ABC317题解报告
我直接从第三题开始讲了。
T3
把数组 \(A\) 从大到小排序。
然后从前往后把前 \(q\) 个数加起来,然后判断这 \(q\) 个数的和与 \(d\) 的大小关系,如果大了就变成 \(d\)。
然后有些细节就看代码吧。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int n,d,p;
int a[maxn];
int cnt,sum;
bool cmp(int a,int b)
{
return a > b;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> d >> p;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
ans += a[i];
}
sort(a + 1,a + n + 1,cmp);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
sum += a[i];
cnt++;
if(cnt >= d && sum <= p)
{
break;
}
if(cnt == d)
{
if(sum >= p)
{
cnt = 0;
ans -= sum - p;
sum = 0;
}
}
}
if(sum >= p)
{
ans -= sum - p;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
T4
看到 \(n \le 16\),想到状压 DP。
然后就没有然后了, DP式就是很普通的 DP 式。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,ans = -1e9;
int d[20][20];
int dp[1 << 17];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
{
if(i != j && i < j)
cin >> d[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < (1 << n);i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
{
if(!(i & (1 << j)))
{
continue;
}
for(int k = j + 1;k < n;k++)
{
if(!(i & (1 << k)))
{
continue;
}
int befor = i xor (1 << j) xor (1 << k);
dp[i] = max(dp[befor] + d[j][k],dp[i]);
}
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < (1 << n);i++)
{
ans = max(ans,dp[i]);
// cout << dp[i] << " " << i << '\n';
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
/*
16
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1
1
*/
T5
有很多种方法。
比如liangbowen先生说的:e你直接从后往前枚举 i 不就做完了。
又比如ran_qwq所写到的:

谔谔,大家的方法都比我高级。
我是直接容斥。
首先先算出以这个点为 \(k\) 的组数并且忽略第二条。
然后减去 \(a_i = a_j = a_k\) 的情况即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
int n,ans;
int cnt[maxn],sum[maxn];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
ans += cnt[x] * (i - 1) - sum[x];
sum[x] += i;
cnt[x]++;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
ans -= cnt[i] * (cnt[i] - 1) * (cnt[i] - 2) / 6;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
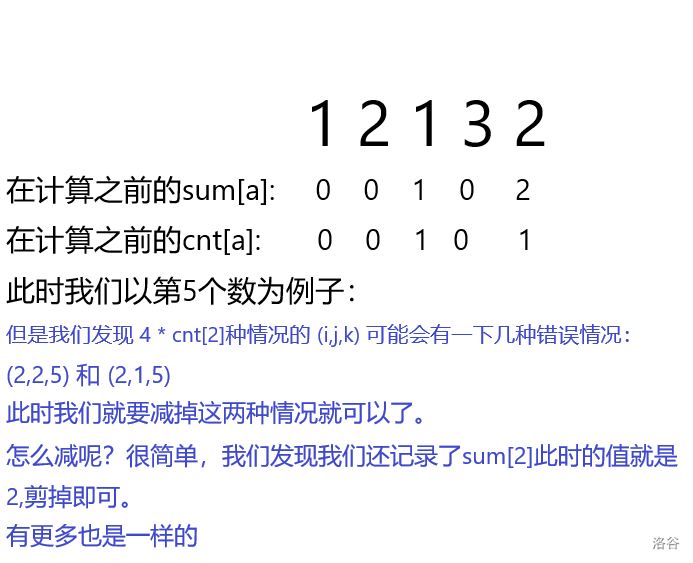
但是呢,你有可能对 ans += cnt[x] * (i - 1) - sum[x]; 有疑问,我们画个图就知道了。