Java - 17 this关键字
Java - 17 this关键字
哪个对象调用,this就代表哪个对象,this存储代表对象的地址,指向代表对象
public class This01{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog dog1 = new Dog("A", 2);
System.out.println(dog1.hashcode());
}
}
class Dog{
String name;
int age;
public Dog(String name, int age){
this.name = name; // 没有this的变量就近原则,有this的一定是属性
this.age = age;
}
public void info(){
System.out.println(this.hashcode());
}
}
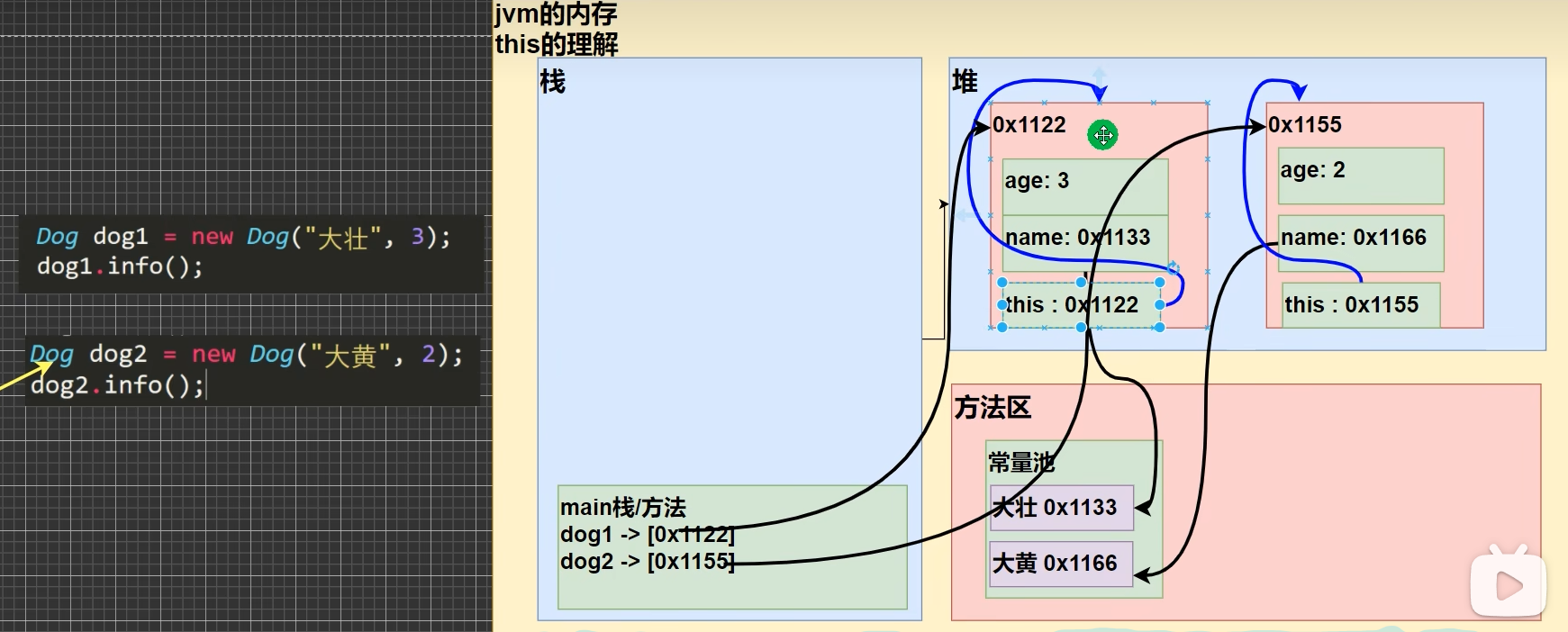
细节
- this可以访问本类的属性,方法,构造器
/* this访问本类的方法 */
class T{
public void f1(){
System.out.println("f1被调用");
}
public void f2(){
System.out.println("f2被调用");
// 法1
f1();
// 法2
this.f1();
}
}
/* this访问本类的构造器(只能在构造器中使用;必须放在第一条语句) */
class T{
public T{
this("wu", 22); // 形参要匹配上
System.out.println("T()构造器");
}
public T(String name, int age){
System.out.println("T(String name, int age)构造器");
}
}
-
this用于区分当前类的属性和局部变量
-
this不能在类定义的外部使用,只能在类定义的方法中使用
比较对象
public class CompareTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p1 = new Person("dabao", 2);
Person p2 = new Person("daba", 2);
System.out.println(p1.compareTo(p2));
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean compareTo(Person cp){
return this.name.equals(cp.name) && this.age == cp.age;
}
}
练习
练习1
先完成正常业务再考虑代码健壮性
/* 返回数组的最大值 */
public class Max{
public static void main(String[] args){
double[] arr = null;
Tool t = new Tool();
Double res = t.max(arr);
if(res!=null){
System.out.println(res);
}else {
System.out.println("没有最大值");
}
}
}
class Tool{
// 包装类:解决需要返回null和double的问题
public Double max(double[] arr){
if(arr != null && arr.length>0){ // 如果arr不存在,arr(null).length就会报错,所以添加if的条件1
double max = arr[0]; // 如果arr里没有元素,就会报错,所以添加if的条件2
for(int i = 0; i<arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i]>max)
max = arr[i];
}
return max;
}else{
return null;
}
}
}
反思:
- 要使用
.length就要考虑数组是否是null - 要取数组中的元素,要考虑下标是否一定合法
练习2
public class Test{
int count = 9;
public void count1(){
count = 10;
System.out.println(count);
}
public void count2(){
System.out.println(count++);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
/* 匿名对象,只能使用一次后被销毁 */
new Test().count1; // 10
Test t = new Test();
t.count2(); // 9
t.count2(); // 10
}
}