OOP PTA题目集4-6总结性BLOG
一、前言
题目集总结:
题目集4: 一共7道编程题,题量适中难度也适中(除了第1题,题目描述过于繁琐复杂以至于无从下手),考察的内容从基础语法和基础算法的运用到部分高级容器的使用(set等)和Java中部分库类的使用(LocalDate等)再到类的设计以及类的封装性的运用,由浅入深,循序渐进。
题目集5: 一共6道编程题,题量依然不是很多,难度不算大,这次考察的内容较为单一,一个是正则表达式的运用,另一个则是类的设计中聚合关系的运用,让我们见识到了同一个题目,同一批类,却有不同的设计理念使得类之间的组合关系并不相同。
题目集6: 仅仅只有1道编程题,但难度却是直线上升,与前面的题目完全不在一个量级,其考察的是复杂类的设计,“题目如此多娇,引无数英雄竞折腰”,这道题的描述加要求的字数就已经达到了2600+,这致使很多同学望而却步。
题目集感悟:
1) 通过这些编程题的练习,我深刻地认识到编程能力的提高需要不断地练习和学习。从基础语法和算法的应用到高级容器和Java库类的使用,再到类的设计和封装性的运用,这些题目涵盖了编程的多个方面,每个练习都让我从中学到了新的知识和技能。
在练习过程中,我也意识到了编程中的一些重要概念,如封装、聚合关系等。对于类的设计和封装性的运用,我也开始慢慢理解和掌握。同时,我也发现了自己在某些方面的不足和需要进一步提高的地方,比如对于复杂类的设计,我需要更加深入地了解和掌握相关知识。
除了学习和练习,我还需要不断地思考和总结,将所学所练习到的知识和技能整合起来,形成自己的思维模型和编程风格。通过不断地思考和总结,我相信我的编程能力将会得到进一步的提高。
2) 通过这次3个题目集,我终于能够理解老师所说的培养我们的坚韧不拔的品质是什么意思了,题目集6中唯一的1道编程题是题目集4中第1题迭代了2个版本之后的产品,然而我对于题目集4的第1题无从下手,却在题目集6中侥幸得到了96分,事实证明,审题时切忌浮躁,正因如此我才能把题目所给的有价值的信息全部Get到。
3) 不过还是得吐槽一下,题目难度梯度跨度太大,许多同学包括我在内都不是很适应,如果是从难度1一直做到现在的难度5或许同学们的成绩也就不会这么难看了吧。
二、设计和分析
OOP训练集04
7-1 菜单计价程序-3
题目:
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:3
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\
Dish d;//菜品\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“** does not exist”,**是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 12/2/3
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 38
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 17/0/0
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 22
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 16/59/59
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1 out of opening hours
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/5 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
5 delete
7 delete
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
7 delete
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
delete error;
table 2:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
table 1 out of opening hours
table 2: 63
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/3 19/5/12
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
1 4 麻婆豆腐 1 1
7 delete
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
table 2:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
4 table 2 pay for table 1 12
delete error;
table 1: 63
table 2: 75
解释和心得:
心得:
第一次见到这道题的时候我和大多数人的想法一样,题目太长,要求太多,设计太复杂,以至于望而却步,不想写,觉得自己写不出来,再看看其他同学,基本和我的情况一致,也就让我放心地放弃这道题,可是当我写完后面那道第5代的题目再回头看看这道题时,内心既佩服之前被懒惰和困难打败的自己又佩服后来坚韧不拔和迎难而上的自己。介于这道题我并没有写,但又写了它的迭代版本,所以我将在后面的第5代版本的题解中再详细介绍做法与思路。
OOP训练集05
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
题目:
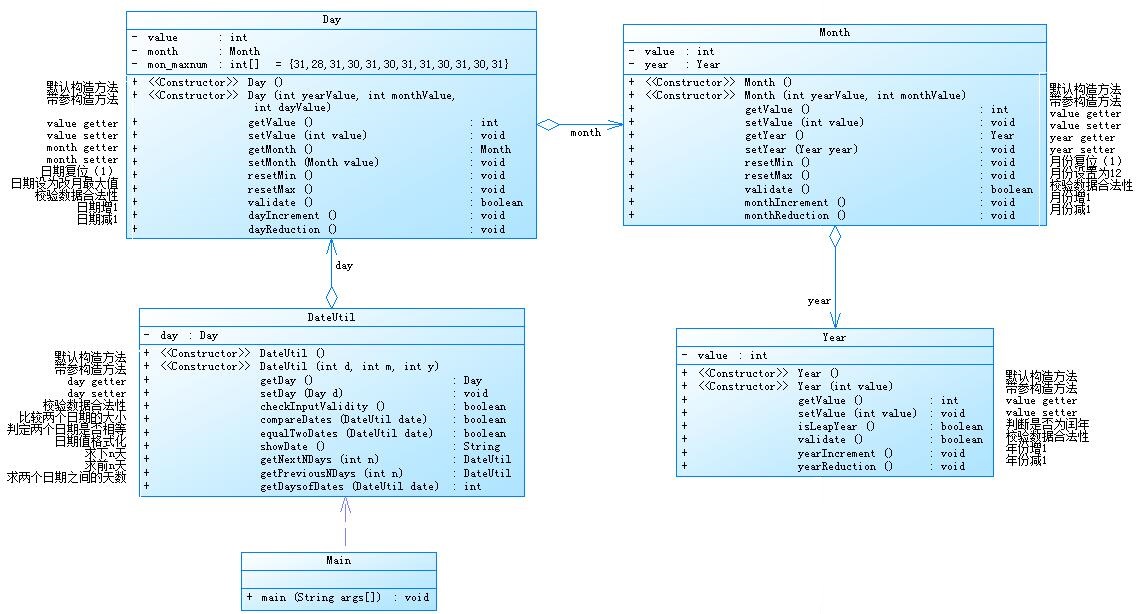
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
1.求下n天
2.求前n天
3.求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format
- 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
- 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day
- 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(day, month, year);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherDay, anotherMonth, anotherYear);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Year {
private int value;
//默认构造函数
Year() {
}
//有参构造函数
Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//获取value值的方法
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
//设置value值的方法
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//判断该年份是否为闰年
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if(value % 400 == 0 || (value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0)) return true;
return false;
}
//判断该年份是否在合法范围内
public boolean validate() {
return value >= 1900 && value <= 2050;
}
//年份增加1
public void yearIncrement() {
value = value + 1;
}
//年份减少1
public void yearReduction() {
value = value - 1;
}
}
class Month {
private int value;
private Year year;
Month() {
}
Month(int yearValue, int monthValue) {
value = monthValue;
year = new Year(yearValue);
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {
return value >= 1 && value <= 12;
}
void monthIncrement() {
if(value == 12) {
value = 1;
year.yearIncrement();
} else value += 1;
}
void monthReduction() {
if(value == 1) {
value = 12;
year.yearReduction();
}
else value -= 1;
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
private int[] mon_maxnum = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
Day() {
}
Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) {
value = dayValue;
month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear() && month.getValue() == 2) value = 29;
else value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear() && month.getValue() == 2) {
return value <= 29 && value >= 1;
} else {
if(month.validate()) return value <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()] && value >= 1;
else return false;
}
}
public void dayIncrement() {
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear() && month.getValue() == 2) {
if(value == 28) value = 29;
else if(value == 29) {
value = 1;
month.monthIncrement();
} else value += 1;
} else if(value == mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) {
value = 1;
month.monthIncrement();
} else value += 1;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value -= 1;
if(value < 1) {
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear() && month.getValue() == 3) {
value = 29;
month.setValue(2);
} else {
month.monthReduction();
value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()];
}
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private Day day;
DateUtil() {
}
DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) {
day = new Day(y,m,d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
return this.day.validate() && this.day.getMonth().validate() && this.day.getMonth().getYear().validate();
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true;
else if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() < date.day.getMonth().getValue()) return true;
else if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue()) {
if(this.day.getValue() < date.day.getValue()) return true;
}
} return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
return this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() &&
this.day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() &&
this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue();
}
public String showDate() {
return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + day.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + day.getValue();
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.day.dayIncrement();
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.day.dayReduction();
}
return this;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return 0;
else {
int n = 0;
if(this.compareDates(date)) {
while (true) {
this.getNextNDays(1);
n ++;
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return n;
}
} else {
while (true) {
this.getPreviousNDays(1);
n ++;
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return n;
}
}
}
}
}
代码质量的分析报告:
1.可读性
这段代码相对来说可读性较好。变量名清晰易懂,函数名也比较符合命名规范。代码结构清晰,缩进合理。但是,在类内部的函数定义中,函数之间缺少空行,不利于代码阅读。代码注释较少,对函数和算法的解释不够详细,需要进一步完善。
2.可维护性
这段代码的可维护性比较好,因为代码结构清晰,变量和函数命名规范。但是,由于函数之间没有空行,代码阅读会有些困难,需要加上空行。另外,代码中存在重复的部分,如输入格式检查部分的代码,可以抽象成一个函数或一个工具类来实现。
3.可测试性
这段代码的可测试性较好,因为它的主要逻辑是基于一些简单的计算和条件判断,这些逻辑都比较容易进行测试。另外,代码中的函数较小,可以单独测试。
4.性能
这段代码的性能一般,因为它没有明显的性能问题,但是它没有对性能进行优化。对于一个简单的日期计算程序来说,性能要求不高,所以这段代码的性能可以接受。
5.可靠性
这段代码的可靠性一般,因为它的输入检查部分有些简单,无法覆盖所有异常情况。在输入不合法的情况下,程序的异常处理部分也不够完善。这些问题可能导致程序出现异常行为,需要进一步完善。
6.安全性
这段代码的安全性一般。它没有直接处理敏感数据,因此不会涉及到安全问题。但是,输入检查不够严格,可能会存在一些潜在的安全问题,需要进一步改进。
7.可扩展性
这段代码的可扩展性较好。它的基本结构比较清晰,函数也比较独立,因此可以比较容易地对其进行扩展。例如,可以增加一个新的日期计算功能,或者修改日期计算逻辑。但是,在代码的结构设计上,需要进一步优化,提高代码的灵活性。
类图:

解释和心得:
代码解释:
包含三个类:Year、Month和Day,以及一个辅助类DateUtil。这些类共同定义了日期对象,可以对日期对象进行一些基本操作,如验证日期是否合法、比较日期、增加/减少日期等。
Year类表示年份,包含一个私有变量value,表示年份的值。类中定义了默认构造函数和一个带参构造函数,分别对value变量进行了初始化。getValue和setValue方法分别用于获取和设置value的值。isLeapYear方法用于判断该年份是否为闰年,如果是闰年则返回true,否则返回false。validate方法用于判断该年份是否在合法范围内(1900年至2050年之间),如果是则返回true,否则返回false。yearIncrement和yearReduction方法分别用于将年份加1和减1。
Month类表示月份,包含两个私有变量value和year,分别表示月份的值和所属的年份。类中定义了默认构造函数和一个带参构造函数,分别对value和year变量进行了初始化。setValue和getValue方法分别用于获取和设置value的值。getYear和setYear方法分别用于获取和设置year的值。resetMin和resetMax方法分别将value的值重置为1和12。validate方法用于判断该月份是否合法(即在1至12之间),如果是则返回true,否则返回false。monthIncrement和monthReduction方法分别用于将月份加1和减1,当value等于12时需要将年份增加1,当value等于1时需要将年份减少1。
Day类表示日期,包含三个私有变量value、month和mon_maxnum,分别表示日期的值、所属的月份和每个月的最大天数。类中定义了默认构造函数和一个带参构造函数,分别对value和month变量进行了初始化。getValue和setValue方法分别用于获取和设置value的值。getMonth和setMonth方法分别用于获取和设置month的值。resetMin和resetMax方法分别将value的值重置为1和每个月的最大天数,如果该月份是闰年的2月,则最大天数为29。validate方法用于判断该日期是否合法,首先需要判断该月份是否合法,如果不合法则直接返回false;如果该月份是闰年的2月,则需要特殊判断该日期是否合法;否则根据该月份的最大天数进行判断。dayIncrement和dayReduction方法分别用于将日期加1和减1,当value等于每个月的最大天数时需要将月份加1,当value等于1时需要将月份减1,如果该月份是闰年的2月,则需要特殊处理。
DateUtil类是整个日期工具类的管理类,主要用于进行日期操作,包括日期初始化、日期比较、日期合法性校验等操作。其中checkInputValidity方法用于检查日期的合法性,compareDates方法用于比较两个日期的大小,equalTwoDates方法用于判断两个日期是否相等。这些方法都是基于Year、Month和Day类提供的方法进行实现的。
心得:
这个题目并没有涉及很高深的算法实现,只是根据老师给的类图完成类的设计,难度不大。
通过这个类图的设计,可以看出良好的面向对象设计理念,将不同的功能分别封装在不同的类中,并通过类之间的相互调用实现了整个日期操作的功能。同时,类中的属性和方法都进行了合理的封装,使得整个程序更加安全和易于维护。
在实际的开发过程中,我们可以根据这个类图的设计思路,借鉴其中的一些设计思想,从而提高程序的可扩展性和可维护性。例如,在开发一个日期操作模块时,可以参考这个类图中的设计思路,将日期的各个部分封装在不同的类中,并提供相应的属性和方法进行操作,同时通过一个管理类进行统一的调用。这样可以有效地避免代码重复和混乱,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
OOP训练集05
7-6 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
题目:
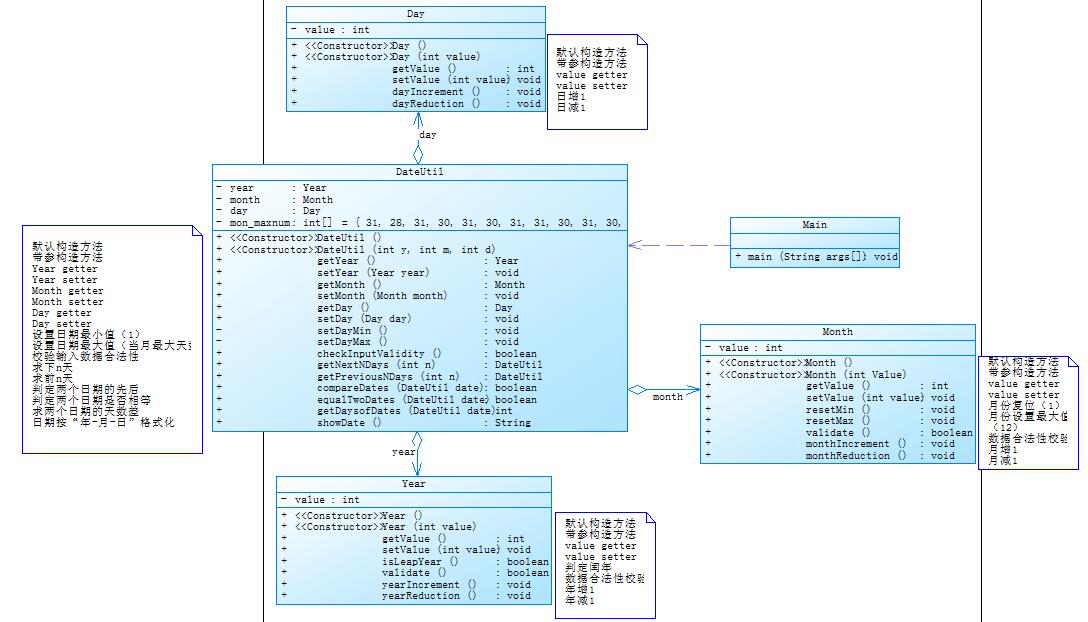
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
1.求下n天
2.求前n天
3.求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format
- 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2
- 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2
- 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Year {
private int value;
//默认构造函数
Year() {
}
//有参构造函数
Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//获取value值的方法
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
//设置value值的方法
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//判断该年份是否为闰年
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if(value % 400 == 0 || (value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0)) return true;
return false;
}
//判断该年份是否在合法范围内
public boolean validate() {
return value >= 1820 && value <= 2020;
}
//年份增加1
public void yearIncrement() {
value += 1;
}
//年份减少1
public void yearReduction() {
value -= 1;
}
}
class Month {
private int value;
Month() {
}
Month(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {
return value >= 1 && value <= 12;
}
void monthIncrement() {
value += 1;
}
void monthReduction() {
value -= 1;
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
Day() {
}
Day( int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value += 1;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value -= 1;
}
}
class DateUtil {
private Year year = new Year();
private Month month = new Month();
private Day day = new Day();
private int[] mon_maxnum = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
DateUtil() {
}
DateUtil(int y, int m, int d) {
year.setValue(y);
month.setValue(m);
day.setValue(d);
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setDayMin() {
day.setValue(1);
}
public void setDayMax() {
day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]);
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
boolean validateDay;
if(year.isLeapYear() && month.getValue() == 2) validateDay = day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= 29;
else validateDay = day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()];
return validateDay && year.validate() && month.validate();
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) return true;
else if(this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue()) {
if(this.month.getValue() < date.month.getValue()) return true;
else if(this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue()) {
return this.day.getValue() < date.day.getValue();
}
} return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
return this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue() &&
this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue() &&
this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue();
}
public String showDate() {
return year.getValue() + "-" + month.getValue() + "-" + day.getValue();
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
else mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
if(day.getValue() + 1 > mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) {
day.setValue(1);
if(month.getValue() + 1 > 12) {
month.resetMin();
year.yearIncrement();
} else month.monthIncrement();
} else day.dayIncrement();
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
else mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
if(day.getValue() - 1 == 0) {
if(month.getValue() - 1 == 0) {
month.resetMax();
year.yearReduction();
day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]);
} else {
month.monthReduction();
day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]);
}
} else day.dayReduction();
}
return this;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return 0;
else {
int n = 0;
if(this.compareDates(date)) {
while (true) {
this.getNextNDays(1);
n ++;
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return n;
}
} else {
while (true) {
this.getPreviousNDays(1);
n ++;
if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) return n;
}
}
}
}
}
代码质量的分析报告:
1.可读性
代码结构清晰,类和方法命名符合命名规范,注释也比较详细,容易理解代码的功能和作用。但是,有一些命名不够具有描述性,例如 Month 和 Day 类中的 setValue 和 getValue 方法,可以考虑修改为 setMonth 和 getMonth 等。
2.可维护性
代码的可维护性良好,因为代码结构清晰,命名规范,注释详细,易于理解和修改。每个类都有默认构造函数和有参构造函数,使得可以方便地创建对象,修改属性值。代码中还使用了常量,如月份天数,增加了代码的可读性,也方便修改。
3.可测试性
代码的可测试性良好。每个类都只包含单一的职责,各方法之间耦合度较低,易于编写单元测试和集成测试。此外,代码中包含了一些判断是否合法、是否闰年等方法,这些方法可以方便地单独测试。
4.性能
这段代码的性能问题不大。因为代码中没有使用到复杂的算法,所以时间复杂度较低,不会对系统性能产生显著的影响。但是 getNextNDays 和 getPreviousNDays 方法中使用了 for 循环,如果 n 很大,可能会造成时间和空间的浪费。
5.可靠性
代码中没有明显的逻辑错误或编译错误,所以代码的可靠性较高。但是,由于没有做足够的异常处理,例如当输入的日期不合法时,会引发异常,需要加入异常处理机制。
6.安全性
从代码本身来看,没有明显的安全问题。但是,如果代码涉及到网络或文件等操作,需要考虑安全性问题,避免信息泄漏等风险。
7.可扩展性
代码中的 Year、Month 和 Day 类具有较好的可扩展性,可以添加新的方法和属性,方便扩展新的功能。但是,DateUtil 类依赖于这三个类,如果需要扩展 DateUtil 的功能,需要先对这三个类进行修改,可能会影响到其他模块的使用。因此,可以考虑使用接口来降低耦合度,提高代码的可扩展性。
类图:

解释和心得:
代码解释:
首先定义了一个Year类,包括一个私有变量value和构造函数,value表示年份,构造函数有默认构造函数和有参构造函数,提供了获取和设置value值的方法,判断是否为闰年的方法,判断年份是否在合法范围内的方法,以及年份增减的方法。
其次定义了一个Month类,包括一个私有变量value和构造函数,value表示月份,构造函数有默认构造函数和有参构造函数,提供了获取和设置value值的方法,判断月份是否在合法范围内的方法,以及月份增减的方法。
然后定义了一个Day类,包括一个私有变量value和构造函数,value表示日期,构造函数有默认构造函数和有参构造函数,提供了获取和设置value值的方法,以及日期增减的方法。
最后定义了一个DateUtil类,包括Year、Month和Day类的对象,提供了一些日期计算相关的方法,如获取下一个或上一个n天的日期,判断输入日期是否合法,判断两个日期的大小关系等等。
其中mon_maxnum数组表示每个月份的天数,可以通过setDayMax方法将Day的值设置为当前月份的最大值,通过setDayMin方法将Day的值设置为1。
此外,还提供了一个showDate方法,用于将日期对象以字符串的形式输出。
getNextNDays(int n):将当前日期向后推 n 天,并返回更新后的日期。具体实现是循环执行 n 次,每次判断是否需要进位(例如跨月或跨年),然后更新年月日的值。
getPreviousNDays(int n):将当前日期向前推 n 天,并返回更新后的日期。具体实现与 getNextNDays(int n) 类似,只是方向相反。
getDaysofDates(DateUtil date):计算当前日期和传入日期 date 之间相差的天数。如果两个日期相等返回 0,如果当前日期早于 date,则循环调用 getNextNDays(1) 直到两个日期相等,返回循环的次数,否则循环调用 getPreviousNDays(1) 直到两个日期相等,返回循环的次数。
这些算法实现比较简单,都是基于年月日的加减法和比较逻辑来实现的,没有使用到复杂的算法和数据结构。
心得:
这个题目并没有涉及很高深的算法实现,也只是根据老师给的类图完成类的设计,难度不大。
这些类的设计展现了一个良好的面向对象设计,将日期相关的类和方法进行了合理的分离和封装。DateUtil类作为日期工具类,封装了日期计算的方法,而Year、Month和Day类则提供了基本的日期操作方法,这样的设计使得代码更加简洁和易于维护。
此外,使用成员变量对Year、Month和Day对象进行封装,可以提高代码的封装性和可读性,同时也方便了其他类对日期的操作。而提供的基本日期操作方法也使得日期的操作变得更加简单和直观。
OOP训练集06
7-1 菜单计价程序-4
题目:
本体大部分内容与菜单计价程序-3相同,增加的部分用加粗文字进行了标注。
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的桌号从小到大的顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计(本内容与计价程序之前相同,其他类根据需要自行定义):
菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号
Dish d;//菜品\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
本次课题比菜单计价系列-3增加的异常情况:
1、菜谱信息与订单信息混合,应忽略夹在订单信息中的菜谱信息。输出:"invalid dish"
2、桌号所带时间格式合法(格式见输入格式部分说明,其中年必须是4位数字,月、日、时、分、秒可以是1位或2位数),数据非法,比如:2023/15/16 ,输出桌号+" date error"
3、同一桌菜名、份额相同的点菜记录要合并成一条进行计算,否则可能会出现四舍五入的误差。
4、重复删除,重复的删除记录输出"deduplication :"+序号。
5、代点菜时,桌号不存在,输出"Table number :"+被点菜桌号+" does not exist";本次作业不考虑两桌记录时间不匹配的情况。
6、菜谱信息中出现重复的菜品名,以最后一条记录为准。
7、如果有重复的桌号信息,如果两条信息的时间不在同一时间段,(时段的认定:周一到周五的中午或晚上是同一时段,或者周末时间间隔1小时(不含一小时整,精确到秒)以内算统一时段),此时输出结果按不同的记录分别计价。
8、重复的桌号信息如果两条信息的时间在同一时间段,此时输出结果时合并点菜记录统一计价。前提:两个的桌号信息的时间都在有效时间段以内。计算每一桌总价要先合并符合本条件的饭桌的点菜记录,统一计价输出。
9、份额超出范围(1、2、3)输出:序号+" portion out of range "+份额,份额不能超过1位,否则为非法格式,参照第13条输出。
10、份数超出范围,每桌不超过15份,超出范围输出:序号+" num out of range "+份数。份数必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
11、桌号超出范围[1,55]。输出:桌号 +" table num out of range",桌号必须为1位或多位数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
12、菜谱信息中菜价超出范围(区间(0,300)),输出:菜品名+" price out of range "+价格,菜价必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
13、时间输入有效但超出范围[2022.1.1-2023.12.31],输出:"not a valid time period"
14、一条点菜记录中若格式正确,但数据出现问题,如:菜名不存在、份额超出范围、份数超出范围,按记录中从左到右的次序优先级由高到低,输出时只提示优先级最高的那个错误。
15、每桌的点菜记录的序号必须按从小到大的顺序排列(可以不连续,也可以不从1开始),未按序排列序号的输出:"record serial number sequence error"。当前记录忽略。(代点菜信息的序号除外)
16、所有记录其它非法格式输入,统一输出"wrong format"
17、如果记录以“table”开头,对应记录的格式或者数据不符合桌号的要求,那一桌下面定义的所有信息无论正确或错误均忽略,不做处理。如果记录不是以“table”开头,比如“tab le 55 2023/3/2 12/00/00”,该条记录认为是错误记录,后面所有的信息并入上一桌一起计算。
次作业比菜单计价系列-3增加的功能:
菜单输入时增加特色菜,特色菜的输入格式:菜品名+英文空格+基础价格+"T"
例如:麻婆豆腐 9 T
菜价的计算方法:
周一至周五 7折, 周末全价。
注意: 不同的四舍五入顺序可能会造成误差,请按以下步骤累计一桌菜的菜价:
计算每条记录的菜价:将每份菜的单价按份额进行四舍五入运算后,乘以份数计算多份的价格,然后乘以折扣,再进行四舍五入,得到本条记录的最终支付价格。
最后将所有记录的菜价累加得到整桌菜的价格。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“** does not exist”,**是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的原始总价+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价
源代码:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> dishOutput = new HashMap<>();
List<Map<String, Integer>> mapList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, List<Map<String, Integer>>> tableDishOutput = new HashMap<>();
int numOutput = -1;
boolean is_equals = false;
List<List<Integer>> ordersDeletes = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录每个order的订单删除记录
List<String> outPuts = new ArrayList<>();
Menu menu = new Menu();
List<Order> orders = new ArrayList<>();
int n = -1; // 记录order的个数,一旦n != 1后,后续则不为菜谱信息
int unit_price = 0;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = scanner.nextLine();
boolean tableFlag = true; // 用来判断桌子信息是否有误
boolean menuFlag = true;
while (!input.equals("end")) {
String[] strings = input.split("\\s+");
if (strings.length == 2 && !strings[1].equals("delete") && n == -1 && menuFlag) { // 判断为普通菜
String pattern = "\\S+ \\d+";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
if(!m.matches()) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
char[] chars = input.toCharArray();
int Numblank = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i ++) {
if(chars[i] == ' ') Numblank ++;
}
if(Numblank > 1) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
char[] arr = strings[1].toCharArray();
if(!isInteger(strings[1]) || arr[0] == '0' && strings[1].length() > 1 || isInteger(strings[0])) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
unit_price = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
if(unit_price > 300 || unit_price <= 0) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(strings[0] + " price out of range " + unit_price);
}
else {
if(menu.searthDish(strings[0]) == null)
menu.addDish(strings[0], unit_price, 'C');
else menu.modDishs(strings[0], unit_price, 'C');
}
}
}
}
} else if(strings.length == 3 && n == -1 && menuFlag) { // 判断为特色菜
String pattern = "\\S+ \\d+ T";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
if(!m.matches()) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
char[] chars = input.toCharArray();
int Numblank = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i ++) {
if(chars[i] == ' ') Numblank ++;
}
if(Numblank > 2) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
char[] arr = strings[1].toCharArray();
if(!isInteger(strings[1]) || arr[0] == '0' && strings[1].length() > 1 || isInteger(strings[0])) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
unit_price = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
if(unit_price >= 300 || unit_price <= 0) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(strings[0] + " price out of range " + unit_price);
}
else {
if(menu.searthDish(strings[0]) == null) // 判断是否有重复的菜品信息
menu.addDish(strings[0], unit_price, 'T');
else menu.modDishs(strings[0], unit_price, 'T');
}
}
}
}
} else if(strings[0].equals("table")) { // 判断为桌子信息
is_equals = false;
String pattern = "table \\d{1,2} \\d{4}/\\d{1,2}/\\d{1,2} \\d{1,2}/\\d{1,2}/\\d{1,2}";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
if(!m.matches()) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
tableFlag = false;
} else {
menuFlag = false;
if(strings.length != 4) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
tableFlag = false;
}
else {
LocalDate localDate = null;
LocalTime localTime = null;
int tableNum;
char[] arr = strings[1].toCharArray();
if(arr[0] == '0') {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
tableFlag = false;
}
else {
int dateN = 0, timeN = 0;
char[] charsDate = strings[2].toCharArray();
char[] charsTime = strings[3].toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < strings[2].length(); i++) {
if(charsDate[i] == '/') dateN ++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < strings[3].length(); i++) {
if(charsTime[i] == '/') timeN ++;
}
if(timeN != 2 || dateN != 2) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
tableFlag = false;
} else {
String[] date = strings[2].split("/+");
String[] time = strings[3].split("/+");
if(!isInteger(strings[1]) || // 判断日期格式
!isInteger(date[0]) ||
!isInteger(date[1]) ||
!isInteger(date[2]) ||
!isInteger(time[0]) ||
!isInteger(time[1]) ||
!isInteger(time[2]) ||
date[0].length() != 4 ||
date[1].length() > 2 ||
date[2].length() > 2 ||
time[0].length() > 2 ||
time[1].length() > 2 ||
time[2].length() > 2) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
tableFlag = false;
}
else {
tableNum = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
if(tableNum > 55 || tableNum < 1) { // 判断桌号是否满足题意
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(tableNum + " table num out of range");
tableFlag = false;
}
else {
boolean flag = false;
try {
int year = Integer.parseInt(date[0]);
int month = Integer.parseInt(date[1]);
int day = Integer.parseInt(date[2]);
int hour = Integer.parseInt(time[0]);
int minute = Integer.parseInt(time[1]);
int second = Integer.parseInt(time[2]);
localDate = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
localTime = LocalTime.of(hour, minute, second);
flag = true;
} catch (DateTimeException e) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(strings[1] + " date error");
tableFlag = false;
}
if(flag) {
if(Order.is_LegalTime(localDate)) {
if(Order.is_OpeningTime(localDate, localTime)) {
tableFlag = true;
for (Order order : orders) {
if (order.getTableNum() == tableNum) { // 判断两次相同桌号订单是否是同一个
int hourBefore = order.getLocalTime().getHour();
int minuteBefore = order.getLocalTime().getMinute();
int hourLater = localTime.getHour();
int minuteLater = localTime.getMinute();
LocalDateTime timeBefore = LocalDateTime.of(order.getLocalDate(), order.getLocalTime());
LocalDateTime timeLater = LocalDateTime.of(localDate, localTime);
LocalDateTime timeBeforePlus = timeBefore.plusMinutes(59).plusSeconds(59);
if((order.getLocalDate().equals(localDate) &&
!(localDate.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || localDate.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY) &&
(((hourBefore >= 17 && hourBefore < 20 || (hourBefore == 20 && minuteBefore <= 30)) && (hourLater >= 17 && hourLater < 20 || (hourLater == 20 && minuteLater <= 30))) ||
((hourBefore >= 11 && hourBefore < 14 || (hourBefore == 14 && minuteBefore <= 30) || (hourBefore == 10 && minuteBefore >= 30)) && (hourLater >= 11 && hourLater < 14 || (hourLater == 14 && minuteLater <= 30) || (hourLater == 10 && minuteLater>= 30)))))
|| (order.getLocalDate().equals(localDate) &&
(localDate.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || localDate.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY) &&
(timeLater.isAfter(timeBefore) && timeLater.isBefore(timeBeforePlus)))
) {
is_equals = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!is_equals){
n ++;
Order order = new Order(menu, tableNum, localTime, localDate);
orders.add(order);
ordersDeletes.add(new ArrayList<>());
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("table " + tableNum + ": ");
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("table " + strings[1] + " out of opening hours");
tableFlag = false;
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("not a valid time period");
tableFlag = false;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
} else if(strings.length == 4 && tableFlag) {
String pattern = "\\d{1,2} \\S+ \\d \\d{1,2}";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
if(!m.matches()) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
menuFlag = false;
Record record;
Order order;
if(!isInteger(strings[2]) || !isInteger(strings[3]) || !isInteger(strings[0])) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
char[] arr = strings[3].toCharArray();
if(strings[2].length() > 1 || arr[0] == '0') {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
int num = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int portion = Integer.parseInt(strings[2]);
int copies = Integer.parseInt(strings[3]);
if(!orders.isEmpty()) {
order = orders.get(n);
int length = order.getRecords().size();
boolean flag = false, flag2 = true;
for (Dish dish : menu.getDishs()) {
if(dish.getName().equals(strings[1])) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
for (Record record1 : order.getRecords()) {
if(num <= record1.getOrderNum()) {
flag2 = false;
break;
}
}
if(length == 0 || flag2 || is_equals) {
if(flag) {
if(menu.searthDish(strings[1]).getType() == 'C' && (portion >= 1 && portion <= 3)) {
if(copies <= 15 && copies >= 1) {
record = order.addARecord(num, strings[1], portion, copies);
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(num + " " + strings[1] + " " + record.getPrice());
}
else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(num + " num out of range " + copies);
}
} else if(menu.searthDish(strings[1]).getType() == 'T' && (portion == 1 || portion == 2)) {
if(copies <= 15 && copies >= 1) {
numOutput ++;
record = order.addARecord(num, strings[1], portion, copies);
outPuts.add(num + " " + strings[1] + " " + record.getPrice());
}
else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(num + " num out of range " + copies);
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(num + " portion out of range " + portion);
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(strings[1] + " does not exist");
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("record serial number sequence error");
}
}
}
}
}
} else if(strings.length == 2 && strings[1].equals("delete") && tableFlag && n != -1) {
menuFlag = false;
Order order = orders.get(n);
int num = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int length = ordersDeletes.get(n).size();
boolean flag = false;
for (Record record : order.getRecords()) {
if(record.getOrderNum() == num) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(!ordersDeletes.get(n).contains(num)) {
if(flag) {
order.delARecordByOrderNum(num);
ordersDeletes.get(n).add(num);
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("delete error");
}
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("deduplication " + num);
}
} else if((strings.length == 2 && !strings[1].equals("delete") || strings.length == 3 && strings[2].equals("T")) && n != -1 && tableFlag) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("invalid dish");
}
else if(strings.length == 5 && isInteger(strings[3]) && isInteger(strings[1]) && tableFlag) {
if(!isInteger(strings[0])) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
else {
int num = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]);
int tableNumBefore = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
int portion = Integer.parseInt(strings[3]);
int copies = Integer.parseInt(strings[4]);
Record recordNew = new Record(num, menu.searthDish(strings[2]), portion, copies);
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < orders.size() - 1; i++) {
if(orders.get(i).getTableNum() == tableNumBefore) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add(num + " table " + orders.get(n).getTableNum() + " pay for table " + tableNumBefore + " " + recordNew.getPrice());
OthersOrder othersOrder = new OthersOrder(orders.get(n), tableNumBefore, recordNew, menu);
orders.get(n).addAOthersOrder(othersOrder);
} else {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("Table number :" + strings[0] + " does not exist");
}
}
} else if(tableFlag) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("wrong format");
}
input = scanner.nextLine();
}
for (Order order : orders) {
numOutput ++;
outPuts.add("table " + order.getTableNum() + ": " + (order.getOwnTotalPriceBefore() + order.getOthersTotalPriceBefore()) + " " + (order.getOthersTotalPriceAfter() + order.getOwnTotalPriceAfter()));
}
for (String i : outPuts) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static boolean isInteger(String str) {
try {
Integer.parseInt(str);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return false;
}
}
}
class Dish { // 菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish() {
}
Dish(String name, int unit_price, char type) {
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
}
Dish(String name, int unit_price) {
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
this.type = 'C';
}
Dish(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public char getType() {
return type;
}
private char type;
private String name; // 菜品名称
private int unit_price; // 单价
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getUnit_price() {
return unit_price;
}
public int getPrice(int portion) {
if(portion == 1) return getUnit_price();
else if(portion == 2) return (int)Math.round(getUnit_price() * 1.5);
else return getUnit_price() * 2;
} // 计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份)
}
class Menu { // 菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息
private List<Dish> dishs = new ArrayList<>(); // 菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Menu() {
}
public void modDishs(String dishName, int unit_price, char type) {
Dish dish = new Dish(dishName, unit_price, type);
for (int i = 0; i < dishs.size(); i++) {
if(dish.getName().equals(dishs.get(i).getName())) {
dishs.set(i, dish);
break;
}
}
}
public Menu(List<Dish> dishs) {
this.dishs = dishs;
}
public List<Dish> getDishs() {
return dishs;
}
public void setDishs(List<Dish> dishs) {
this.dishs = dishs;
}
public Dish searthDish(String dishName) {
List<Dish> dishesNew = getDishs();
for (Dish dish : dishesNew) {
if(dish.getName().equals(dishName)) return dish;
}
return null;
} // 根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
public Dish addDish(String dishName, int unit_price, char type) {
List<Dish> dishsNew = getDishs();
Dish dish = new Dish(dishName, unit_price, type);
dishsNew.add(dish);
setDishs(dishsNew);
return dish;
} // 添加一道菜品信息
}
class Record { // 点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
private int orderNum; // 序号
private Dish d; // 菜品
private int portion; // 份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)
private int copies; // 份数
public Record() {
}
public Record(int orderNum, Dish d, int portion, int copies) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.d = d;
this.portion = portion;
this.copies = copies;
}
public int getOrderNum() {
return orderNum;
}
public Dish getD() {
return d;
}
public int getPrice() {
return d.getPrice(portion) * copies;
} // 计价,计算本条记录的价格
}
class Order { // 订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
private List<OthersOrder> othersOrders = new ArrayList<>();
private int tableNum;
private Menu menu;
private List<Record> records = new ArrayList<>(); // 保存订单上每一道的记录
private LocalDate localDate;
private LocalTime localTime;
private int OwnTotalPriceBefore;
private int OwnTotalPriceAfter;
public Order() {
}
public Order(Menu menu, int tableNum, LocalTime localTime, LocalDate localDate) {
this.menu = menu;
this.localDate = localDate;
this.localTime = localTime;
this.tableNum = tableNum;
}
public Order(List<Record> records, Menu menu, LocalDate localDate, LocalTime localTime) {
this.menu = menu;
this.localDate = localDate;
this.localTime = localTime;
this.records = records;
}
public void addAOthersOrder(OthersOrder othersOrder) {
this.othersOrders.add(othersOrder);
}
public List<OthersOrder> getOthersOrders() {
return othersOrders;
}
public int getTableNum() {
return tableNum;
}
public Menu getMenu() {
return menu;
}
public LocalTime getLocalTime() {
return localTime;
}
public LocalDate getLocalDate() {
return localDate;
}
public void setRecords(List<Record> records) {
this.records = records;
}
public List<Record> getRecords() {
return records;
}
public static boolean is_LegalTime(LocalDate dateToCheck) {
LocalDate startDate = LocalDate.of(2022, 1, 1); // 开始日期
LocalDate endDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 12, 31); // 结束日期
return ((dateToCheck.isEqual(startDate) || dateToCheck.isAfter(startDate))
&& (dateToCheck.isEqual(endDate) || dateToCheck.isBefore(endDate)));
}
public static boolean is_OpeningTime(LocalDate localDate, LocalTime localTime) {
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = localDate.getDayOfWeek();
int hour = localTime.getHour();
int minute = localTime.getMinute();
return ((dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY) && (hour >= 10 && hour < 21 || (hour == 9 && minute >= 30) || (hour == 21 && minute <= 30)))
|| ((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 17 && hour < 20 || (hour == 20 && minute <= 30)))
|| ((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 11 && hour < 14 || (hour == 14 && minute <= 30) || (hour == 10 && minute >= 30)));
} // 判断时间是否营业
public int getOwnTotalPriceAfter() {
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = getLocalDate().getDayOfWeek();
int hour = getLocalTime().getHour();
int minute = getLocalTime().getMinute();
int sum = 0;
List<Record> recordsNew = getRecords();
for (Record record : recordsNew) {
if(record.getD().getType() == 'C') {
if((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 17 && hour < 20 || (hour == 20 && minute <= 30)))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.8);
else if((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 11 && hour < 14 || (hour == 14 && minute <= 30) || (hour == 10 && minute >= 30)))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.6);
else if((dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY) && (hour >=10 && hour < 21 || (hour == 9 && minute >=30) || (hour == 21 && minute <=30)))
sum = sum + record.getPrice();
}
else if(record.getD().getType() == 'T') {
if(!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.7);
else sum = sum + record.getPrice();
}
}
return sum;
} // 计算订单的总价
public int getOwnTotalPriceBefore() {
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = getLocalDate().getDayOfWeek();
int hour = getLocalTime().getHour();
int minute = getLocalTime().getMinute();
int sum = 0;
List<Record> recordsNew = getRecords();
for (Record record : recordsNew) {
sum = sum + record.getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
public int getOthersTotalPriceBefore() {
int sum = 0;
for (OthersOrder othersOrder : othersOrders) {
sum = sum + othersOrder.getPriceBefore();
}
return sum;
}
public int getOthersTotalPriceAfter() {
int sum = 0;
for (OthersOrder othersOrder : othersOrders) {
sum = sum + othersOrder.getPriceAfter();
}
return sum;
}
public Record addARecord(int orderNum, String dishName, int portion, int copies) {
Dish dish = menu.searthDish(dishName);
Record recordNew = new Record(orderNum, dish, portion, copies);
List<Record> recordsNew = getRecords();
recordsNew.add(recordNew);
setRecords(recordsNew);
return recordNew;
} // 添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
public void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) {
List<Record> recordsNew = getRecords();
for (Record record : recordsNew) {
if(record.getOrderNum() == orderNum) {
recordsNew.remove(record);
break;
}
}
setRecords(recordsNew);
} // 根据序号删除一条记录
public Record findRecordByNum(int orderNum) {
List<Record> recordsNew = getRecords();
for (Record record : recordsNew) {
if(record.getOrderNum() == orderNum)
return record;
}
return null;
} // 根据序号查找一条记录
}
class OthersOrder {
private Order order;
private int OwnTableNum;
private Record record;
private Menu menu;
OthersOrder() {}
OthersOrder(Order order, int OwnTableNum, Record record, Menu menu) {
this.OwnTableNum = OwnTableNum;
this.order = order;
this.menu = menu;
this.record = record;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
public int getOwnTableNum() {
return OwnTableNum;
}
public Record getRecord() {
return record;
}
public Menu getMenu() {
return menu;
}
public void setOwnTableNum(int OwnTableNum) {
this.OwnTableNum = OwnTableNum;
}
public void setRecord(Record record) {
this.record = record;
}
public void setMenu(Menu menu) {
this.menu = menu;
}
public int getPriceBefore() {
return record.getPrice();
}
public int getPriceAfter() {
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = order.getLocalDate().getDayOfWeek();
int hour = order.getLocalTime().getHour();
int minute = order.getLocalTime().getMinute();
int sum = 0;
if(record.getD().getType() == 'C') {
if((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 17 && hour < 20 || (hour == 20 && minute <= 30)))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.8);
else if((!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)) && (hour >= 11 && hour < 14 || (hour == 14 && minute <= 30) || (hour == 10 && minute >= 30)))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.6);
else if((dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY) && (hour >=10 && hour < 21 || (hour == 9 && minute >=30) || (hour == 21 && minute <=30)))
sum = sum + record.getPrice();
}
else if(record.getD().getType() == 'T') {
if(!(dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || dayOfWeek == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY))
sum = sum + (int)Math.round(record.getPrice() * 0.7);
else sum = sum + record.getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
}
有关类的代码质量分析:
1.可读性:
代码整体风格清晰简洁,命名符合Java规范,易于理解。
类和方法的注释较少,可能需要增加更多的注释和文档,以便其他开发人员更好地理解和维护该代码。
变量名和方法名较为简洁明了,但是一些名称可能需要更具体、准确。
代码格式较整齐,缩进一致,易于阅读和维护。
2.可维护性:
代码结构清晰,类和方法职责分明,易于维护。
类中的属性和方法都是私有的,符合封装的原则。
部分方法的实现可能需要优化,例如Record类的getPrice()方法可以提取为一个共享方法。
方法名和变量名应该更加准确和具体,以提高代码的可维护性。
3.可测试性:
代码中部分方法未进行单元测试,需要增加更多单元测试来确保代码的正确性。
Dish类的getPrice()方法根据传入的参数返回不同的结果,应该编写多个测试用例来测试该方法的正确性。
4.性能:
代码中未涉及大量数据的处理,性能表现良好。
Dish类的getPrice()方法使用了多重if-else分支语句,可以使用更高效的分支逻辑,例如switch语句。
5.可靠性:
代码中使用了异常处理,增强了代码的可靠性。
在一些方法中,如果输入参数非法,代码可能会出现异常,需要在代码中添加更多的校验。
6.安全性:
代码中未涉及到数据的安全问题,未涉及到用户数据或隐私等敏感数据。
7.可扩展性:
代码中已经定义了多个类,每个类的职责清晰明确,易于扩展和修改。
例如,可以添加更多的方法来实现对订单的处理,比如对订单进行支付、结算等操作。
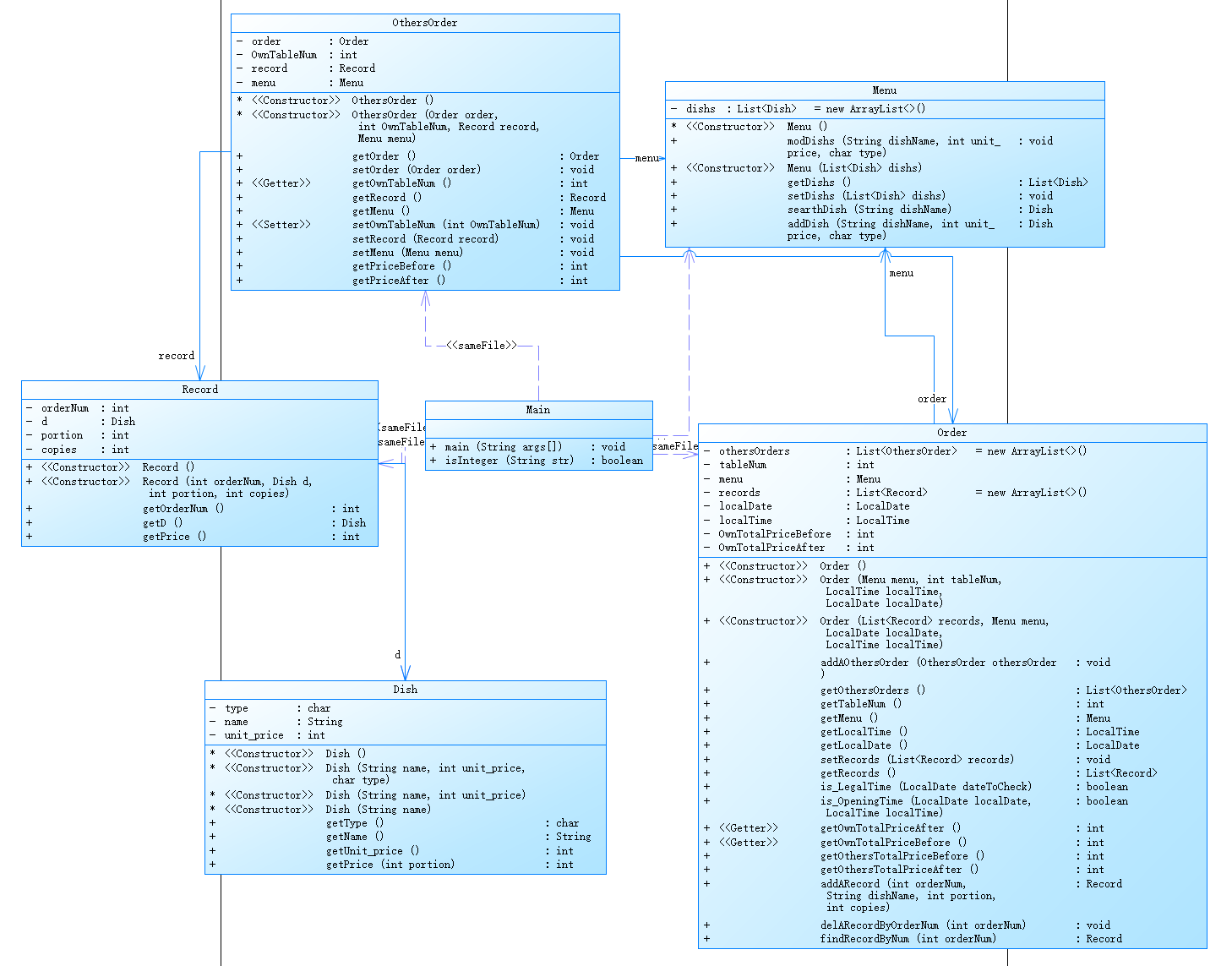
类图:
解释和心得:
有关类的代码解释:
这段代码是一个简单的餐厅点餐系统,包含了菜品类(Dish)、菜谱类(Menu)、点菜记录类(Record)和订单类(Order)。
Dish 类有 4 个构造函数,分别为无参数构造函数、根据菜品名称、单价和种类构造菜品的构造函数、根据菜品名称和单价构造菜品的构造函数、根据菜品名称构造菜品的构造函数。它有 4 个成员变量,分别为菜品名称(name)、单价(unit_price)、种类(type)和 getPrice() 方法。getPrice() 方法接受一个参数 portion,返回根据不同的 portion 值计算出的菜品价格。这里的 portion 取值为 1/2/3,分别代表小/中/大份。
Menu 类包含菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息。它有 3 个构造函数,分别为无参数构造函数、根据菜品列表构造菜谱的构造函数、修改菜品信息的方法和查询菜品信息的方法。查询菜品信息的方法接受一个参数 dishName,返回菜品名称为 dishName 的 Dish 对象。
Record 类保存订单上的一道菜品记录。它有 2 个构造函数,分别为无参数构造函数和根据序号、菜品、份额和份数构造记录的构造函数。它有 4 个成员变量,分别为序号(orderNum)、菜品(d)、份额(portion)和份数(copies)。它还有一个 getPrice() 方法,返回根据记录的菜品、份额和份数计算出的价格。
Order 类保存用户点的所有菜的信息。它有 4 个构造函数,分别为无参数构造函数、根据菜谱、桌号、时间和日期构造订单的构造函数、根据记录、菜谱、日期和时间构造订单的构造函数和添加附加订单信息的方法。它有 8 个成员变量,分别为附加订单信息的列表(othersOrders)、桌号(tableNum)、菜谱(menu)、点菜记录的列表(records)、日期(localDate)、时间(localTime)和两个变量 OwnTotalPriceBefore 和 OwnTotalPriceAfter(后者代表折扣后的价格)。它还有一个 addAOthersOrder() 方法,用于添加附加订单信息。
心得:
从这段代码中,我们可以看到几个重要的面向对象编程的概念,比如类、对象、方法、封装和多态。这些概念是OOP的核心,使得程序的结构更加清晰和可维护,同时也方便了程序的复用和扩展。
在这段代码中,我们可以看到定义了几个类,每个类都有不同的功能,比如菜品类(Dish)、菜谱类(Menu)、点菜记录类(Record)和订单类(Order)。这些类之间通过组合等方式建立了关系,实现了不同类之间的交互。
封装也是OOP的一个重要概念,封装通过将类的属性和方法进行限制和隐藏,保证了程序的安全性和可维护性。在这段代码中,我们可以看到许多属性和方法都被定义为私有的(private),只能通过公共的方法(public)进行访问,这样可以避免属性和方法被误操作和修改。
多态是OOP的另一个重要概念,它允许不同的对象对同一消息做出不同的响应。在这段代码中,我们可以看到菜品类(Dish)有多个构造方法,每个方法具有不同的参数和实现方式,这样可以根据实际需要来调用不同的构造方法,实现了多态的效果。
三、踩坑心得
OOP训练集04
7-1 菜单计价程序-3
这个题目比较幸运,避开了所有坑,这是因为我连踩坑的机会都没有给自己,第一次见这道题便产生了畏惧以至于没有去思考这道题就打了退堂鼓。
OOP训练集05
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
这道题由于有前面和这个题目类似的题做铺垫,以及这个题目是根据老师给的类图来完成整个程序的设计,按部就班的工作,一步一个脚印,以至于基本没踩坑。
OOP训练集05
7-6 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
同 7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一),两道题本质上是同一道,只是把类的设计换了种模式。
OOP训练集06
7-1 菜单计价程序-4
1)输出格式存在问题:

自以为 “ :” 后面是空白啥也没有,于是在输出时大意了,但谁又能想到后面还有个空格呢

结果可想而知,首次提交只得了11分,这个错误其实是很难发现的,毕竟题目给的输出格式也是没有空格的,至于怎么发现的,我在PTA上跑了个自动填充的输入样例,结果上提示我少了个空格,就不知道是不是老师有意而为之了 ^ ^
2)数组越界访问:
这个问题我最开始确实是没有考虑到
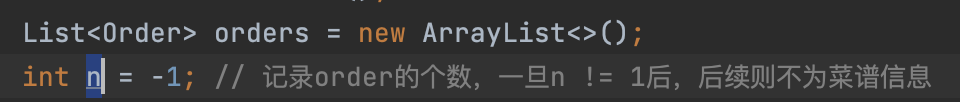
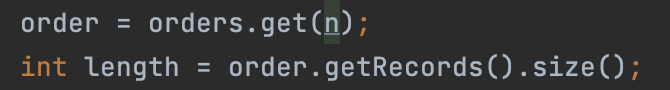
在order.get(n)时 如果n没有更新仍为-1的话(没有更新订单记录或没有正确的订单记录输入)则会报数组越界访问。
这时我们只需加一个判断条件即可完美解决这个问题:
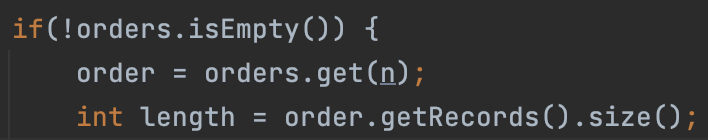
先判空,再操作
四、改进建议
OOP训练集04
7-1 菜单计价程序-3
无
OOP训练集05
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
代码中没有注释,建议添加注释来帮助理解代码。
对于重复代码,可以使用封装来避免重复。
可以添加对边界条件的测试,以确保程序能够正确处理边界情况。
对于频繁使用的计算结果,可以使用缓存来提高性能。
可以在程序中添加异常处理,以确保程序在出现异常情况时能够正确处理。
OOP训练集05
7-6 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
在方法名前面添加注释说明方法的作用,增加代码的可读性。
增加日期格式化等方法,以增加代码的可扩展性。
OOP训练集06
7-1 菜单计价程序-4
为类添加构造函数的注释,以便其他人可以更好地理解代码。此外,可以为类的属性和方法添加注释,以便读者更好地理解其用途。
变量和方法名建议使用有意义的名称,例如在 Record 类中, getPrice 方法的名字可以改为 calculatePrice 更清晰地表达其用途。对于长的方法,可以考虑使用换行符,将代码格式化为多个行,从而更清晰地展示代码结构。
在 Menu 类的 searthDish 方法中,每次调用该方法时,都会重新获取 dishs 列表,这会导致性能问题。可以在 Menu 类的构造函数中,将 dishs 列表转换为 Map 类型,以便更快地查找菜品信息。
在 Record 类的 getPrice 方法中,没有对输入参数进行有效性检查,可能导致错误的计算。建议添加输入参数的有效性检查,以避免出现错误的计算。
在 Dish 类的构造函数中,没有对输入参数进行有效性检查,可能导致错误的创建。建议添加输入参数的有效性检查,以避免创建错误的菜品信息。
总结
设计类时需要合理考虑类的属性和方法,避免属性和方法冗余和不必要的公共方法和属性。
需要对代码进行注释,让其他人更容易理解代码的意图。
代码的命名应该简明易懂,避免使用缩写和简写,同时也需要避免使用过于具体的命名,增加代码的可扩展性。
应该遵循良好的代码规范,如代码缩进、代码结构等,以增加代码的可读性。
需要考虑如何增加代码的可维护性,如重构冗长的方法、合并重复的代码段等。
最重要的一点,我学到了坚韧不拔的精神品质 ^ ^ , 这将让我终身受益