2024牛客暑期多校训练营10 - VP记录
Preface
这次赛时六道题做对了三道题,一些小技巧还是使用地蛮好的(包括 H 题猜测结论),就是 K 题原本思路算法都是对的,只是实现起来应当二分点位而非值域,加上代码复用程度比较低,增加了代码复杂程度导致没调出来。
总体来说这次题目要注意的细节挺多的,比如我调炸的 K 题和两眼一抹黑的 L 题。
A. Surrender to My Will
直接判断当前是否不可翻盘。
点击查看代码
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[10]; scanf("%s",str);
int y=0,n=0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='Y') y++;
if(str[i]=='N') n++;
}
if(y>=4) printf("1\n");
else if(n>=2) printf("-1\n");
else printf("0\n");
return 0;
}
B. std::pair
让我想起了去年 CSP-S2023 T3 的没好回忆(手写结构体)。
把题目中给的类型递归建成一棵(二叉)树,叶节点表示 double 或 int,非叶节点表示 pair。
以样例为例,建出来的大概就是这样一个森林:
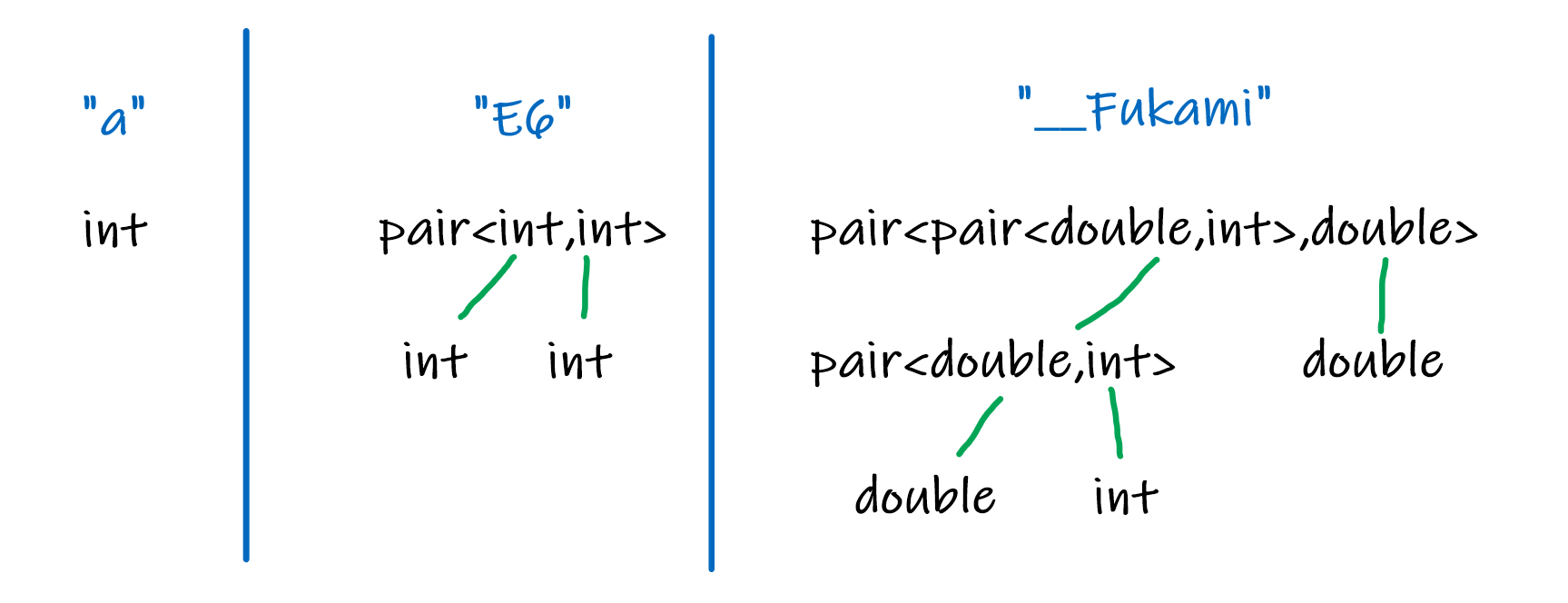
通过首字母判断当前是哪一种,如果是叶节点就设置完节点信息直接返回;否则先找递归找左叶节点(first),递归的同时返回子节点编号和该节点对应的字符串右端点,通过左叶节点的右端点找到字符串中右叶节点的起始位置,再递归处理寻找右子节点。
查询就更简单了,把字符串拆解成一连串 first 和 second,根据这个决定走左叶节点还是右叶节点。
注意存储的时候不要在节点内存整个节点对应的字符串,会爆空间。可以存类型编号或直接存类型名称之类的。
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1005;
int n,q;
map<string,int> raw;
struct JC_Pair{
string name;
int p1,p2;
}p[N*N];
int pidx=0;
string type,var;
pair<int,int> get_pair(int l) //返回 {索引,右端点}
{
int now=++pidx;
if(type[l]=='p') //pair<first,second>
{
pair<int,int> sonl=get_pair(l+5); //first
int sonl_idx=sonl.first,mid=sonl.second;
p[now].p1=sonl_idx;
pair<int,int> sonr=get_pair(mid+2); //second
int sonr_idx=sonr.first,end=sonr.second;
p[now].p2=sonr_idx;
p[now].name="pair";
return {now,end+1};
}
if(type[l]=='i') //int
{
p[now]={"int",0,0};
return {now,l+2};
}
if(type[l]=='d') //double
{
p[now]={"double",0,0};
return {now,l+5};
}
printf("ERROR!\n");
return {-1,-1};
}
void print_pair(int x)
{
printf("%s",p[x].name.c_str());
if(p[x].name=="pair")
{
putchar('<');
print_pair(p[x].p1);
putchar(',');
print_pair(p[x].p2);
putchar('>');
}
return;
}
string ts,tt;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>type>>var;
pair<int,int> tmp=get_pair(0);
raw[var]=tmp.first;
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
cin>>ts;
tt.clear();
int pos=0; bool is_name=true;
int now=0;
while(pos<=(int)ts.length())
{
if(pos==(int)ts.length() || ts[pos]=='.')
{
if(is_name)
{
now=raw[tt+';'];
is_name=false;
}
else
{
if(tt=="first") now=p[now].p1;
else if(tt=="second") now=p[now].p2;
else printf("ERROR!\n");
}
tt.clear();
}
else
{
tt+=ts[pos];
}
pos++;
}
print_pair(now);
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
F. Collinear Exception
因为每行出现超过两个点就一定会在这一行三点共线,所以每行最多两个,一共最多 \(2n\) 个点。
那么我们就可以维护一张图,标明空位和被某条直线覆盖的位置。每次一个点若成功加入,则将它与其它所有已经加入的点组合连直线来标记图上被这条直线覆盖的点。
本人数学不好,只能算出来时间复杂度不高于 \(O(N^3)\),但看这个样子应该是 \(O(N^2 \ln N)\) 之类的复杂度吧。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int read_u()
{
int x=0; char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(ch^'0');ch=getchar();}
return x;
}
const int N=1005,M=N*N;
int n,x[M],y[M];
int avail_n,avail_x[M],avail_y[M];
bool unavail[N][N];
int gcd(int x,int y){return y?gcd(y,x%y):x;}
int main()
{
n=read_u();
for(int i=1;i<=n*n;i++)
{
x[i]=read_u(),y[i]=read_u();
if(unavail[x[i]][y[i]]) putchar('0');
else
{
putchar('1');
unavail[x[i]][y[i]]=true;
for(int j=1;j<=avail_n;j++)
{
int ax=avail_x[j],ay=avail_y[j];
int dx=x[i]-ax,dy=y[i]-ay; //绝对值不能再这里取!否则斜率一定非负!
int d=gcd(abs(dx),abs(dy)); dx/=d,dy/=d;
int tx=x[i],ty=y[i];
while(tx>=1&&tx<=n && ty>=1&&ty<=n)
{
unavail[tx][ty]=true;
tx+=dx,ty+=dy;
}
tx=x[i],ty=y[i];
while(tx>=1&&tx<=n && ty>=1&&ty<=n)
{
unavail[tx][ty]=true;
tx-=dx,ty-=dy;
}
}
avail_n++,avail_x[avail_n]=x[i],avail_y[avail_n]=y[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
H. All-in at the Pre-flop
观察样例:1 3 \(\rightarrow\) 748683265 249561089
输出的两数差不多是 \(3:1\) 的比例,和输出貌似有点关系;
输出两数之和为 \(998244354\) 刚好是 \(998244353+1\);
再联系一下逆元,欸~结论就出来了!答案就是 \(\dfrac{a}{a+b}\) 和 \(\dfrac{b}{a+b}\)。
(好吧实际上我也不会证,但是蒙了一个结论交上去居然对了)
还是看下官方题解吧(官方题解和我一样逗)
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int P=998244353;
long long quick_pow(long long x,long long y)
{
long long res=1;
while(y)
{
if(y&1) res=res*x%P;
x=x*x%P;
y>>=1;
}
return res;
}
inline long long inv(long long x){return quick_pow(x,P-2);}
int main()
{
long long a,b; scanf("%lld%lld",&a,&b);
printf("%lld %lld\n",a*inv(a+b)%P,b*inv(a+b)%P);
return 0;
}
K. Doremy's IQ 2
赛时做法想对了的,就是实现方法有点复杂没调出来,可恶!
首先有一个贪心思想,全局最多转向一次。因为要到达同样的点,转多次所消耗的点数不会比转一次更少。
然后就可以分类讨论,先左再右或先右再左。
以先左再右(先负后正)为例,枚举在左边哪一个点位转向(一定是在某个有点的点位上转向,因为再多走是浪费),然后如果知道它最多能走到右边哪个位置,就可以直接找出其中的点数。
找右边极限位置时,因为出发点越靠左(不升),所以其有单调性,可以通过二分或双指针等来维护,我这里用的是双指针(因为赛时二分写炸了)。
注意要判断是否可以达到这个转向点,且必须保证转向位置非正,结束点非负。这样可以保证输入全为负数时右端点始终在 \(n\) 上,表示最右边始终可达。
至于先右再左,直接将原序列全部取相反数,重排序后再跑一边即可。同时这样可以把全正的特殊情况转为全负,通过上面的处理,同样可以正确计算全正时的答案。
当全正或全负的时候,都只会正确运行一种正负上的 Solve(),而另一种上全部 continue,相当于没有运行。
时间复杂度 \(O(N)\)。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+5;
int n,a[N];
int ans;
void Solve()
{
//先向左再向右走
int r=n;
for(int l=n;l>=1;l--) //走到第i个点位
{
if(a[l]>0) continue;
if(0-(l-1)>a[l]) continue; //用完前面所有(i-1)个点后,所能到达的最左位置仍然不够a[i]
while(a[r]>0 && a[r]-a[l]>n-r) r--;
ans=max(ans,r-l+1);
/*
* 必须保证a[l]<=0且a[r]>=0,这样可以处理全为负数的情况
* 序列取反后同样可以处理全为正数的情况
* 这两种情况下都是某一种正负下全continue不处理,另一种可以正常运行
*/
}
return;
}
void Take_reverse()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=-a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n>>1;i++)
swap(a[i],a[n-i+1]);
return;
}
int main()
{
int T; scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
ans=0;
Solve();
Take_reverse();
Solve();
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
L. Tada!
已分离独立成篇,点击查看
本文采用 「CC-BY-NC 4.0」 创作共享协议,转载请注明作者及出处,禁止商业使用。
作者:Jerrycyx,原文链接:
