优化原理 (1)高斯牛顿 线性
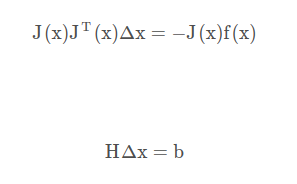



/*
* Gauss-Newton iteration method
* author:Davidwang
* date :2020.08.24
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
void GN(const int, vector<double> &, vector<double> &, double &, double &, double &, double const);
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
double ar = 18.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值
double ae = 2.0, be = 4.0, ce = 3.0; // 估计参数值
int N = 50; // 数据点
double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值
double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma; // 信息值
cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器
vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 生成真值数据
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double x = i / 100.0;
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(ar * x + exp(br * x + cr) + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma));
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
GN(N, x_data, y_data, ae, be, ce, inv_sigma);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl;
cout << "estimated abc = " << ae << ", " << be << ", " << ce << endl;
return 0;
}
///高斯牛顿法,N数据个数,x:X值,y:Y值,ae:a估计值,be:b估计值,ce:c估计值,inv_sigma:信息值(1/σ)
void GN(const int N, vector<double> &x, vector<double> &y, double &ae, double &be, double &ce, double const inv_sigma)
{
int iterations = 50; // 迭代次数
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; // 本次迭代的cost和上一次迭代的cost
double xi, yi, error, e;
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++)
{
Matrix3d H = Matrix3d::Zero();
Vector3d b = Vector3d::Zero();
cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
xi = x[i], yi = y[i]; // 第i个数据点
e = ae * xi + exp(be * xi + ce); // 计算估计值
error = yi - e; // 误差
Vector3d J; // 雅可比矩阵
J[0] = -xi; // de/da
J[1] = -xi * exp(be * xi + ce); // de/db
J[2] = -exp(be * xi + ce); // de/dd
H += inv_sigma * inv_sigma * J * J.transpose(); //H = J^T * W^{-1} * J,inv_sigma 为信息值,本示例可以去掉
b += -inv_sigma * inv_sigma * error * J; //b= -W^{-1} * f(x)*J ,inv_sigma 为信息值,本示例可以去掉
cost += error * error;
cout << "The " << iter + 1 << " iteration, The " << i << " factor " << endl;
cout << "THe Value, x: " << xi << ",y:" << yi << ",e:" << e << ",error:" << error << endl
<< endl;
}
Vector3d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b); // 求解线性方程 HΔx=b
if (isnan(dx[0]))
{
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost)
{
cout << "cost: " << cost << ">= last cost: " << lastCost << ", break." << endl;
break;
}
ae += dx[0];
be += dx[1];
ce += dx[2];
lastCost = cost;
cout << "total cost: " << cost << ", \t\tupdate: " << dx.transpose() << "\t\testimated params: " << ae << "," << be << "," << ce << endl;
}
}

CMakeLists如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(gaussNewton)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++14 -O3")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
add_executable(GN gaussNewton_GN.cpp)
target_link_libraries(GN ${OpenCV_LIBS})
