); } } else { Check check = new Check(accountList, str[0], str[1], str[2], Double.parseDouble(str[3])); if (check.check1()) { Change change = new Change(accountList, str[0], str[1], str[2], Double.parseDouble(str[3])); change.changeMoney(); Show show = new Show(accountList, str[0], str[1], str[2], Double.parseDouble(str[3])); show.show1(); } } s = sc.nextLine(); } } }
代码分析
对于类的分析:
Bank 类:代表银行,包含银行名称和 ATM 列表。Account 类:代表银行账户,包含姓名、账户、密码、余额、银行列表、银行和银行卡列表。
Check 类:检查用户输入的卡号、密码、ATM 编号以及金额是否符合要求。
Change 类:根据用户输入的信息更改账户余额。
Show 类:显示用户的操作信息和当前余额。
Main 类:主类,用于运行程序,完成初始化并接收用户输入。
代码大致思路如下:
初始化银行、ATM 机、银行账户信息。
使用 Scanner 类接收用户输入的信息。
根据用户输入的信息进行检查(使用 Check 类)。
如果检查通过,则进行相应的操作(存款或取款),更改账户余额(使用 Change 类)。
显示操作信息和当前余额(使用 Show 类)。
重复上述步骤,直到用户输入“#”。

代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Iterator; public class Main { public static void main(String []args) { Card bankList=new Card(); bankList.list.add(new Banks("中国建设银行")); bankList.list.add(new Banks("中国工商银行")); bankList.list.add(new Banks("中国农业银行")); User user1=new User("杨过","88888888",10000.00); user1.setAccount("借记"); User user2=new User("郭靖","88888888",10000.00); user2.setAccount("借记"); User user3=new User("张无忌","88888888",10000.00); user3.setAccount("借记"); User user4=new User("韦小宝","88888888",10000.00); user4.setAccount("借记"); User user5=new User("张三丰","88888888",10000.00); user5.setAccount("贷记"); User user6=new User("令狐冲","88888888",10000.00); user6.setAccount("贷记"); User user7=new User("乔峰","88888888",10000.00); user7.setAccount("贷记"); User user8=new User("洪七公","88888888",10000.00); user8.setAccount("贷记"); user1.addAccount(new Account("6217000010041315709",user1)); user1.addAccount(new Account("6217000010041315715",user1)); user1.addAccount(new Account("6217000010041315718",user1)); user2.addAccount(new Account("6217000010051320007",user2)); user3.addAccount(new Account("6222081502001312389",user3)); user3.addAccount(new Account("6222081502001312390",user3)); user3.addAccount(new Account("6222081502001312399",user3)); user3.addAccount(new Account("6222081502001312400",user3)); user4.addAccount(new Account("6222081502051320785",user4)); user4.addAccount(new Account("6222081502051320786",user4)); user5.addAccount(new Account("6640000010045442002",user5)); user5.addAccount(new Account("6640000010045442003",user5)); user6.addAccount(new Account("6640000010045441009",user6)); user7.addAccount(new Account("6630000010033431001",user7)); user8.addAccount(new Account("6630000010033431008",user8)); bankList.getBank("中国建设银行").addPerson(user1); bankList.getBank("中国建设银行").addPerson(user2); bankList.getBank("中国工商银行").addPerson(user3); bankList.getBank("中国工商银行").addPerson(user4); bankList.getBank("中国建设银行").addPerson(user5); bankList.getBank("中国工商银行").addPerson(user6); bankList.getBank("中国农业银行").addPerson(user7); bankList.getBank("中国农业银行").addPerson(user8); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); String str; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while(true) { str = in.nextLine(); if(str.equals("#") == true) { break; } sb.append(str + "\n"); } String strNew = sb.toString(); String strs[] = strNew.split("\n"); for(int i = 0;i<strs.length;i++) { String array[] = strs[i].split("\\s+"); if(array.length==1) { //只输入了一串银行账号 if(bankList.check(array[0])!=null){ System.out.println("业务:查询余额 "+bankList.check(array[0]).People.getmoney()); } else { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist.");//一旦检测到输入有误,则程序立即停止运行,之前正确的输入则给予相应的输出 System.exit(0); } } else { if(array.length==4) { if(bankList.check(array[0])==null) {//银行账户的检测 System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); System.exit(0); } else { Account one=bankList.check(array[0]); if(!array[1].equals(one.People.password)) {//密码始终为88888888 System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); System.exit(0); } else { if(!bankList.idex(array[2])) {//检测ATM编号 System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); System.exit(0); } else { Banks target=bankList.bkforID(array[2]); double loan=Double.parseDouble(array[3]); if(!one.action(target, loan)) {//取款额超过了余额 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); System.exit(0); }else {//如果全部没有问题,则继续输出 one.outPut(loan,target,array[2]); } } } } } } } } } class Card { ArrayList<Banks> list=new ArrayList<>(); public Card() { } public void addbank(Banks one) { list.add(one); } public Banks getBank(String name) { for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { if(list.get(i).name.equals(name)) { return list.get(i); } } return null; } public Account check(String id) { for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { Banks one=list.get(i); if(one.check(id)!=null) { return one.check(id); } } return null; } public boolean idex(String id) { for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { if(list.get(i).idexist(id)) { return true; } } return false; } public Banks bkforID(String id) { for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { if(list.get(i).idexist(id)) { return list.get(i); } } return null; } } class Account{ String id; User People; public Account(String id,User symbolUser) { this.id=id; this.People=symbolUser; } public void addmoney(double money) { People.addmoney(money); } public void getMoney(double money) { People.getMoney(money); } public void outPut(double partMoney,Banks bankfor,String id) { if(partMoney>0) { System.out.println("业务:取款 "+People.name+"在"+bankfor.name+"的"+id+"号ATM机上取款¥"+String.format("%.2f",partMoney)); System.out.println("当前余额为"+People.getmoney()); } } public boolean action(Banks bankfor,double partMoney) { if(bankfor.name.equals(People.mybank.name)) { //非跨行 if(People.kind.equals("借记")) { if(People.money-partMoney<0) { return false; }else { getMoney(partMoney); return true; } } else { double out; if(People.money>0) { out=People.money-partMoney; }else { out=partMoney*(-1); } if(out<0) { double after=People.money-partMoney-out*(-1)*0.05; if(after+50000<0) { return false; }else { getMoney(partMoney+out*(-1)*0.05); return true; } }else { getMoney(partMoney); return true; } } } else { //跨行 double more=partMoney*bankfor.Crossratio; if(People.kind.equals("借记")) { if(People.money-partMoney-more<0) { return false; }else { getMoney(partMoney+more); return true; } } else { double out; if(People.money>0) { out=People.money-partMoney; } else { out=partMoney*(-1); } if(out<0) { double after=People.money-partMoney-out*(-1)*0.05; if(after+50000+more<0) { return false; } else { getMoney(partMoney+out*(-1)*0.05+more); return true; } } else { getMoney(partMoney+more); return true; } } } } } class User { Banks mybank; String name; String id; String password; String kind; double money; ArrayList<Account> accounts=new ArrayList<>(); public User(String name,String password,double money) { this.name=name; this.password=password; this.money=money; } public void setbank(Banks mybank) { this.mybank=mybank; } public void addmoney(double money) { this.money=this.money+money*(-1); } public void getMoney(double money) { this.money=this.money-money; } public void addAccount(Account one) { accounts.add(one); } public String getmoney() { return "¥"+String.format("%.2f", money); } public Account check(String id) { for(int i=0;i<accounts.size();i++) { if(accounts.get(i).id.equals(id)) { return accounts.get(i); } } return null; } public void setAccount(String kind) { this.kind=kind; } } class Banks { ArrayList<User> list=new ArrayList<>(); String name; double Crossratio; ArrayList<String> numbers=new ArrayList<>(); public Banks(String name) { this.name=name; if(name.equals("中国建设银行")) { numbers.add("01"); numbers.add("02"); numbers.add("03"); numbers.add("04"); Crossratio=0.02;//手续费 } if(name.equals("中国工商银行")) { numbers.add("05"); numbers.add("06"); Crossratio=0.03;//手续费 } if(name.equals("中国农业银行")) { numbers.add("07"); numbers.add("08"); numbers.add("09"); numbers.add("10"); numbers.add("11"); Crossratio=0.04;//手续费 } } public void addPerson(User one) { list.add(one); one.setbank(this); } public Account check(String id) { for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { User one=list.get(i); if(one.check(id)!=null) { return one.check(id); } } return null; } public boolean idexist(String number) { for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();i++) { if(numbers.get(i).equals(number)) { return true; } } return false; } } class Bank { private String bankNO; private String bankName; private ArrayList<Account> accountList = new ArrayList<Account>(); public Bank() { super(); } public Bank(String bankNO, String bankName) { super(); this.bankNO = bankNO; this.bankName = bankName; } public String getBankNO() { return bankNO; } public void setBankNO(String bankNO) { this.bankNO = bankNO; } public String getBankName() { return bankName; } public void setBankName(String bankName) { this.bankName = bankName; } public void addAccount(Account account) { this.accountList.add(account); } public void removeAccount(Account account) { this.accountList.remove(account); } public ArrayList<Account> getAccountList() { return accountList; } public void setAccountList(ArrayList<Account> accountList) { this.accountList = accountList; } } class ATM { private String ATMID; private Bank bank = null; public ATM() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public ATM(String aTMID, Bank bank) { super(); ATMID = aTMID; this.bank = bank; } public String getATMID() { return ATMID; } public void setATMID(String aTMID) { ATMID = aTMID; } public Bank getBank() { return bank; } public void setBank(Bank bank) { this.bank = bank; } } class Withdraw { private ChinaUnionPay unionPay; private String cardNO; private String cardPassword; private String ATMID; private double amount; public Withdraw() { super(); } public Withdraw(ChinaUnionPay unionPay, String cardNO, String cardPassword, String aTMID, double amount) { super(); this.unionPay = unionPay; this.cardNO = cardNO; this.cardPassword = cardPassword; ATMID = aTMID; this.amount = amount; } public Withdraw(String cardNO, String cardPassword, String aTMID, double amount) { super(); this.cardNO = cardNO; this.cardPassword = cardPassword; ATMID = aTMID; this.amount = amount; } public void withdraw() { //校验该卡是否存在 Card card = ValidateData.getCardbyCardNO(unionPay, cardNO); if(card == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); System.exit(0); } //校验ATM是否存在 ATM aTM = ValidateData.getATMbyATMID(unionPay, ATMID); if(aTM == null) { System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); System.exit(0); } } public void showResult(Account account,int flag) { String type = ""; if(flag == 1) { type = "取款"; }else { type = "存款"; amount *= -1; } } } class ChinaUnionPay { private ArrayList<Bank> bankList = new ArrayList<Bank>(); public ChinaUnionPay() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public ChinaUnionPay(ArrayList<Bank> bankList) { super(); this.bankList = bankList; } public ArrayList<Bank> getBankList() { return bankList; } public void setBankList(ArrayList<Bank> bankList) { this.bankList = bankList; } public void addBank(Bank bank) { this.bankList.add(bank); } public void removeBank(Bank bank) { this.bankList.remove(bank); } } class ValidateData { //校验卡号是否存在 public static Card getCardbyCardNO(ChinaUnionPay unionPay,String cardNO) { Card card = null; Iterator<Bank> bankItr = unionPay.getBankList().iterator(); while(bankItr.hasNext()) { ArrayList<Account> accountList = bankItr.next().getAccountList(); Iterator<Account> accountItr = accountList.iterator(); } return null; } //校验ATM ID是否存在 public static ATM getATMbyATMID(ChinaUnionPay unionPay,String ATMID) { Iterator<Bank> bankItr = unionPay.getBankList().iterator(); Bank bank = null; ATM aTM = null; while(bankItr.hasNext()) { bank = bankItr.next(); } return null; } }
代码分析
本题主要分析以上题没有的类
Withdraw类:表示一个提款操作,包含了银联系统、银行卡号、卡密码、ATM编号和提款金额等属性。这个类提供了执行提款操作的方法,以及显示交易结果的方法。
ChinaUnionPay类:表示银联系统,包含了一个银行列表。这个类提供了添加和删除银行的方法。
ValidateData类:提供了一些用于数据验证的静态方法,如根据卡号获取卡信息和根据ATM编号获取ATM信息等。
重点对跨行借记和信用卡进行说明
对于跨行借记的实现主要是在Banks类中的Crossratio属性来进行的。这里的Crossratio表示不同银行之间进行转账时所收取的手续费比率。从Banks类的构造方法中看到,不同银行的跨行手续费比率是不同的。
在以下代码我们可以看到跨行手续费比率的设置:
public Banks(String name) {
this.name=name;
if(name.equals("中国建设银行")) {
numbers.add("01");
numbers.add("02");
numbers.add("03");
numbers.add("04");
Crossratio=0.02;//手续费
}
if(name.equals("中国工商银行")) {
numbers.add("05");
numbers.add("06");
Crossratio=0.03;//手续费
}
if(name.equals("中国农业银行")) {
numbers.add("07");
numbers.add("08");
numbers.add("09");
numbers.add("10");
numbers.add("11");
Crossratio=0.04;//手续费
}
}
Withdraw类表示一个提款操作,虽然这个操作并未涉及信用卡。在Withdraw类中,有一个名为cardNO的属性,但这个属性仅仅表示卡号,也是我用来表达信用卡的。但是可以再对代码进行进一步的改进。
三:代码改进
OOP4 7-1菜单计价
代码关联性很差,固可以做如下改进:
将逻辑分离到各个类中:将与 Dish、Order、Table 相关的逻辑分离到各个类中,以便更好地利用面向对象的特性。例如,可以在 Order 类中添加一个方法来处理删除订单的逻辑。
优化类和方法的设计:对类和方法进行重构,使它们更加简洁和易于理解。例如,在 Table 类中,可以将折扣计算的逻辑封装到一个单独的方法中。
简化循环和条件判断:使用更简洁的循环和条件判断结构,例如使用 switch 语句替换多个 if 语句。
使用 Java 集合类:使用 Java 集合类(如 List)代替数组,以便更好地管理和操作数据。
以下是部分重构后的代码示例:
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Dish> dishes = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Order> orders = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录菜单信息
while (input.hasNext()) {
String dishName = input.next();
if (dishName.equals("table")) break;
if (dishName.equals("end")) break;
int price = input.nextInt();
dishes.add(new Dish(dishName, price));
}
// 处理订单信息
while (input.hasNext()) {
// ...
}
}
}
class Dish {
private String dishName;
private int price;
public Dish(String dishName, int price) {
this.dishName = dishName;
this.price = price;
}
public String getDishName() {
return dishName;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isDish(String theName) {
return theName.equals(dishName);
}
}
class Order {
// ...
}
class Table {
// ...
}(同上)
OOP6 7-5
对于银行卡的概念可以更精细一点,为了引入信用卡的概念,我们可以创建一个新的类,如CreditCard类,并在该类中添加信用卡相关的属性和方法,例如信用额度、透支额度等。同时,我们也需要在User类中添加一个新的属性来保存用户的信用卡信息,并在Withdraw类中修改提款操作的逻辑,以便支持信用卡提款。
四:一些感想
学无止境,JAVA的知识可能我一生都学不完的,想要提高自己,我也可以从这几个方面来入手:
学习基础知识:学习变量、数据类型、运算符、控制结构(如条件语句、循环语句等)、函数/方法、数组等基本概念。
面向对象编程(OOP):尝试用面向对象的思维方式来解决问题。
练习编码:可以从一些简单的编程任务开始,例如计算阶乘、斐波那契数列等。随着技能的提高,可以尝试解决更复杂的问题。
阅读和理解代码:在网上寻找开源项目或代码示例,试着理解它们的工作原理,并尝试修改或扩展它们。
学习Java标准库:Java有丰富的标准库,提供了许多有用的功能。熟悉这些库可以提高编程效率。例如,学习java.util包中的集合框架(如ArrayList、HashSet、HashMap等)和java.io包中的文件和流操作。
阅读文档和书籍:Java有大量的文档和书籍可供学习。阅读官方文档(如Java API文档)、教程和书籍,以便更深入地了解Java的特性和最佳实践。
希望自己能一直走在提升自己的道路上!